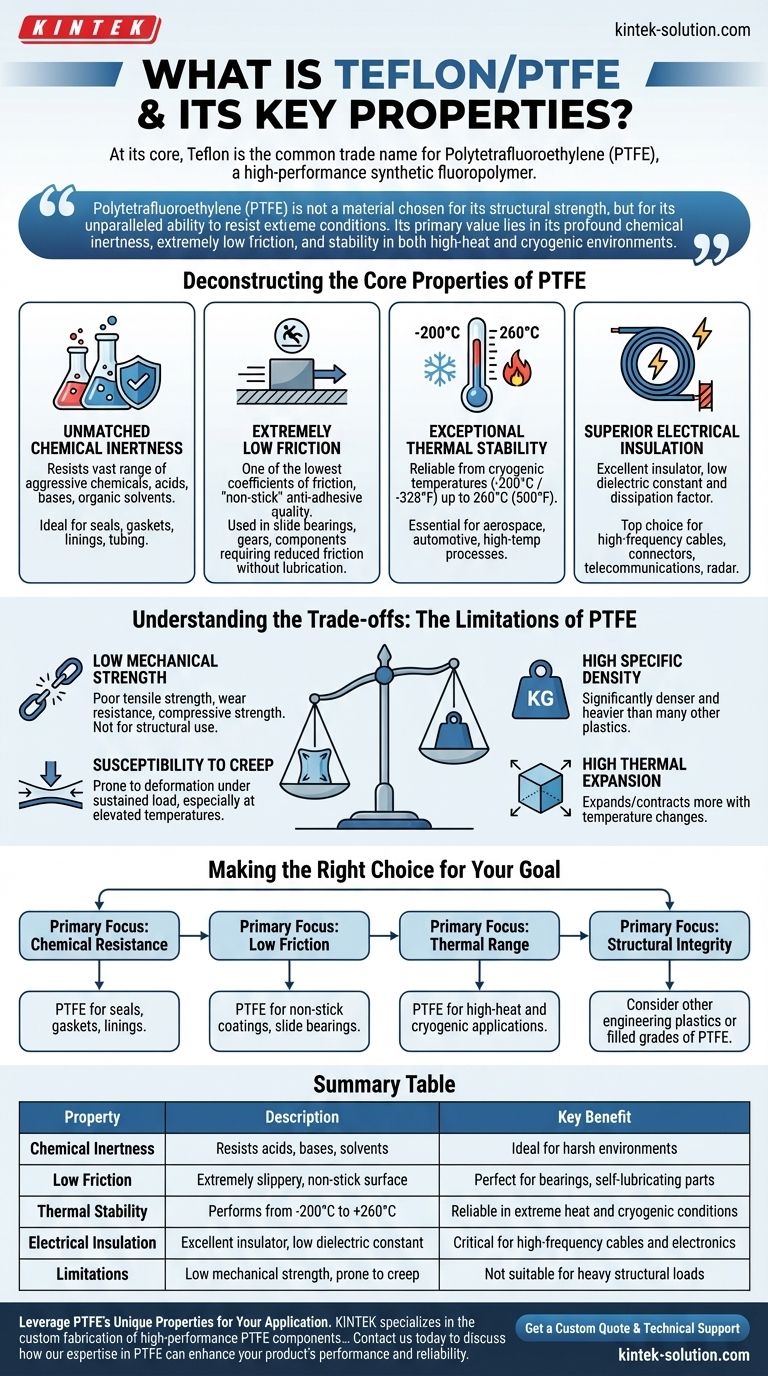
At its core, Teflon is the common trade name for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer built from carbon and fluorine atoms. It is renowned for an exceptional and rare combination of properties: it is famously non-stick, almost completely chemically inert, and stable across an extremely wide temperature range. This unique profile makes it an indispensable material in applications from industrial coatings to high-tech electronics.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not a material chosen for its structural strength, but for its unparalleled ability to resist extreme conditions. Its primary value lies in its profound chemical inertness, extremely low friction, and stability in both high-heat and cryogenic environments.

Deconstructing the Core Properties of PTFE
To understand when and why to use PTFE, we must look beyond a simple list of features and analyze the practical impact of each core property.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. The carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong, making the material resistant to a vast range of aggressive chemicals.
This means it will not degrade when exposed to most acids, bases, and organic solvents. This makes it a first-choice material for seals, gaskets, linings, and tubing in chemical processing and laboratory equipment.
Extremely Low Friction (The "Non-Stick" Quality)
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, which is why it feels slippery to the touch. This property is responsible for its famous "non-stick" or anti-adhesive quality.
