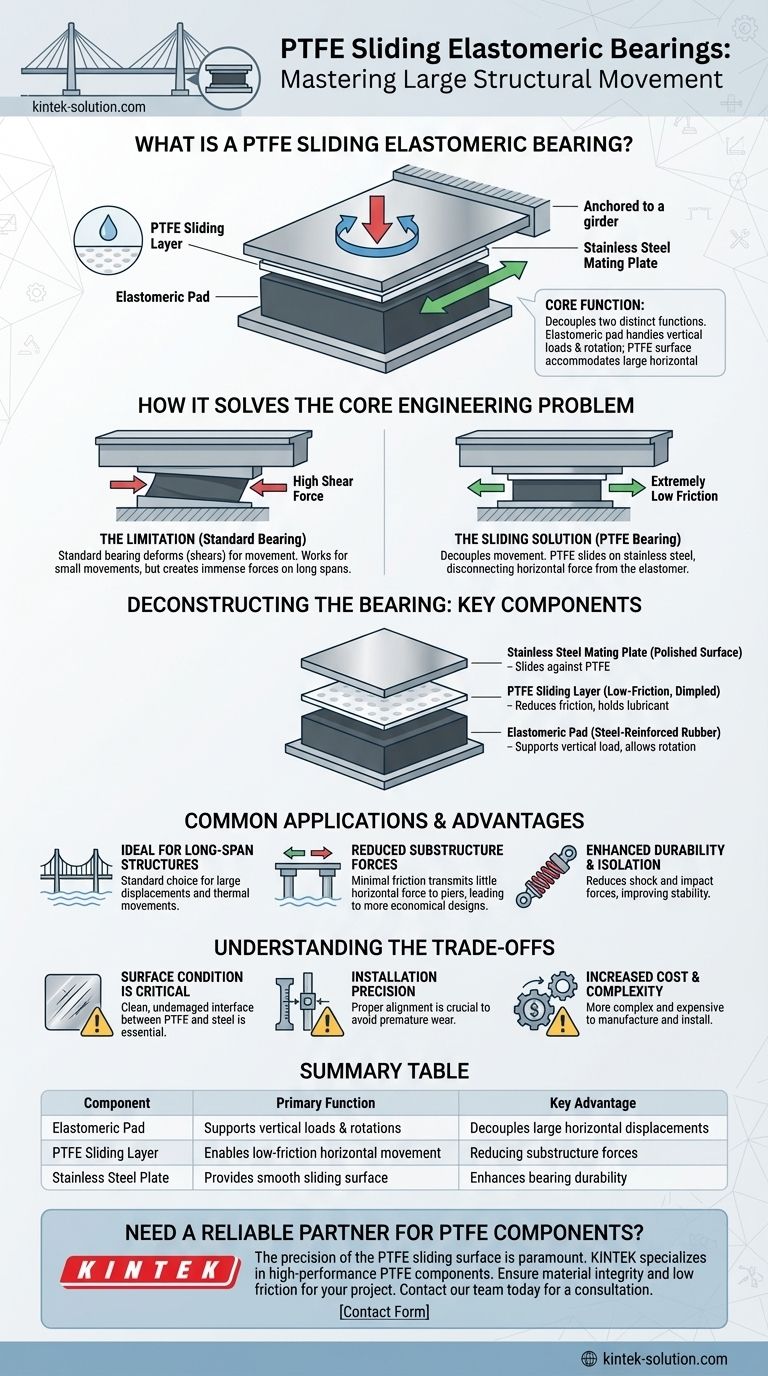
At its core, a PTFE sliding elastomeric bearing is a standard bridge bearing enhanced with a high-performance, low-friction sliding system. It consists of a steel-reinforced rubber (elastomeric) pad with a layer of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) bonded to its top surface. This PTFE layer slides against a polished stainless steel plate, allowing for significant horizontal movement while the rubber pad continues to support vertical loads and accommodate rotations.
The critical insight is that this design separates two distinct functions. The elastomeric pad handles vertical loads and rotational movements, while the PTFE sliding surface accommodates large horizontal displacements, overcoming the physical limits of a standard elastomeric bearing.
