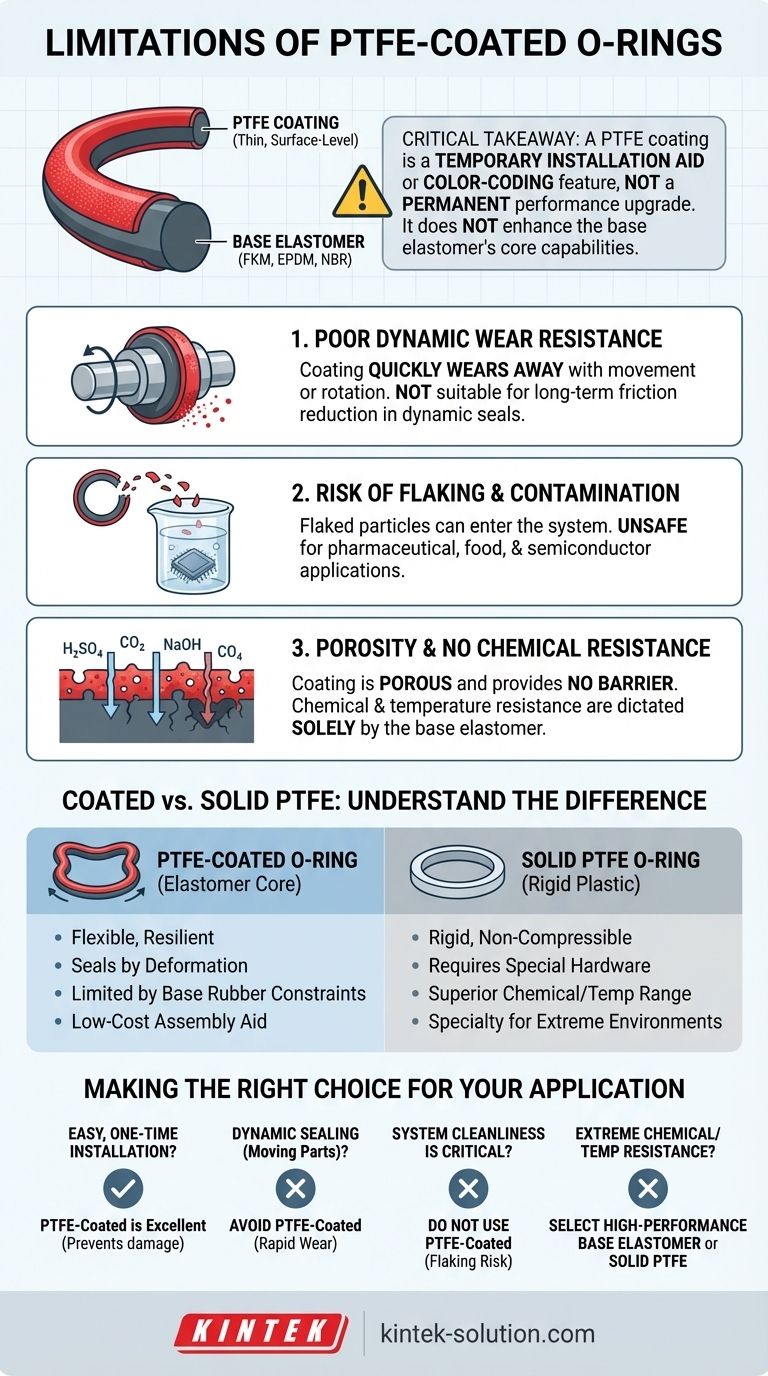
Ultimately, the limitations of a PTFE-coated O-ring stem from the fact that the coating is a very thin, superficial layer. The three primary drawbacks are poor dynamic wear resistance where the coating quickly rubs off, the potential for flaked coating particles to contaminate sensitive systems, and the coating's porosity, which means it adds no chemical or temperature resistance to the underlying O-ring material.
The central takeaway is this: A PTFE coating should be viewed as a temporary installation aid or a color-coding feature, not as a permanent performance enhancement. The core sealing capabilities and environmental resistance of the O-ring are determined entirely by the base elastomer, not the coating.

