At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets are exceptionally suitable for the electrical and electronics industry because they are one of the best commercially available electrical insulators. This high-performance polymer combines superior dielectric properties with an outstanding resistance to high temperatures and corrosive chemicals, making it ideal for protecting sensitive components, insulating wiring, and ensuring the reliability of electronic assemblies.
In an industry where preventing electrical leakage is as critical as sealing out environmental contaminants, PTFE stands out. It uniquely provides both a robust physical seal and elite electrical insulation, a dual-capability that ensures the safety and longevity of sensitive electronic systems.
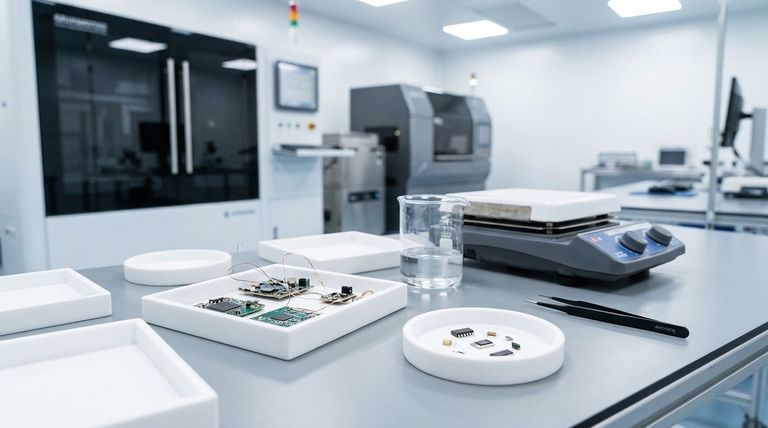

The Fundamental Properties of PTFE for Electronics
To understand why PTFE is a default choice for demanding electrical applications, we must examine its key material properties. These characteristics work in concert to protect and isolate electronic systems.
Unmatched Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with very high volume resistivity. This means it strongly resists the flow of electric current.
This property is fundamental for preventing short circuits, stopping current leakage between conductors, and preserving the integrity of signals in high-frequency applications like computer and communications wiring.
High Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength measures a material's ability to withstand a strong electric field without breaking down and becoming conductive.
PTFE exhibits a very high dielectric strength, making it the ideal choice for insulating high-voltage cables, connectors, and components. This prevents dangerous electrical arcing and ensures operational safety under significant electrical stress.
Resilience to High Temperatures
Electronic components often generate significant heat, and manufacturing processes like soldering expose materials to extreme temperatures.
PTFE has a very high melting point (around 327°C or 621°F) and a wide operating temperature range. This thermal stability ensures that gaskets and insulators will not melt, deform, or degrade when placed near heat sources or during assembly.
Superior Chemical and Moisture Resistance
Electronic devices are frequently exposed to moisture, cleaning solvents, and other chemicals that can cause corrosion and failure.
PTFE is almost universally inert, meaning it does not react with chemicals. This property, combined with its low moisture absorption, allows it to form a durable seal that reliably protects sensitive circuit boards and internal components from environmental damage.
Common Applications in Electrical and Electronics
These properties translate directly into critical roles across the industry, from consumer devices to industrial control systems.
Sealing for Sensitive Components
The primary role of a PTFE gasket is to create a seal. In electronics, this involves sealing enclosures for circuit boards, connectors, and other sensitive hardware.
The gasket prevents the ingress of dust, moisture, and corrosive agents, while its insulating properties ensure it doesn't interfere with the electrical function of the components it protects.
Insulation for Wires and Cables
PTFE is frequently used as a high-performance insulating jacket or wrapping for wires and cables, especially in aerospace and computer applications.
Its combination of high-temperature resistance and excellent dielectric properties allows for thinner, lighter wiring that can handle high-frequency signals without loss or interference.
Components in Manufacturing
Beyond the final product, PTFE is used in the manufacturing process itself. Its chemical inertness and thermal stability make it suitable for parts used in semiconductor and circuit board fabrication.
These processes often involve harsh chemicals and high temperatures where lesser materials would quickly fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While PTFE is a superior material, no choice is without context. A trusted advisor must also highlight the practical limitations to ensure it is applied correctly.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material and can be susceptible to creep, or cold flow. Under sustained compressive load (like a tightened bolt), the material can slowly deform over time.
Proper flange and gasket design are critical to mitigate this effect and maintain a long-term, effective seal. Forgetting this can lead to a loss of sealing pressure over the product's lifespan.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance materials come with a higher price tag. PTFE is more expensive than common elastomers like silicone or neoprene.
Therefore, its use is typically reserved for applications where its specific properties—high heat, aggressive chemicals, or critical electrical insulation—are non-negotiable and justify the investment.
The Role of Fillers
It is crucial to specify virgin (unfilled) PTFE for applications requiring maximum electrical insulation.
Some PTFE variants are blended with fillers like carbon or glass to enhance mechanical properties like wear resistance or compressive strength. However, these fillers can compromise its insulating capabilities and, in some cases (like carbon), can even make the material statically dissipative or conductive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material selection should be driven by the most critical demand of your specific design.
- If your primary focus is isolating high-voltage components or ensuring signal integrity: Virgin PTFE's high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive electronics from heat, chemicals, and moisture: PTFE's thermal stability and chemical inertness provide unparalleled long-term reliability.
- If your primary focus is sealing a general-purpose, low-voltage device: A less expensive material like silicone may suffice, but you should specify PTFE whenever performance under stress cannot be compromised.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is an investment in the safety, reliability, and operational integrity of your electrical system.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Electronics |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Electrical Insulation | Prevents short circuits and current leakage, ideal for high-frequency applications. |
| High Dielectric Strength | Withstands strong electric fields, preventing arcing in high-voltage components. |
| High-Temperature Resilience | Stable up to 327°C (621°F), ensuring performance near heat sources and during assembly. |
| Superior Chemical & Moisture Resistance | Protects sensitive components from corrosive agents and environmental damage. |
Invest in the reliability of your electronic systems with KINTEK's precision PTFE components.
As detailed in this article, PTFE's unique combination of electrical insulation and environmental sealing is critical for the safety and longevity of sensitive electronics in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and labware that meet these exacting demands.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication services, from initial prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get the perfect component for your application. Let us help you protect your most critical designs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What advantages do PTFE bars offer in chemical industries? Ensure Safety and Efficiency in Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE typically processed in manufacturing? A Guide to Molding, Sintering & Machining
- What are the main features of PTFE bellow mechanical seals? A Guide to Extreme Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why are PTFE sheets used for lining acid tanks? Achieve Unmatched Chemical Resistance
- How does the non-stick property of PTFE benefit gasket applications? Ensure Clean, Durable, and Low-Maintenance Seals
- How can PTFE be fabricated and what forms is it available in? Mastering Molding, Machining, and Coatings
- What are the key properties of PTFE pipes? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What industries extensively use PTFE membrane? The Critical Material for Safety & Purity



















