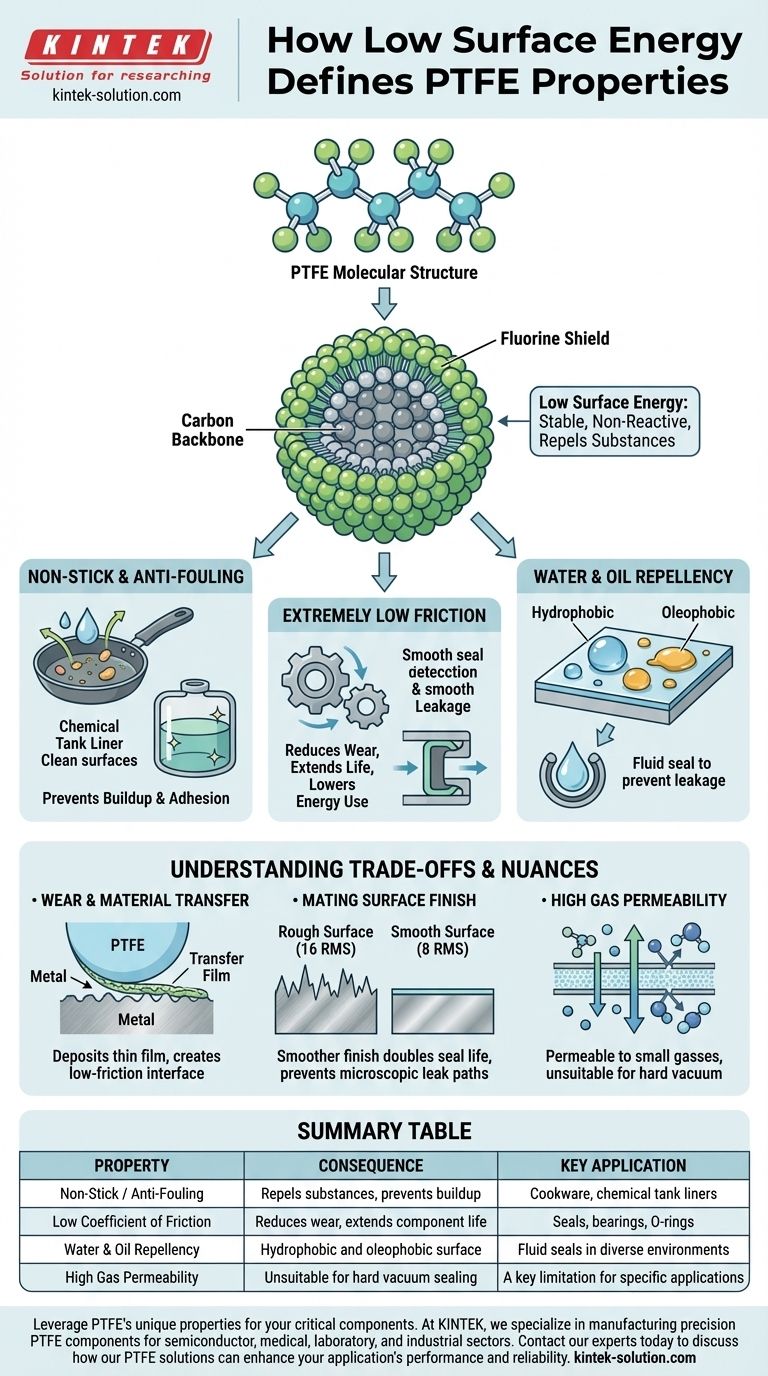
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene's (PTFE) low surface energy is the direct cause of its most valued characteristics: its non-stick nature and its extremely low coefficient of friction. This single property stems from its unique molecular structure, where a backbone of carbon atoms is completely shielded by a dense layer of fluorine atoms, creating a highly stable and non-reactive surface.
The essential takeaway is that PTFE's low surface energy is not just one property among many; it is the fundamental principle that dictates how it interacts with the physical world. This principle makes it repel virtually all substances, leading directly to its use in applications ranging from non-stick cookware to high-performance industrial seals.

The Molecular Origin of Low Surface Energy
To understand PTFE's performance, we must first look at its atomic structure. The properties are not accidental; they are a direct result of its chemical makeup.
The Carbon-Fluorine Shield
PTFE's structure consists of a long chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is bonded to two fluorine atoms.
These carbon-fluorine bonds are exceptionally strong and stable. The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are attached to, causing them to form a tight, protective sheath around the entire carbon backbone.
This fluorine sheath effectively creates a surface with extremely low electrical reactivity.
