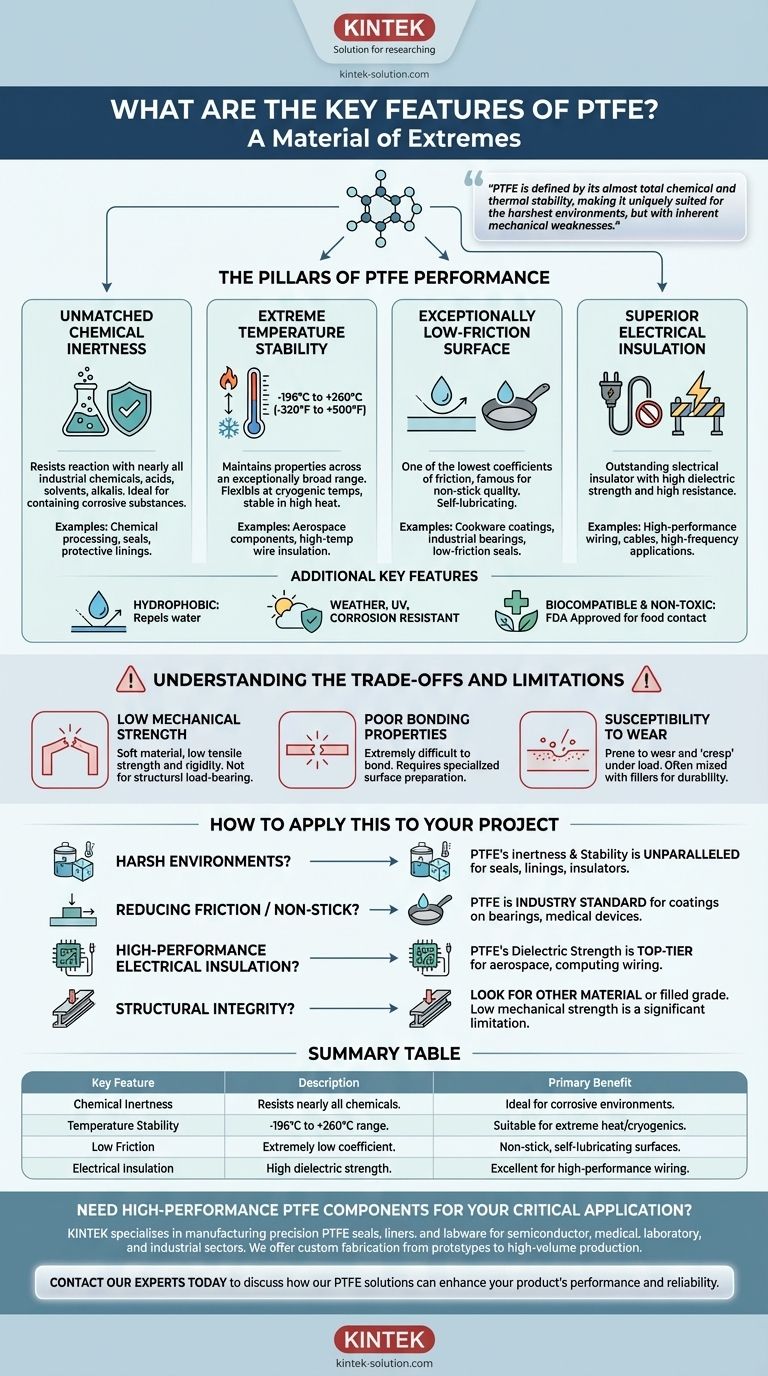
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of extremes. It is best known for its exceptional chemical resistance, an extremely wide operating temperature range, excellent electrical insulation, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, making it uniquely non-stick and slippery. These properties stem from its stable chemical structure, defining its use in specialized, demanding applications.
PTFE is defined by its almost total chemical and thermal stability, making it uniquely suited for the harshest environments. However, these defining strengths come with inherent mechanical weaknesses, making it a specialized material rather than a general-purpose plastic.

