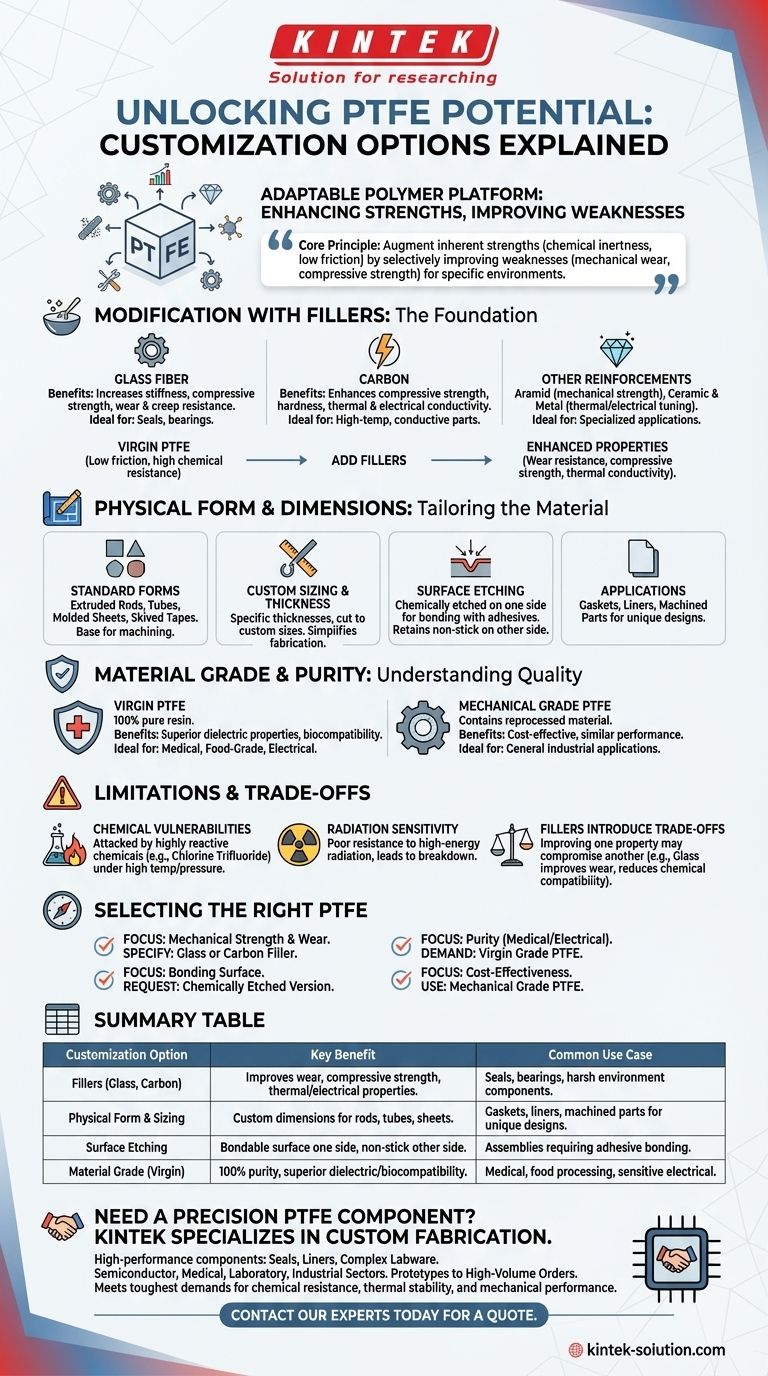
To be clear, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not a single material but a highly adaptable polymer platform. The most common customization options involve introducing specific fillers to enhance its properties, altering its physical form and dimensions for fabrication, and applying surface treatments to enable bonding. These modifications allow its exceptional chemical and thermal resistance to be leveraged in demanding industrial applications.
The core principle of PTFE customization is to augment its inherent strengths—like chemical inertness and low friction—by selectively improving its weaknesses, such as mechanical wear and compressive strength, to meet the precise demands of a specific environment.

The Foundation: Modifying PTFE with Fillers
The most significant performance changes in PTFE come from the addition of filler materials. These additives are compounded directly into the PTFE matrix to create a material with enhanced characteristics.
