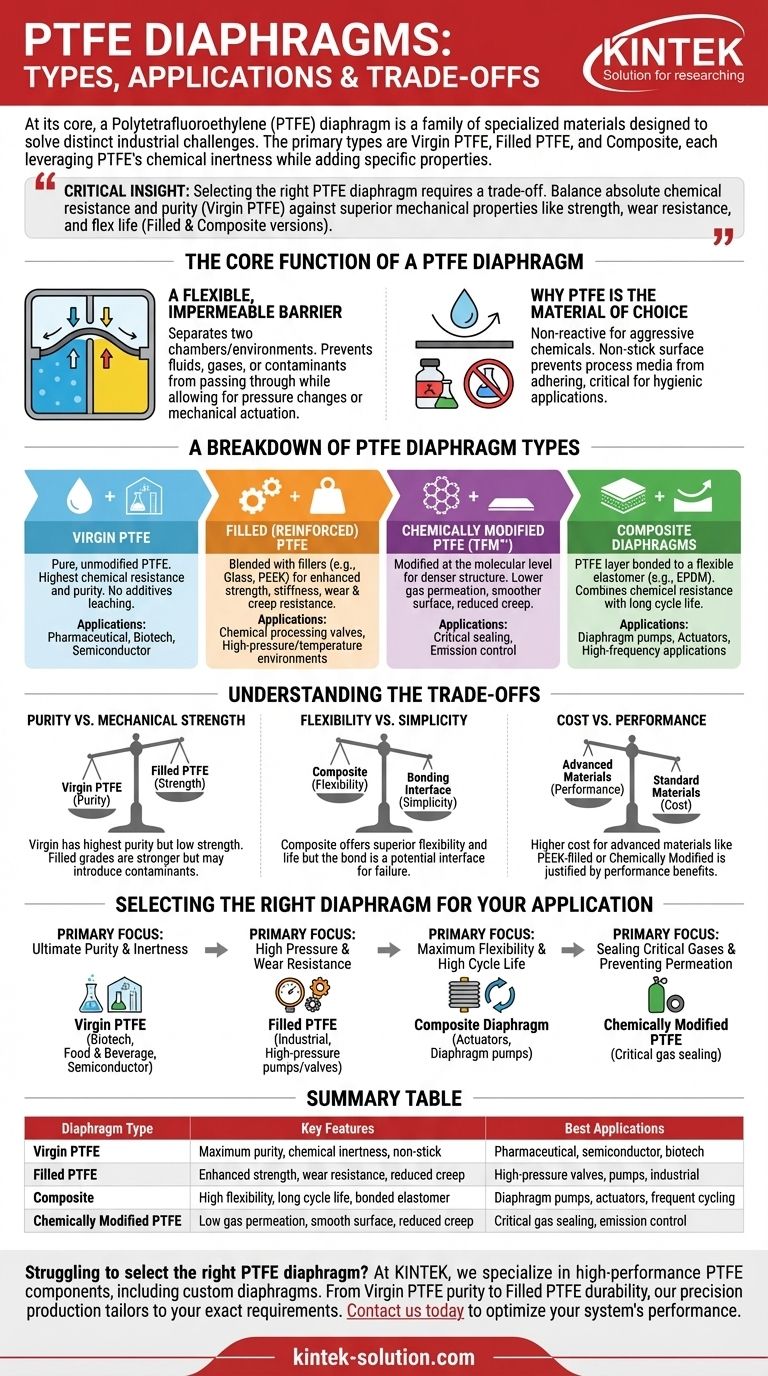
At its core, a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) diaphragm is not a single product but a family of specialized materials designed to solve distinct industrial challenges. The primary types are Virgin PTFE for purity, Filled PTFE for strength and wear resistance, and Composite diaphragms that bond PTFE with an elastomer for enhanced flexibility and durability. Each variant leverages PTFE's inherent chemical inertness while adding specific properties to meet application demands.
The critical insight is that selecting the right PTFE diaphragm requires a trade-off. You must balance the absolute chemical resistance and purity of virgin PTFE against the superior mechanical properties—like strength, wear resistance, and flex life—offered by filled and composite versions.

The Core Function of a PTFE Diaphragm
A Flexible, Impermeable Barrier
The fundamental job of any diaphragm is to act as a flexible barrier that separates two chambers or environments. It prevents fluids, gases, or contaminants from passing through while allowing for pressure changes or mechanical actuation.
