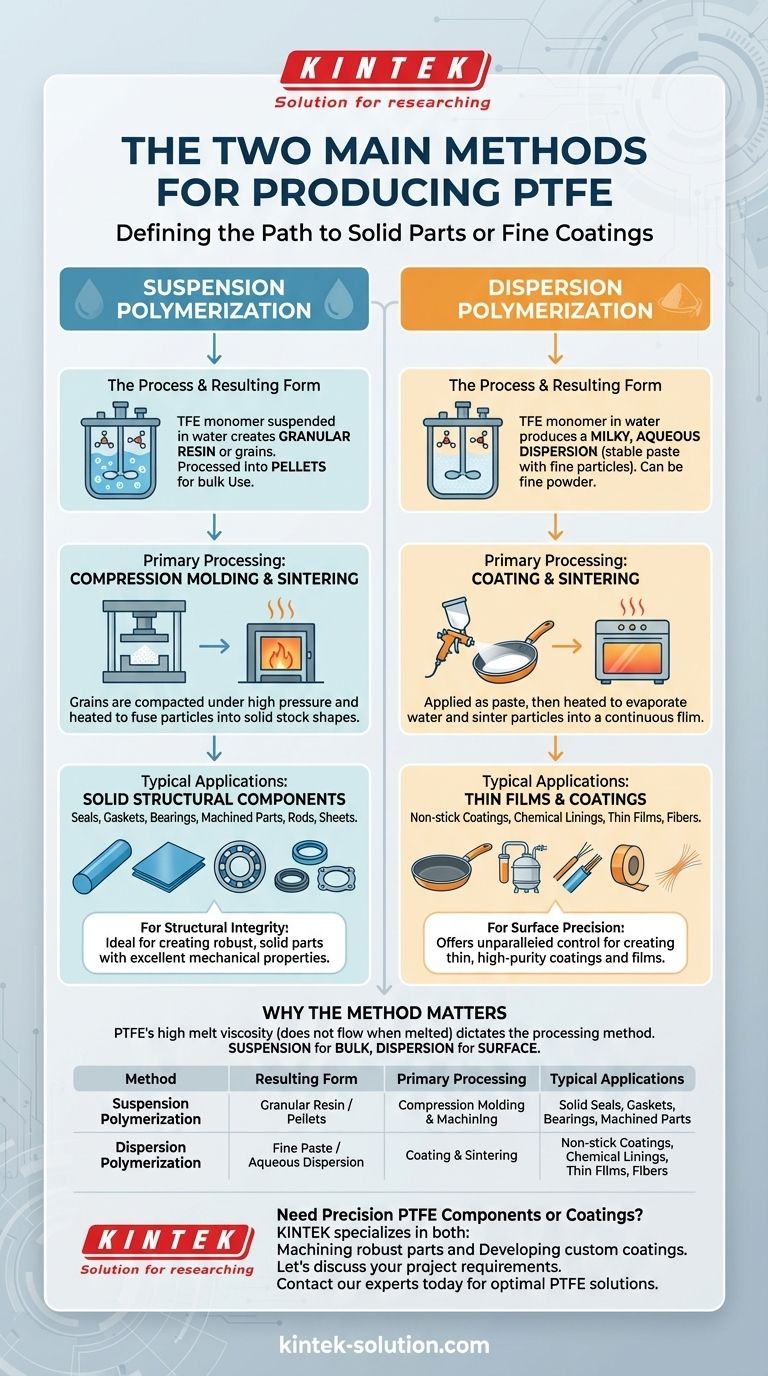
The production of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is defined by two distinct and primary methods: suspension polymerization and dispersion polymerization. The fundamental difference between them lies in the physical form of the resulting raw material. Suspension polymerization creates granular PTFE destined for solid, molded components, while dispersion polymerization produces a fine paste used for thin coatings and films.
The choice between PTFE production methods is not an operational detail; it is the single most important factor determining the material's final form and its viable applications. One path leads to solid, structural parts, while the other leads to thin, functional surfaces.
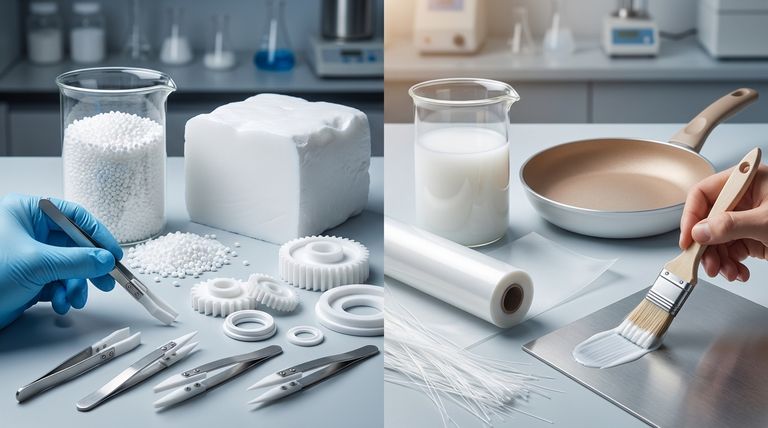

The Two Paths of Polymerization
The initial polymerization process sets the stage for all subsequent processing. Because PTFE does not melt and flow like conventional plastics, its initial form—either a grain or a paste—is critical.