Why Add Fillers to PTFE?
Virgin PTFE excels in chemical resistance and has a low coefficient of friction, but it can be mechanically weak. Fillers are introduced primarily to improve properties like wear resistance, compressive strength, and thermal conductivity.
Common Filler: Glass
Adding glass fiber is one of the most common modifications. It significantly increases the material's stiffness and compressive strength, making it far more resistant to wear and creep.
Common Filler: Carbon
Carbon is another popular filler that enhances compressive strength and hardness. Crucially, it also improves thermal conductivity and can add electrical conductivity to the otherwise insulating PTFE.
Other Reinforcements
For specialized applications, other fillers are used. Aramid fibers improve mechanical strength, while ceramic and metal fillers can be used to precisely modify thermal and electrical properties for unique challenges.
Tailoring Physical Form and Dimensions
Beyond its chemical composition, PTFE's physical characteristics can be tailored to fit nearly any design requirement.
Standard and Custom Forms
PTFE is commonly processed into standard shapes like extruded rods and tubes, molded sheets, and skived tapes. These serve as the base material for machining finished products.
Custom Sizing and Thickness
PTFE sheets can be manufactured to specific thicknesses and cut to custom sizes. This foundational level of customization simplifies the fabrication process for components like gaskets and liners.
Surface Etching for Bonding
Because of its non-stick nature, PTFE will not bond with adhesives. To solve this, one side of a PTFE sheet can be chemically etched, creating a bondable surface without compromising the integrity of the opposing side.
Understanding Material Grade and Purity
Not all PTFE is created equal. The purity of the base material is a critical specification, especially for sensitive applications.
Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE is made from 100% pure resin without any reprocessed material. It is the required grade for most medical, food-grade, and electrical applications due to its purity and superior dielectric properties.
Mechanical Grade PTFE
Mechanical grade PTFE contains a small percentage of reprocessed material. While nearly identical in appearance and performance for most non-critical uses, it offers a more cost-effective solution for general industrial applications.
Acknowledging the Limitations
While highly versatile, PTFE is not infallible. Understanding its inherent trade-offs is crucial for successful application.
Chemical Vulnerabilities
Despite its reputation, PTFE is not completely inert. It is vulnerable to attack from highly reactive chemicals like chlorine trifluoride, elementary fluorine, and other alkali metals under high temperatures and pressures.
Radiation Sensitivity
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation. Exposure can cause the polymer's molecular structure to break down, leading to a rapid loss of mechanical properties.
Fillers Introduce Trade-offs
Adding fillers to improve one property can sometimes compromise another. For example, adding glass fiber improves wear resistance but can reduce the material's chemical compatibility in certain aggressive environments.
Selecting the Right PTFE for Your Application
Choosing the correct customization requires matching the material's properties to the application's primary challenge.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: Specify a PTFE with a glass or carbon filler to prevent premature failure.
- If your primary focus is purity for medical or electrical use: Demand Virgin grade PTFE to ensure compliance and optimal insulating properties.
- If your primary focus is bonding PTFE to another surface: Request a chemically etched version to enable the use of adhesives.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general use: Mechanical grade PTFE often provides the necessary performance without the premium cost.
Ultimately, customizing PTFE is about transforming a remarkable polymer into a precision-engineered solution.
Summary Table:
| Customization Option | Key Benefit | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Fillers (Glass, Carbon) | Improves wear resistance, compressive strength, and thermal/electrical properties. | Seals, bearings, and components in harsh environments. |
| Physical Form & Sizing | Provides custom rods, tubes, sheets, and tapes to specific dimensions. | Gaskets, liners, and machined parts for unique designs. |
| Surface Etching | Creates a bondable surface on one side while maintaining non-stick properties on the other. | Assemblies requiring PTFE to be adhesively bonded. |
| Material Grade (Virgin) | Ensures 100% purity for superior dielectric properties and biocompatibility. | Medical devices, food processing, and sensitive electrical applications. |
Need a precision PTFE component tailored to your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in custom fabricating high-performance PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise in material customization ensures your solution meets the toughest demands for chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















