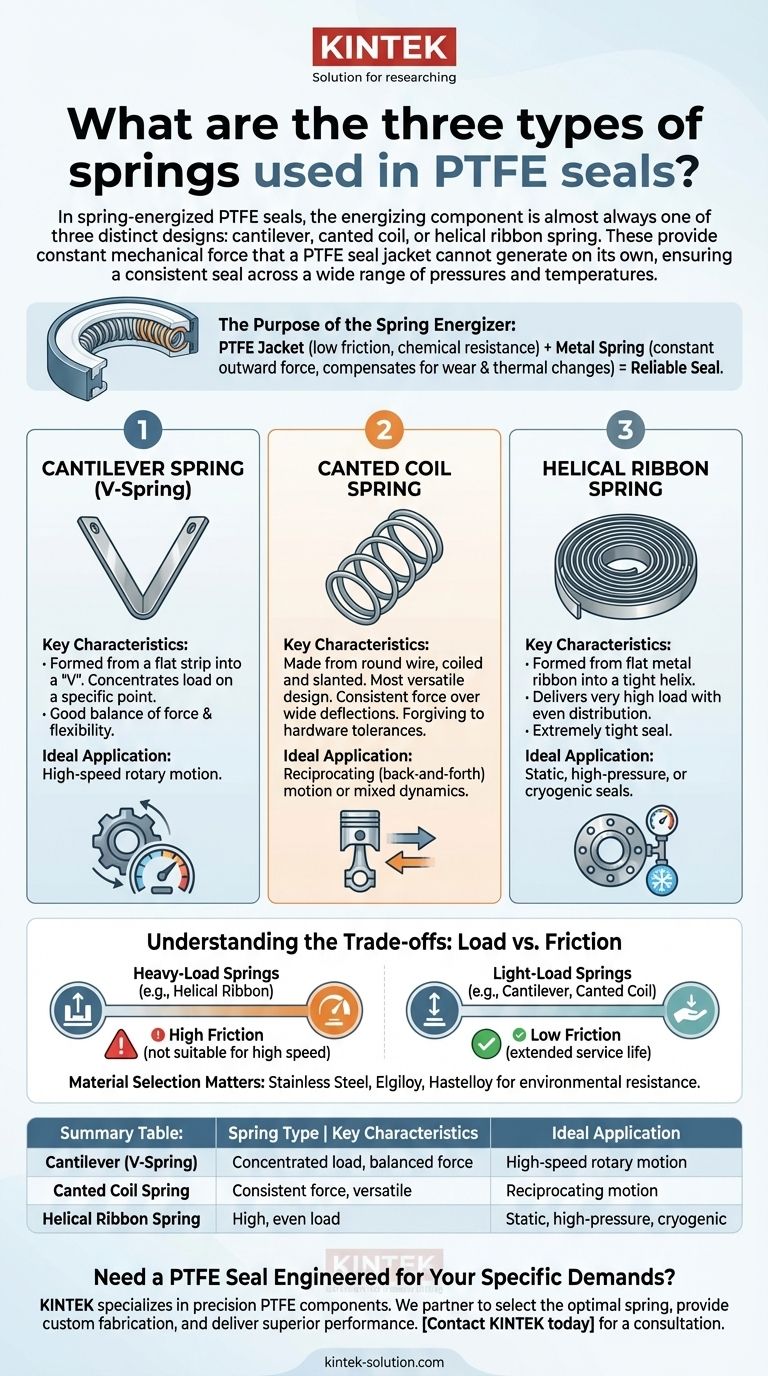
In spring-energized PTFE seals, the energizing component is almost always one of three distinct designs: the cantilever spring, the canted coil spring, or the helical ribbon spring. These metal springs provide the constant mechanical force that a PTFE seal jacket cannot generate on its own. This ensures a consistent, effective seal against a mating surface across a wide range of pressures and temperatures.
The choice of spring is not arbitrary; it is dictated by the application's specific demands. Each spring type is engineered to provide a distinct load profile optimized for either dynamic motion, static holding power, or a balance of both.

The Purpose of the Spring Energizer
A spring-energized seal is a two-part system: a high-performance polymer jacket (usually PTFE) and a metal spring. Understanding why the spring is necessary is key to selecting the right one.
The Jacket Provides the Interface
The PTFE jacket is the component that makes contact with the hardware. It is chosen for its extremely low friction, broad chemical resistance, and wide temperature tolerance. However, PTFE is not an elastomer; it does not "bounce back" once compressed.