The Pillars of PTFE Performance
To understand where PTFE excels, it's best to examine its core characteristics. These features rarely work in isolation; they combine to create a uniquely capable material.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert, meaning it resists reaction with nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, solvents, and alkalis. This makes it an ideal choice for containing or transporting corrosive substances.
This property is critical for applications like chemical processing equipment, seals, and protective linings for pipes and vessels.
Extreme Temperature Stability
This material maintains its properties across an exceptionally broad temperature range, typically cited from -196°C to +260°C (-320°F to +500°F).
It remains flexible even at cryogenic temperatures and does not degrade in high-heat industrial processes, making it suitable for everything from aerospace components to high-temperature wire insulation.
An Exceptionally Low-Friction Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid, even lower than wet ice on wet ice. This gives it its famous non-stick quality.
This characteristic is the reason it's used as a coating for cookware, but it's also vital for industrial applications like self-lubricating bearings and low-friction seals.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with high dielectric strength and high electrical resistance.
It does not conduct electricity, making it a first-choice material for insulating high-performance wires and cables, especially in high-frequency or high-temperature applications.
Additional Key Features
Beyond the primary pillars, PTFE is also hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and does not absorb moisture.
It is also highly resistant to weather, UV light, and corrosion, and is considered biocompatible and non-toxic, earning it FDA approval for food contact.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect, and PTFE's unique strengths come with equally important limitations. Acknowledging these is crucial for proper material selection.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength and rigidity. It is not suitable for structural, load-bearing applications on its own.
Its primary value comes from its surface properties and stability, not its mechanical might.
Poor Bonding Properties
The same non-stick quality that makes PTFE so valuable also makes it extremely difficult to bond to other materials.
Adhering PTFE to another surface requires specialized and often costly surface preparation techniques, such as chemical etching.
Susceptibility to Wear
While its low-friction surface is a major benefit, virgin PTFE can be prone to wear and deformation under mechanical load, a phenomenon known as "creep."
For applications requiring higher wear resistance, PTFE is often mixed with fillers like glass, carbon, or graphite to improve its mechanical durability.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing PTFE is about matching its specific profile to a clear engineering need. Use these guidelines to determine if it's the right fit.
- If your primary focus is survival in harsh environments: PTFE's chemical inertness and extreme temperature stability make it an unparalleled choice for seals, linings, and insulators.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction or creating non-stick surfaces: PTFE is the industry standard for coatings on everything from industrial bearings to medical devices.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: Its high dielectric strength makes it a top-tier material for critical wiring in the aerospace, computing, and industrial sectors.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity or strength: You should look for another material or consider a filled grade of PTFE, as its low mechanical strength is a significant limitation.
Understanding both PTFE's exceptional strengths and its clear limitations is the key to leveraging it effectively in your design.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all chemicals, acids, and solvents. | Ideal for corrosive environments. |
| Temperature Stability | Performs from -196°C to +260°C. | Suitable for extreme heat and cryogenics. |
| Low Friction | Extremely low coefficient of friction. | Non-stick, self-lubricating surfaces. |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength and resistance. | Excellent for high-performance wiring. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand how to leverage PTFE's unique properties to solve complex challenges, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of polyamide fillers in PTFE? Protect Soft Mating Surfaces with Non-Abrasive Performance
- What does PTFE stand for? The Science Behind the Super-Material
- What are the key properties and limitations of PTFE? Leveraging its Strengths for Your Application
- What are the benefits of using PTFE? Achieve Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are some key facts about Teflon/PTFE? The Ultimate Guide to Its Unique Properties and Applications
- What is the tensile strength range of PTFE? Understanding Its Mechanical Limits for Your Design
- How is Teflon used in electronics? As a High-Performance Insulator and Semiconductor Component
- How does PTFE perform as an electrical insulator? Unmatched Signal Integrity & High-Voltage Reliability



