Suspension Polymerization: Building Solid Forms
In suspension polymerization, the Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) monomer is polymerized while suspended in water.
This process yields solid particles of PTFE known as granular resin or grains. These grains are then processed into more usable forms, such as free-flowing powders or solid pellets.
The primary purpose of this method is to create bulk material ideal for compression molding, where it is pressed and heated to form solid stock shapes like rods, sheets, and blocks.
Dispersion Polymerization: Creating Fine Films and Coatings
Dispersion polymerization also occurs in water but results in a different output.
This method produces a milky, aqueous dispersion—essentially a stable paste containing extremely fine particles of PTFE. This paste can be used directly or further processed into a fine, non-free-flowing powder.
The fine particle size makes this form ideal for creating thin films and coatings, such as the non-stick layer on cookware, or for producing fine fibers.
Why the Method Dictates the Application
Understanding how raw PTFE is processed into a final product clarifies why the two polymerization methods are not interchangeable. They solve two completely different manufacturing challenges.
The Unique Challenge of Processing PTFE
PTFE has an exceptionally high melt viscosity, meaning it does not flow when it melts.
This property prevents the use of common, high-volume thermoplastic processing techniques like injection molding. Manufacturers must instead rely on methods that can consolidate PTFE particles without requiring them to flow.
From Suspension Grains to Machined Parts
The pellets and grains from suspension polymerization are perfectly suited for compression molding and sintering. In this process, the material is compacted under high pressure and then heated to fuse the particles into a solid block.
These solid stock shapes are then machined using traditional techniques like CNC milling and turning to create precise, durable components such as seals, gaskets, and bearings.
From Dispersion Paste to Surface Coatings
The fine paste from dispersion polymerization is designed to be applied to a substrate, often by spraying or roller coating.
After application, the part is heated. This evaporates the water and sinters the PTFE particles together, forming a continuous, non-porous, and durable film. This is the core process for creating chemical-resistant linings and non-stick surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each polymerization method is optimized for a different set of outcomes, presenting a clear trade-off between bulk form and fine application.
Suspension: For Structural Integrity
The key advantage of suspension polymerization is its ability to produce large quantities of resin suitable for creating robust, solid parts with excellent mechanical properties.
The limitation is that this granular form cannot be used to create the ultra-thin, uniform films and coatings that are possible with dispersion-grade PTFE.
Dispersion: For Surface Precision
Dispersion polymerization offers unparalleled control for creating thin, high-purity coatings and films. It is essential for surface-level applications.
Its limitation is that it is not intended for producing thick, structural components. The material form is specifically engineered for surface coverage, not bulk mass.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The PTFE you encounter in an application was set on its path from the moment of polymerization. Understanding this origin helps you specify the correct material for your project.
- If your primary focus is creating solid, structural components: You will work with PTFE derived from suspension polymerization, typically supplied as molded blocks, rods, or sheets ready for machining.
- If your primary focus is applying a non-stick or chemical-resistant coating: You require PTFE produced via dispersion polymerization, which will be supplied as a liquid paste or fine powder.
- If your primary focus is producing thin tapes, membranes, or fibers: You will also start with material from dispersion polymerization, as its fine particle structure is necessary for these delicate forms.
Ultimately, knowing whether you need to build a solid object or coat a surface will tell you everything you need to know about the material's manufacturing origin.
Summary Table:
| Method | Resulting PTFE Form | Primary Processing | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suspension Polymerization | Granular Resin / Pellets | Compression Molding & Machining | Solid Seals, Gaskets, Bearings, Machined Parts |
| Dispersion Polymerization | Fine Paste / Aqueous Dispersion | Coating & Sintering | Non-stick Coatings, Chemical Linings, Thin Films, Fibers |
Need Precision PTFE Components or Coatings?
Understanding the production method is the first step. The next is partnering with a manufacturer who masters the processing.
KINTEK specializes in both:
- Machining robust parts from suspension-polymerized PTFE blocks and rods.
- Developing custom coatings using dispersion-polymerized PTFE pastes.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring precision and performance.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our experts today to find the optimal PTFE solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















