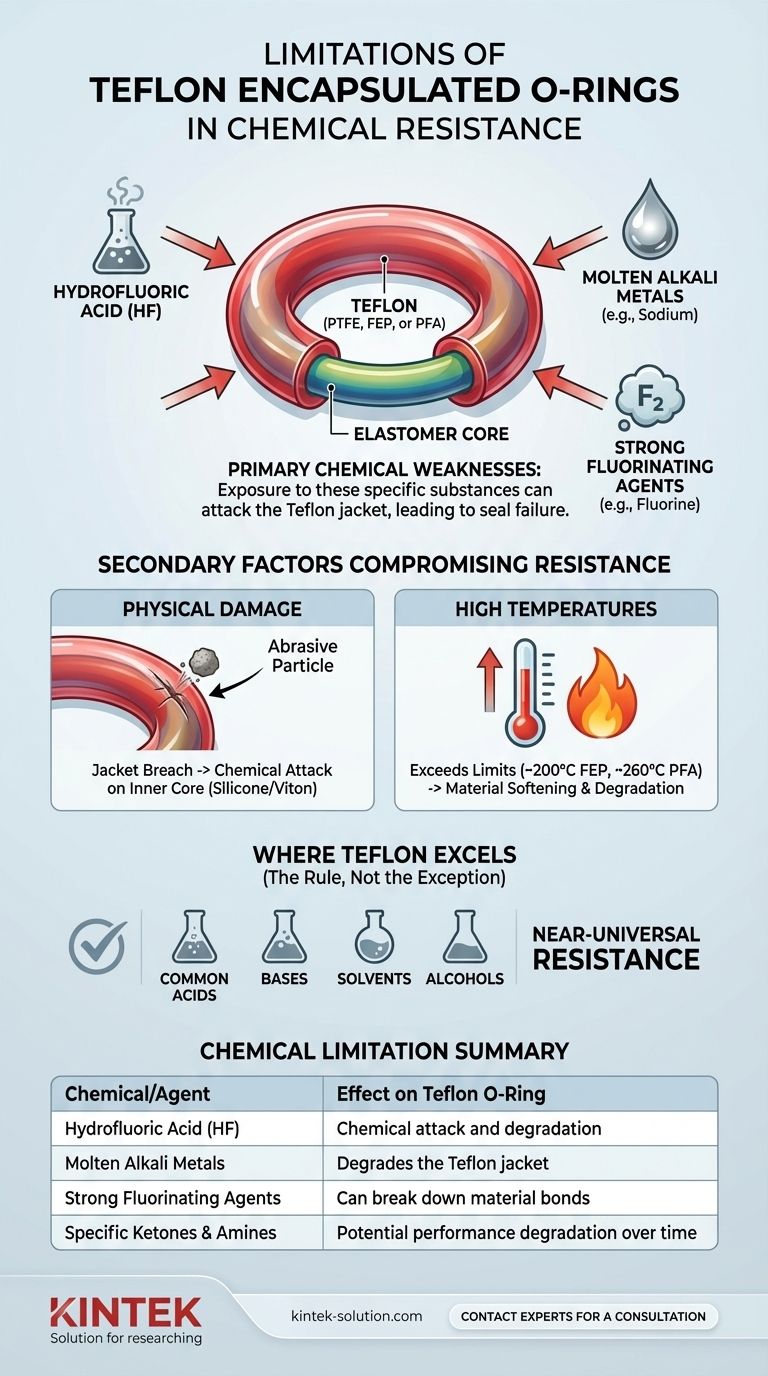
The primary chemical limitations of Teflon encapsulated O-rings are exposure to hydrofluoric acid (HF), molten alkali metals like sodium, and powerful fluorinating agents such as elemental fluorine. While renowned for their exceptional chemical inertness, these specific substances can attack the Teflon (PTFE, FEP, or PFA) jacket, leading to seal failure.
The core takeaway is that while Teflon encapsulated O-rings offer near-universal chemical resistance, their integrity is compromised by a very specific and highly reactive set of chemicals. Understanding these few exceptions is critical for ensuring safety and reliability in demanding applications.