Why PTFE is the Material of Choice
PTFE is chosen for its remarkable combination of properties. It is nearly universally non-reactive, making it ideal for handling aggressive chemicals. Its non-stick surface prevents process media from adhering, which is critical in hygienic applications like biotechnology and food processing where cleanliness is paramount.
A Breakdown of PTFE Diaphragm Types
The term "PTFE" refers to a base polymer. By adding fillers or combining it with other materials, we can engineer diaphragms with vastly different performance characteristics.
Virgin PTFE
This is pure, unmodified PTFE. It offers the highest level of chemical resistance and purity because it contains no additives or fillers that could leach into the process media.
Its primary applications are where purity is non-negotiable, such as in the pharmaceutical, biotech, and semiconductor industries. It's also an excellent electrical insulator.
Filled (Reinforced) PTFE
To enhance mechanical properties, PTFE can be blended with various filler materials. This significantly improves strength, stiffness, and resistance to wear and creep (deformation under load).
Common variants include:
- Glass-Filled PTFE: Offers excellent compressive strength and wear resistance. It is a workhorse material in many chemical processing valves and pumps.
- PEEK-Filled PTFE: PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a high-performance polymer. Adding it as a filler creates a diaphragm with exceptional stiffness and wear resistance, suitable for the most demanding high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
Chemically Modified PTFE (TFM™)
This is a second-generation PTFE that has been chemically modified at the molecular level. This modification results in a denser polymer structure.
The key benefits are lower gas permeation and a smoother surface finish. It also exhibits reduced creep, making it a superior choice for critical sealing applications where fugitive emissions must be minimized.
Composite Diaphragms
A composite diaphragm is a multi-layer component. It typically consists of a thin layer of PTFE that handles chemical contact, bonded to a thicker, more flexible backing material like a rubber elastomer (e.g., EPDM).
The PTFE layer is often etched on one side. This chemical etching process roughens the surface, allowing a strong adhesive bond to form with the rubber. The result is a diaphragm that combines PTFE's chemical resistance with the flexibility and long cycle life of rubber, making it ideal for high-frequency applications like diaphragm pumps.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right diaphragm is an exercise in engineering trade-offs. No single type is best for every situation.
Purity vs. Mechanical Strength
Virgin PTFE offers the highest purity but has the lowest mechanical strength and is more susceptible to creep. Filled PTFE grades are dramatically stronger but introduce a potential (though often negligible) source of contamination and can have reduced chemical compatibility if the filler itself is attacked.
Flexibility vs. Simplicity
A composite diaphragm provides superior flexibility and can withstand millions of cycles in a pump. However, the bond between the PTFE and the rubber backing introduces an interface that could potentially become a failure point over time or under extreme chemical attack.
Cost vs. Performance
More advanced materials come at a higher cost. A standard glass-filled PTFE diaphragm might be perfectly suitable for a general chemical valve, while a more expensive PEEK-filled or Chemically Modified PTFE diaphragm is reserved for applications where the performance benefits justify the investment.
Selecting the Right Diaphragm for Your Application
Use your primary operational goal to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and inertness: Choose Virgin PTFE for applications in biotechnology, food and beverage, or semiconductor manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is high pressure and wear resistance: Select a Filled PTFE, such as glass-filled for general use or PEEK-filled for extreme temperature and pressure.
- If your primary focus is maximum flexibility and high cycle life: A Composite diaphragm with a rubber backing is the optimal choice for actuators and pumps.
- If your primary focus is sealing critical gases or preventing permeation: Use Chemically Modified PTFE for its denser polymer structure and superior barrier properties.
Understanding these material distinctions empowers you to design a more reliable, efficient, and cost-effective system.
Summary Table:
| Diaphragm Type | Key Features | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Maximum purity, chemical inertness, non-stick | Pharmaceutical, semiconductor, biotech |
| Filled PTFE | Enhanced strength, wear resistance, reduced creep | High-pressure valves, pumps, industrial |
| Composite | High flexibility, long cycle life, bonded elastomer | Diaphragm pumps, actuators, frequent cycling |
| Chemically Modified PTFE | Low gas permeation, smooth surface, reduced creep | Critical gas sealing, emission control |
Struggling to select the right PTFE diaphragm for your specific application? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including custom diaphragms—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need the absolute purity of Virgin PTFE for sensitive processes or the rugged durability of Filled PTFE for high-wear environments, our precision production and custom fabrication capabilities ensure you get a solution tailored to your exact requirements. Contact us today to discuss your project and let our experts help you optimize your system's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications



