Repelling External Substances
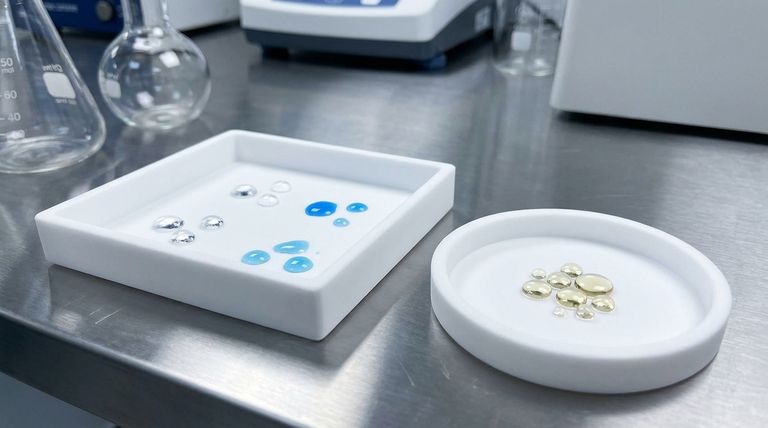
Surface energy is a measure of the disruption of bonds that occurs when a surface is created. Materials with high surface energy are "sticky" and attract other molecules.
Because of its stable fluorine shield, PTFE has one of the lowest surface energies of any known solid. There are very few available forces at the surface to attract other materials, causing liquids to bead up and roll off and solids to slide past with minimal interaction.
Direct Consequences in Application
This fundamental property of low surface energy translates directly into tangible, high-value performance characteristics that engineers rely on.
Non-Stick and Anti-Fouling Behavior
The most famous property of PTFE is its non-stick nature. Because other substances cannot easily "wet" or adhere to its low-energy surface, it is highly resistant to sticking and bio-fouling.
This makes it invaluable for cookware, food processing equipment, and linings for chemical tanks where preventing material buildup is critical.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
A low surface energy means there is very little adhesion between PTFE and another surface. This results in an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, one of the lowest of any solid material.
In dynamic applications like seals, bearings, and O-rings, this property dramatically reduces wear and tear, extends the component's service life, and lowers the energy required to operate the system.
Water and Oil Repellency
The low surface energy makes PTFE both hydrophobic (water-repellent) and oleophobic (oil-repellent).
This dual-repellency is a key advantage in sealing applications, where it must prevent leakage of a wide range of fluids under various conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While powerful, the properties derived from low surface energy come with practical considerations that are critical for successful implementation.
Wear and Material Transfer
PTFE does not resist wear through hardness. Instead, it wears by depositing a very thin film of itself onto the mating surface.
This transfer film is beneficial, as it eventually creates a low-friction PTFE-on-PTFE sliding interface. However, this wear mechanism must be accounted for in the design.
The Critical Role of Mating Surface Finish
The performance of a PTFE seal is directly tied to the finish of the surface it runs against. A rough mating surface acts like a file, dramatically accelerating wear until its crevices are filled with transferred PTFE.
Improving a metal surface finish from a rough 16 RMS to a smoother 8 RMS can double the operational life of a PTFE seal. Furthermore, a rough finish can create microscopic leak paths, which is especially problematic for sealing small gas molecules.
High Gas Permeability
A crucial limitation of PTFE is its relatively high permeability to gasses, a property it shares with silicones.
While it is an outstanding barrier for liquids, its molecular structure allows small gas molecules to pass through it over time. This makes it unsuitable for certain high-vacuum or critical gas-sealing applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is about leveraging its unique surface properties for a specific goal. Your primary objective should guide your design decisions.
- If your primary focus is minimizing friction and wear: Use PTFE in dynamic seals or bearings, but ensure the mating metal surface is finished to a high degree of smoothness (ideally 8 RMS or better).
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination or buildup: PTFE is an ideal choice for linings in food, chemical, or medical applications where a clean, non-stick, and inert surface is paramount.
- If your primary focus is sealing: PTFE is an excellent choice for sealing a wide variety of liquids, but you must consider its high gas permeability if your application involves sealing small gas molecules or maintaining a hard vacuum.
By understanding that PTFE's performance stems directly from its low surface energy, you can make more intelligent design choices that capitalize on its strengths while mitigating its inherent limitations.
Summary Table:
| Property | Consequence | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Stick / Anti-Fouling | Repels substances, prevents buildup | Cookware, chemical tank liners |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Reduces wear, extends component life | Seals, bearings, O-rings |
| Water & Oil Repellency | Hydrophobic and oleophobic surface | Fluid seals in diverse environments |
| High Gas Permeability | Unsuitable for hard vacuum sealing | A key limitation for specific applications |
Leverage PTFE's unique properties for your critical components.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get the full benefit of PTFE's low surface energy, whether you need custom prototypes or high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your application's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