The True Role of a PTFE Coating
To understand the limitations, you must first understand the coating's intended purpose. It is not a structural part of the seal.
A Surface-Level Enhancement
The PTFE coating is an extremely thin layer applied to the surface of a standard elastomeric O-ring (like FKM, EPDM, or NBR).
Its primary function is to impart the low-friction, non-stick surface properties of PTFE onto the flexible, resilient body of the rubber O-ring.
The Primary Benefit: Dry Lubrication
The main advantage of this coating is providing a dry lubricant on the seal's surface.
This significantly reduces friction during assembly, preventing the O-ring from twisting, binding, or tearing during installation—a common failure mode, especially in automated processes.
A Secondary Benefit: Color Coding
Coatings can be produced in virtually any color. This makes them a simple and inexpensive way to visually differentiate between O-rings of different materials or sizes, preventing mix-ups in inventory and on the assembly line.
Critical Limitations and Failure Modes
The coating's thin, topical nature is the source of all its weaknesses. It is a surface treatment, and it behaves as such.
Poor Dynamic Wear Resistance
This is the most significant limitation. In any application involving movement, rotation, or even significant vibration, the PTFE coating will quickly wear away.
The coating is best thought of as a one-time-use lubricant for installation. It cannot be relied upon to reduce friction during the operational life of a dynamic seal.
Risk of Flaking and Contamination
As the coating wears off, it creates small flakes of PTFE. These particles can enter the system fluid or environment.
This makes PTFE-coated O-rings entirely unsuitable for applications where particulate contamination is a concern, such as in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, or semiconductor industries.
Porosity and Chemical Resistance
A common misconception is that the coating enhances the O-ring's chemical resistance. This is incorrect. The coating is porous and does not provide a hermetic barrier.
The chemical and temperature resistance of the seal is dictated solely by the base elastomer. You must select an O-ring material that is fully compatible with your application's media and temperature range, as the coating offers no protection.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Coated vs. Solid PTFE
It is critical not to confuse a PTFE-coated O-ring with a solid PTFE O-ring. They are fundamentally different components with distinct applications.
Flexibility and Sealing
A PTFE-coated O-ring is a flexible, resilient elastomer that deforms to create a seal.
A solid PTFE O-ring is a rigid, non-compressible plastic. It cannot be used in a standard O-ring gland and requires special hardware designs to achieve a seal.
Performance in Extreme Environments
The coated O-ring is limited by the temperature and chemical constraints of its base rubber.
A solid PTFE O-ring offers a vastly superior range of chemical compatibility and can withstand much higher and lower temperatures than almost any elastomer.
Cost and Application
PTFE-coated O-rings are a low-cost solution for simplifying assembly. Solid PTFE O-rings are a specialty material used in aggressive chemical or high-temperature environments where elastomers would fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select your seal based on the demands of the application, not the appeal of a surface treatment.
- If your primary focus is easy, one-time installation: A PTFE-coated O-ring is an excellent, low-cost choice to prevent damage during assembly.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing (moving parts): Avoid PTFE-coated O-rings due to rapid wear and choose an internally lubricated elastomer or a different seal design entirely.
- If your primary focus is system cleanliness: Do not use PTFE-coated O-rings because the risk of flaking and particulate contamination is too high.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical or temperature resistance: The coating is irrelevant; select a high-performance base elastomer (like FFKM) or a solid PTFE seal that meets your specific requirements.
Ultimately, understanding that the coating is a helpful tool for assembly, not a fundamental upgrade to the seal's performance, is the key to using it correctly.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Application Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Dynamic Wear Resistance | Coating wears off quickly with movement | Not suitable for dynamic seals |
| Risk of Flaking & Contamination | PTFE particles can enter system fluid | Unsafe for pharmaceutical, semiconductor, or food industries |
| Porosity & No Chemical Resistance | Coating adds no protection; base elastomer determines performance | Misleading for harsh chemical environments |
Need a reliable sealing solution tailored to your exact application?
PTFE-coated O-rings are a temporary aid, not a performance upgrade. For truly robust performance in demanding environments, you need the right material and design from the start.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you select or fabricate the perfect seal for your needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and ensure system integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry



















