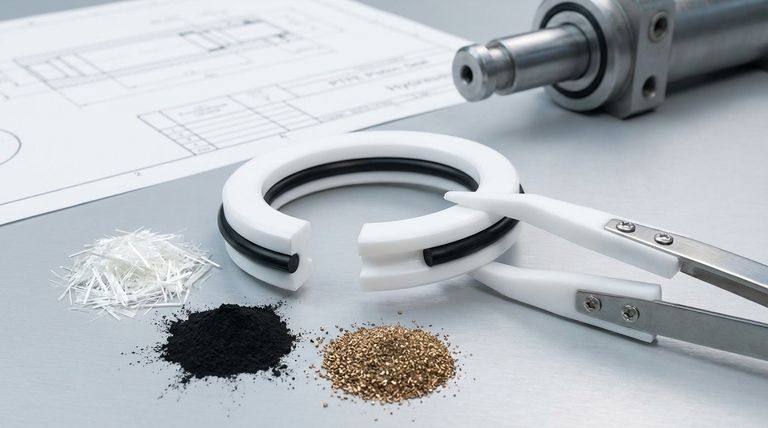
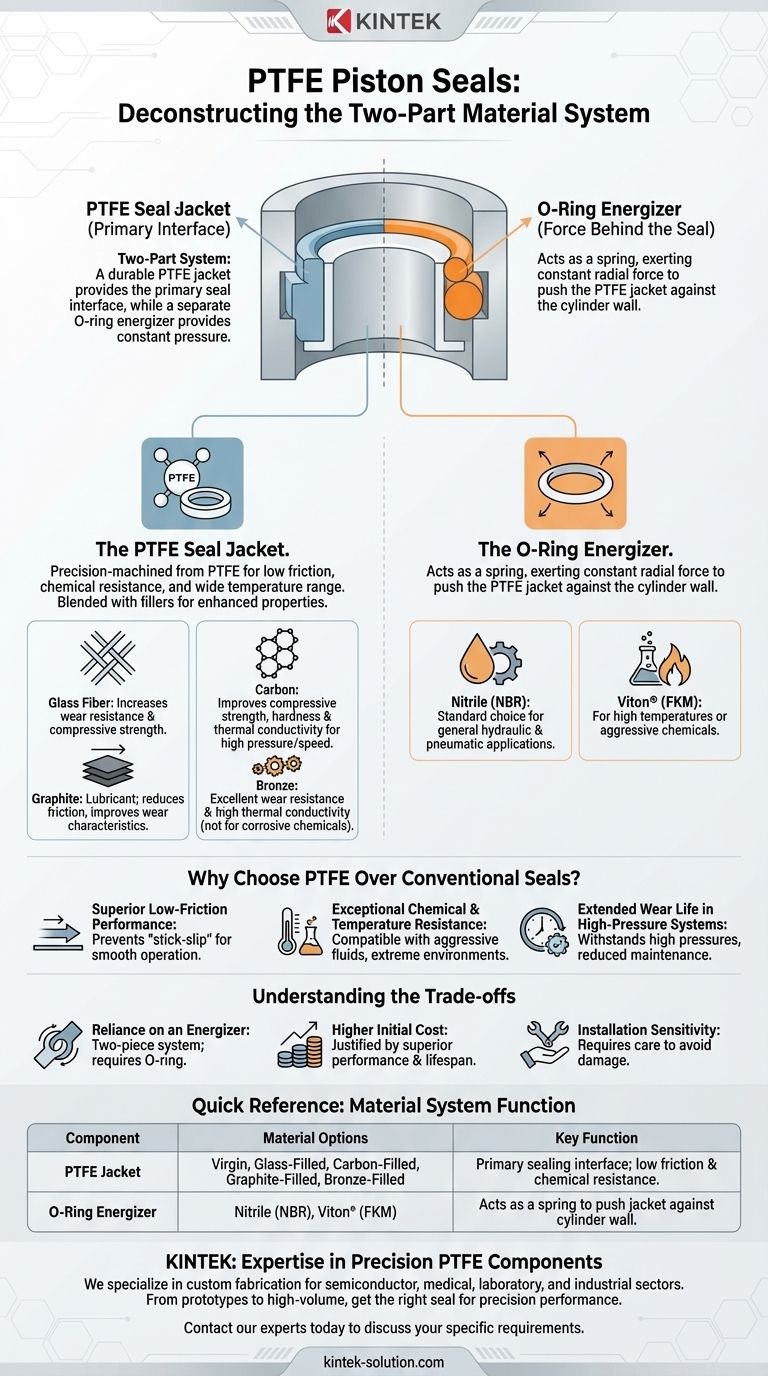
At their core, PTFE piston seals are not made from a single material but are engineered as a two-part system. The main sealing ring is made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a high-performance polymer, which is often blended with various fillers to enhance its mechanical properties. This PTFE ring, or jacket, is almost always used in conjunction with a separate O-ring that acts as an energizer to ensure a consistent seal.
