In short, the general continuous operating temperature for PTFE (Teflon) components is exceptionally wide, ranging from approximately -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). However, this range represents the capability of the raw material itself. The effective operating range of a specific O-ring or seal depends heavily on its specific construction and the mechanical demands of the application.
While pure PTFE boasts one of the broadest thermal operating windows of any polymer, the true performance of a seal depends on its design. The difference between a static backup ring and a dynamic encapsulated O-ring can significantly alter the effective temperature range you can rely on.
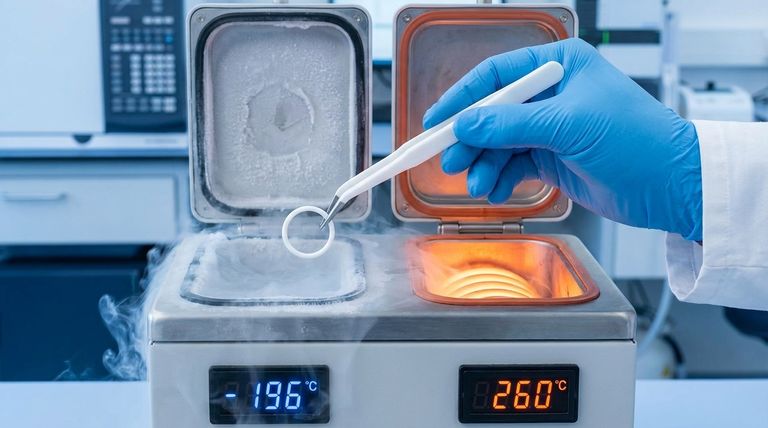
The Factors Defining PTFE's Temperature Range
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a remarkable material known for its extreme chemical inertness and very low coefficient of friction. Its thermal properties are a key reason for its widespread use in demanding industrial environments.
The High-Temperature Limit
PTFE maintains excellent structural integrity and material properties up to 260°C (500°F). In this range, it retains its non-stick characteristics and high resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it a primary choice for seals in high-temperature processing, automotive, and aerospace applications.
The Low-Temperature Limit
At the other extreme, PTFE performs reliably in cryogenic conditions, with some grades functional down to -200°C (-328°F). At these temperatures, the material remains strong, but a critical change occurs: it becomes significantly more rigid and less flexible. This loss of pliability is a crucial design consideration.
Why Published Ranges Vary
You will often see different temperature ranges cited for various PTFE components. This variance is not an error; it reflects the specific design and intended use of the part.
-
Solid PTFE Rings: These components, often used as spacers or backup rings, reflect the full temperature range of the raw material (-200°C to 260°C). Their primary function is mechanical support, where flexibility is less critical than compressive strength.
-
Encapsulated O-Rings: These seals combine a flexible core (like Silicone or FKM rubber) with a thin outer layer of PTFE. Here, the core material dictates the effective temperature range. For example, a silicone-core O-ring is typically limited to around -60°C to 230°C.
-
Dynamic Seals (e.g., Piston Rings): In applications with movement, factors like friction-generated heat and wear resistance become paramount. This can narrow the practical operating window to a range like -60°C to 200°C to ensure a long service life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting PTFE solely based on its wide temperature range without understanding its mechanical limitations is a common pitfall. Its properties present distinct trade-offs compared to traditional rubber elastomers.
Low-Temperature Rigidity
While a PTFE seal will not crack or fail catastrophically at cryogenic temperatures, its increasing stiffness can compromise its ability to conform to surfaces. In applications with significant thermal cycling or vibration, a rigid seal may be unable to maintain its sealing force, leading to leaks.
High-Temperature Creep (Cold Flow)
PTFE is susceptible to creep, also known as cold flow. This is the tendency of the material to slowly deform over time when under a constant load. This process accelerates significantly at higher temperatures, potentially causing the seal to lose its shape and effectiveness, especially in high-pressure applications.
Poor Elastic Memory
Unlike rubber O-rings, PTFE has very little elasticity. Once compressed, it does not spring back to its original shape effectively. This makes solid PTFE O-rings unsuitable for applications that require repeated assembly and disassembly or where the sealing surfaces may have imperfections.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision must balance the thermal environment with the specific mechanical function of the seal.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature range in a static, high-pressure application: Use a solid PTFE O-ring in conjunction with a PTFE backup ring to prevent extrusion and support the seal.
- If your primary focus is reliable sealing with some flexibility across a broad temperature range: An encapsulated O-ring is often the best choice, but verify its temperature rating is based on its core material (Silicone, FKM, etc.).
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal with low friction: A specialized, filled-PTFE piston ring or lip seal is likely required, as pure PTFE may wear too quickly under constant movement.
Ultimately, matching the specific type of PTFE component to the precise thermal and mechanical loads of your application is the key to reliable performance.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Material/Component Type | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Solid PTFE (Backup Rings, Spacers) | Full raw material range; best for static, high-pressure support. |
| Limited by Core Material (e.g., -60°C to 230°C) | Encapsulated O-Rings (PTFE shell) | Effective range depends on the elastomer core (Silicone, FKM). |
| Often -60°C to 200°C | Dynamic Seals (Piston Rings) | Compromise for movement; considers friction, wear, and service life. |
Ensure Reliable Performance in Extreme Environments
Understanding the nuances of PTFE's temperature capabilities is critical for your application's success. The difference between a static seal and a dynamic one can significantly impact performance and longevity.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We don't just supply parts; we provide solutions engineered for your specific thermal and mechanical demands.
We help you navigate the trade-offs:
- Material Selection: Advising on pure PTFE versus filled compounds for enhanced properties.
- Design for Application: Ensuring the component type (O-ring, backup ring, piston seal) is perfectly matched to your operating conditions.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototyping to high-volume production, we deliver parts that meet exact specifications for temperature, pressure, and chemical resistance.
Ready to solve your high-temperature or cryogenic sealing challenge? Contact our engineering team today for a consultation. Let's discuss your requirements and develop a PTFE solution that ensures reliability and peak performance.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of Teflon bushings in machinery? Solve Friction in Harsh Environments
- What are dynamic applications and why are PTFE O-Rings suitable for them? Unlock Low-Friction, Chemical-Resistant Sealing
- What are the limitations of PTFE-coated O-rings? Understand the risks of wear, flaking, and contamination.
- In what applications are PTFE liners commonly used? Critical Solutions for Harsh Environments
- What are the non-stick properties of PTFE impellers? Achieve Purity & Prevent Buildup in Critical Mixing
- What are the three types of springs used in PTFE seals? Optimize Your Seal Performance
- What are the limitations of Teflon encapsulated O-rings in terms of chemical resistance? Key Weaknesses to Avoid Seal Failure
- What are the characteristics of PTFE coatings? Unlock Extreme Performance for Your Components



