The Spring Provides the Force
The internal spring provides the constant outward force needed to press the jacket lips against the sealing surfaces. This ensures a reliable seal, especially in low-pressure conditions where system pressure is insufficient to fully actuate the seal. It also compensates for material expansion or contraction during temperature fluctuations and accounts for any wear over the seal's life.
The Three Core Spring Designs
Each spring type has a unique geometry that defines its performance characteristics and ideal use case.
Cantilever Spring (V-Spring)
Formed from a flat strip of metal into a "V" shape, this spring is a workhorse for dynamic applications.
Its design concentrates the load on a specific point, making it excellent for sealing in high-speed rotary equipment. It provides a good balance of force and flexibility.
Canted Coil Spring
This spring is made from round wire that is coiled and then slanted, giving each coil an elliptical shape.
It is the most versatile design, suitable for both dynamic rotary and reciprocating (back-and-forth) motion. It provides a very consistent force over a wide range of deflections, making it forgiving to hardware tolerances.
Helical Ribbon Spring
This spring is formed from a flat metal ribbon wound into a tight helix, similar to a traditional compression spring but with different load characteristics.
It delivers a very high load with even distribution, making it the ideal choice for static or very slow dynamic applications. Its primary function is to create an extremely tight seal where movement and friction are not the main concerns.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Load vs. Friction
The core decision in spring selection comes down to a trade-off between sealing force and friction.
Heavy-Load Springs for Maximum Sealing
High-load springs, such as the helical ribbon, exert significant force. This is critical for applications like high-pressure gas sealing or cryogenic systems where preventing leakage is the absolute priority.
The trade-off is higher friction, which generates more heat and increases wear on both the seal and the mating hardware. This makes them unsuitable for high-speed dynamic applications.
Light-Load Springs for Dynamic Performance
Lighter-load springs, common in cantilever and canted coil designs, are engineered to minimize friction. This reduces heat generation and extends the service life of seals in rotary or reciprocating equipment.
The trade-off is a lower sealing force. This is perfectly acceptable in applications where dynamic performance is paramount and a microscopic level of leakage or weeping is tolerable.
Material Selection Matters
Beyond the shape, the spring's material is chosen for environmental resistance. Common options like stainless steel, Elgiloy, and Hastelloy are selected based on the specific needs for corrosion resistance and temperature stability.
Selecting the Right Spring for Your Application
Your operational goal is the single most important factor in determining the correct spring design.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotary motion: A cantilever (V-spring) or a light-load canted coil spring is your best choice to minimize friction and wear.
- If your primary focus is reciprocating motion or mixed dynamics: The canted coil spring offers the most versatility and a consistent sealing force across a range of movements and hardware conditions.
- If your primary focus is a static, high-pressure, or cryogenic seal: A helical ribbon spring provides the high, evenly distributed load required for maximum sealing integrity.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental spring designs empowers you to specify a seal that is precisely engineered for your operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Spring Type | Key Characteristics | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Cantilever (V-Spring) | Concentrated load, good balance of force and flexibility | High-speed rotary motion |
| Canted Coil Spring | Consistent force, versatile, forgiving to tolerances | Reciprocating motion or mixed dynamics |
| Helical Ribbon Spring | High, evenly distributed load | Static, high-pressure, or cryogenic seals |
Need a PTFE Seal Engineered for Your Specific Demands?
Choosing the correct spring energizer is critical for seal performance, longevity, and reliability. The experts at KINTEK specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom spring-energized seals for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We partner with you to:
- Select the optimal spring type (cantilever, canted coil, or helical ribbon) for your application's pressure, temperature, and dynamic motion.
- Provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring a perfect fit and function.
- Deliver superior performance with our focus on precision production and material expertise.
Let's optimize your sealing solution. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE Teflon washers used in aerospace applications? Solving Critical Engineering Challenges
- What are the advantages of using PTFE guide strips in industrial applications? Enhance Equipment Life & Efficiency
- What is PTFE gland packing and what is it commonly known as? Discover Teflon's Superior Sealing Power
- What are common applications of machined Teflon/PTFE parts? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- How does the chemical resistance of PTFE gaskets benefit industrial applications? Achieve Unmatched Reliability
- What are the mechanical applications of PTFE rods? Solve Friction and Corrosion Problems
- What makes PTFE butterfly valves special compared to other types? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What makes PTFE V-rings suitable for sealing applications? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions



