The effectiveness of a PTFE piston seal doesn't come from a single material, but from a two-part system. A durable, low-friction PTFE jacket provides the primary seal interface, while a separate O-ring energizer provides the constant pressure needed for a reliable, long-lasting seal.

Deconstructing the PTFE Piston Seal Assembly
To understand the materials, you must first understand the two distinct components that work together: the seal jacket and the energizer.
The PTFE Seal Jacket (The Primary Interface)
The outer component that makes direct contact with the cylinder bore is the seal jacket. This is precision-machined from PTFE, a material chosen for its unique combination of properties.
Virgin PTFE provides extremely low friction, outstanding chemical resistance, and a very wide operating temperature range.
However, pure PTFE is relatively soft. To improve its performance under pressure and extend its wear life, it is blended with various fillers.
Common Fillers and Their Purpose
Fillers are added to the PTFE resin before it is formed to dramatically improve specific characteristics. The choice of filler is critical and adapts the seal for a specific application.
- Glass Fiber: A common, general-purpose filler that significantly increases wear resistance and compressive strength.
- Carbon: Improves compressive strength, hardness, and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-pressure and high-speed applications where heat can build up.
- Graphite: Often used in combination with carbon, graphite acts as a lubricant to reduce the coefficient of friction even further and improve wear characteristics.
- Bronze: Adds excellent wear resistance and high thermal conductivity. It is very effective in hydraulic systems but is not suitable for applications with corrosive chemicals.
The O-Ring Energizer (The Force Behind the Seal)
PTFE is a rigid plastic, not a flexible rubber. On its own, it has poor "memory" and cannot conform to the sealing surface or compensate for wear.
The O-ring energizer sits in a groove on the inner diameter of the PTFE jacket. It functions as a spring, exerting a constant radial force that pushes the PTFE jacket firmly against the cylinder wall.
The material for the O-ring is selected based on the application's temperature and fluid compatibility, such as:
- Nitrile (NBR): The standard choice for general-purpose hydraulic and pneumatic applications.
- Viton® (FKM): Used for high-temperature applications or when exposed to aggressive chemicals.
Why Choose PTFE Over Conventional Seals?
While conventional seals are often made from simpler rubber or polyurethane compounds, PTFE systems are specified for more demanding conditions.
Superior Low-Friction Performance
PTFE's extremely low coefficient of friction prevents the "stick-slip" phenomenon common with rubber seals, where the seal sticks to the cylinder wall at rest. This ensures smooth, judder-free movement, which is critical in precision hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Exceptional Chemical and Temperature Resistance
PTFE is nearly chemically inert, making it compatible with a vast range of aggressive industrial fluids. It also maintains its integrity in both cryogenic and high-temperature environments where traditional elastomers would fail.
Extended Wear Life in High-Pressure Systems
The combination of a hard, filler-reinforced PTFE jacket and a high-force energizer creates a seal that can withstand high pressures and significant wear. This results in a much longer service life and reduced maintenance intervals, especially in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PTFE seal system has specific characteristics that must be considered.
Reliance on an Energizer
A PTFE seal is fundamentally a two-piece system. Without the O-ring energizer, the stiff PTFE jacket cannot create a reliable seal, especially at low pressures or during startup.
Higher Initial Cost
A two-piece, precision-machined PTFE seal assembly typically has a higher upfront cost than a simple, single-piece molded rubber seal. This cost is justified by its superior performance and extended lifespan in demanding applications.
Installation Sensitivity
Care must be taken during installation to avoid scratching the PTFE jacket or damaging the O-ring. The two-piece design requires proper tools and procedures to ensure the seal is seated correctly without compromising its integrity.
Selecting the Right Material Combination for Your Application
Choosing the correct materials is key to ensuring the seal performs as intended.
- If your primary focus is standard hydraulic or pneumatic service: A glass- or bronze-filled PTFE jacket with a standard NBR O-ring energizer is a robust and cost-effective choice.
- If you are dealing with high temperatures or aggressive chemicals: Select a virgin PTFE or chemically inert filled jacket with an FKM (Viton®) O-ring energizer.
- If your application demands maximum wear resistance and high pressure: A carbon- or bronze-filled PTFE jacket provides the necessary compressive strength and durability.
- If eliminating stick-slip is your top priority: A graphite-filled PTFE jacket offers the lowest coefficient of friction for exceptionally smooth operation.
Understanding this two-part material system empowers you to specify a seal that delivers precision performance and long-term reliability.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material Options | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Jacket | Virgin PTFE, Glass-Filled, Carbon-Filled, Graphite-Filled, Bronze-Filled | Provides primary sealing interface; low friction & chemical resistance. |
| O-Ring Energizer | Nitrile (NBR), Viton® (FKM) | Acts as a spring to push the PTFE jacket against the cylinder wall. |
Need a high-performance PTFE piston seal for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a seal engineered with the right material combination for low friction, chemical resistance, and long-term reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution that delivers precision performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications



