Known Chemical Weaknesses of Teflon Encapsulation
While the list of chemicals that Teflon resists is vast, the list of those that can cause degradation is short, specific, and crucial to know. Failure to account for these substances can lead to catastrophic seal failure.
Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)
Hydrofluoric acid is one of the few acids that can chemically attack the Teflon encapsulation. This is a well-documented limitation and a primary contraindication for using these seals.
Molten Alkali Metals
Alkali metals such as sodium and potassium in their molten state are highly reactive and will degrade the Teflon jacket. This is a specific concern in high-temperature, specialized industrial processes.
Strong Fluorinating Agents
Extremely powerful fluorinating agents, most notably elemental fluorine gas, can affect the seal, particularly at elevated temperatures and pressures. These are highly reactive chemicals that can break down the strong carbon-fluorine bonds in Teflon.
Specific Ketones and Amines
While generally resistant to most solvents, certain specific ketones and amines have been shown to potentially degrade seal performance over time. This is a less common issue but requires consideration in specialized chemical applications.
Understanding the Real-World Limitations
Chemical resistance on paper does not always translate to perfect performance in a dynamic system. Mechanical and thermal factors can compromise the seal, creating a path for chemical attack.
Physical Damage Compromises Resistance
The Teflon jacket is a relatively thin layer encapsulating an elastomer core. This outer shell is prone to scratching and damage in any application with abrasive media or sharp hardware.
Once the jacket is breached, the aggressive chemical media can attack the less-resistant inner core (typically Silicone or Viton), causing the seal to fail rapidly.
High Temperatures as a Failure Point
Teflon encapsulation has strict temperature limits, typically around 200°C (392°F) for FEP and 260°C (500°F) for PFA. Exceeding these temperatures can cause the material to soften or degrade, compromising its chemical barrier properties.
Direct exposure to flame will destroy the seal almost instantly.
Where Teflon Excels: Near-Universal Resistance
Understanding the limitations is only part of the story. It is their incredible resistance to nearly everything else that makes these seals so valuable.
Resistance to Common Acids, Bases, and Solvents
Teflon encapsulated O-rings provide superior, often perfect (rated 10 out of 10), resistance against the most common and aggressive chemicals.
This includes substances like corrosive acids, bases, alcohols, aromatic solvents, petroleum spirits, and naphtha.
Inertness to Standard Solvents
They are effectively inert when exposed to water, ethanol, acetone, methanol, chloroform, hexane, toluene, benzene, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), making them a default choice for many laboratory and chemical processing applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires matching the material's capabilities to the system's demands.
- If your primary focus is handling hydrofluoric acid, molten metals, or fluorine gas: You must seek a different sealing material, as a Teflon encapsulated O-ring is not a safe choice.
- If your primary focus is general chemical processing with aggressive acids, bases, or solvents: Teflon encapsulated O-rings are an excellent and highly reliable option.
- If your primary focus is an application with abrasive particles or potential for mechanical damage: You must carefully consider if the Teflon jacket can maintain its integrity, as any scratch can become a point of chemical failure.
Understanding these specific limitations is the key to leveraging their exceptional performance reliably.
Summary Table:
| Chemical/Agent | Effect on Teflon O-Ring |
|---|---|
| Hydrofluoric Acid (HF) | Chemical attack and degradation |
| Molten Alkali Metals (e.g., Sodium) | Degrades the Teflon jacket |
| Strong Fluorinating Agents (e.g., Fluorine) | Can break down material bonds |
| Specific Ketones & Amines | Potential performance degradation over time |
Need a reliable, chemically inert seal for your demanding application?
While Teflon encapsulated O-rings have specific limitations, their near-universal resistance to most aggressive chemicals makes them a top choice for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom O-rings. We prioritize material integrity to ensure your seals perform reliably, even in the most challenging environments.
Let us help you select or custom-fabricate the perfect seal for your needs—from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