While widely known for cookware, this characteristic is critical in industrial applications for slide bearings, gears, and any component where reducing friction and wear is paramount without traditional lubrication.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
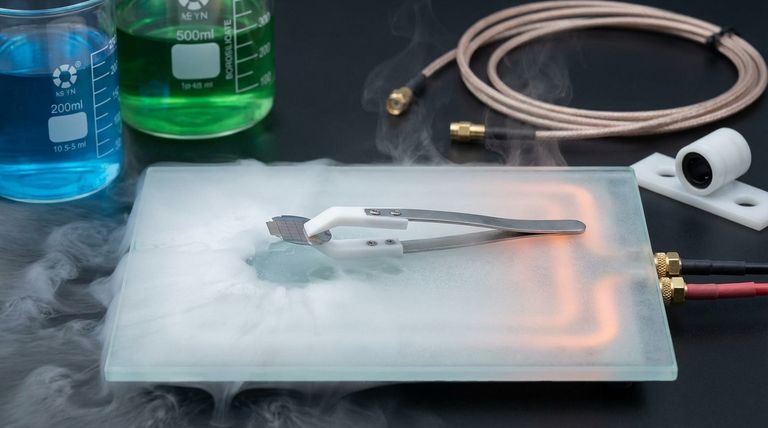
PTFE performs reliably across a remarkably broad temperature spectrum. It remains functional from cryogenic temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F).
Unlike many plastics that become brittle in extreme cold or melt in high heat, PTFE maintains its key properties, making it essential for aerospace, automotive, and high-temperature industrial processes.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with a very low dielectric constant and dissipation factor. This means it resists the flow of electricity and does not absorb significant energy from radio waves passing through it.
These properties make it a top choice for insulating high-frequency cables and connectors, particularly in telecommunications and radar systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Limitations of PTFE
No material is perfect. An objective evaluation of PTFE requires acknowledging its significant mechanical weaknesses, which often dictate its proper application.
Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics like nylon or PEEK, PTFE has relatively poor tensile strength, wear resistance, and compressive strength. It is a soft material and is not suitable for structural or heavy load-bearing applications in its pure form.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a sustained load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE is prone to "creep," which is the tendency to slowly and permanently deform over time. This must be accounted for in the design of parts like seals and gaskets.
High Specific Density
PTFE is significantly denser and heavier than many other plastics. This can be a disadvantage in applications where minimizing weight is a primary design goal.
High Thermal Expansion
The material has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it expands and contracts more than other materials with changes in temperature. This requires careful consideration for parts that demand tight dimensional tolerances.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is an almost unbeatable choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemically aggressive environments.
- If your primary focus is low friction: PTFE is ideal for non-stick coatings, slide bearings, and any application requiring a self-lubricating surface.
- If your primary focus is thermal range: PTFE excels in both high-heat (up to 260°C) and cryogenic applications where other polymers would become brittle or melt.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: You should look to other engineering plastics or use filled grades of PTFE to improve its mechanical properties.
By understanding both its unique strengths and its distinct limitations, you can leverage PTFE to solve engineering challenges that few other materials can.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists almost all acids, bases, and solvents. | Ideal for seals and linings in harsh environments. |
| Low Friction | Extremely slippery, non-stick surface. | Perfect for bearings and self-lubricating parts. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from -200°C to +260°C. | Reliable in extreme heat and cryogenic conditions. |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent insulator with low dielectric constant. | Critical for high-frequency cables and electronics. |
| Limitations | Low mechanical strength, prone to creep. | Not suitable for heavy structural loads. |
Leverage PTFE's Unique Properties for Your Application
PTFE's combination of chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction solves complex challenges in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. However, its successful application depends on precision manufacturing and design that accounts for its limitations.
KINTEK specializes in the custom fabrication of high-performance PTFE components—from prototypes to high-volume production. We manufacture critical parts like seals, liners, and labware with the precision your industry demands.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in PTFE can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Get a Custom Quote & Technical Support
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- How is PTFE used in food processing applications? Ensuring Hygiene, Efficiency, and Product Integrity
- What customization options are available for PTFE materials? Tailor Performance for Your Application
- What is PTFE chemically composed of? Discover the Simple Chemistry Behind Its Extreme Performance
- How does the low surface energy of PTFE contribute to its properties? Unlock Non-Stick, Low-Friction Performance
- What are the general properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)? Master Its Strengths and Limitations
- What is the chemical structure that gives PTFE its unique properties? The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
- What are the key features of PTFE? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- How does Teflon compare to rubber in terms of performance? A Guide to Selecting the Right Material for Extreme Conditions



