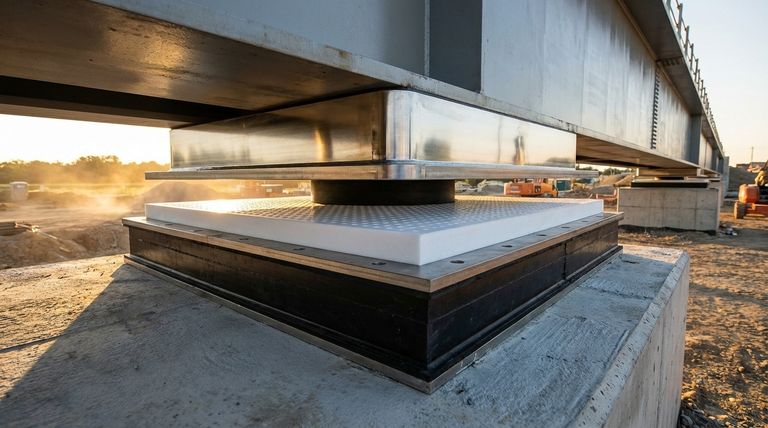

How It Solves the Core Engineering Problem
A bridge or large structure naturally expands and contracts due to temperature changes. It also moves under live loads and seismic events. This movement must be accommodated without transferring damaging stress into the support columns and abutments.
The Limitation of a Standard Bearing
A standard elastomeric bearing accommodates horizontal movement by deforming—the rubber pad shears sideways. This works well for small movements.
However, on long-span bridges, the required movement can be substantial. Forcing a standard bearing to shear that far would create immense horizontal forces on the substructure and over-stress the bearing itself.
The Sliding Solution: Decoupling Movement
The PTFE sliding bearing solves this by creating an independent mechanism for large horizontal movement.
The extremely low coefficient of friction between the PTFE and the polished stainless steel plate allows the bridge superstructure to slide freely. This effectively disconnects, or "decouples," the horizontal movement from the elastomer, which no longer needs to absorb it through shear.
Deconstructing the Bearing: The Key Components
This bearing is a composite assembly where each part has a specific job.
The Elastomeric Pad
This is the foundation of the bearing. Composed of layers of rubber bonded to steel shims, it supports the immense vertical weight of the structure. Its flexibility also allows the beam end to rotate slightly as it deflects under load.
The PTFE Sliding Layer
A thin (1.5mm - 3mm) layer of PTFE is bonded into a recess on the top steel plate of the elastomeric pad. Often, this PTFE surface has dimples which act as reservoirs for a specialized lubricant, ensuring consistently low friction over the bearing's lifespan.
The Stainless Steel Mating Plate
The PTFE does not slide against concrete. It slides against a highly polished stainless steel plate that is part of a separate upper bearing element anchored to the bridge girder. The combination of PTFE and polished stainless steel creates one of the lowest-friction solid-on-solid pairings available.
Common Applications and Advantages
The unique capabilities of PTFE sliding bearings make them essential for specific structural designs.
Ideal for Long-Span Structures
They are the standard choice for structures that experience large displacements. This includes multi-span continuous beams, simply supported beams with long spans, and other configurations where thermal movement is significant.
Reduced Substructure Forces
Because the bearing slides with minimal resistance, it transmits very little horizontal force to the piers and abutments. This can lead to a more economical substructure design, as the columns do not have to be engineered to resist high shear forces from the superstructure.
Enhanced Durability and Isolation
By smoothly accommodating movement, the bearing reduces the shock and impact forces transmitted through the structure from traffic and even seismic activity. This contributes to the overall stability and long-term durability of the bridge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, this design introduces complexities not found in simpler bearings.
Surface Condition is Critical
The low-friction performance depends entirely on the clean, undamaged interface between the PTFE and the stainless steel. Debris, corrosion, or scoring of the steel plate can dramatically increase friction and impair function.
Installation Precision
Proper alignment between the upper and lower elements is crucial. Misalignment can lead to uneven pressure on the PTFE, edge loading, and premature wear.
Increased Cost and Complexity
The addition of the PTFE layer, lubricant, and the separate stainless steel mating plate makes these bearings more complex and expensive to manufacture and install compared to a simple laminated elastomeric pad.
Making the Right Choice for Your Structure
Selecting the correct bearing is about matching the component's capabilities to the demands of the structure.
- If your primary focus is a short span with minimal expected movement: A standard elastomeric bearing is often the most cost-effective and sufficient solution.
- If your primary focus is a long span with significant thermal movement: A PTFE sliding elastomeric bearing is necessary to accommodate the displacement without overstressing the structure.
- If your primary focus is minimizing horizontal forces on sensitive piers: The low-friction sliding mechanism makes this bearing a superior choice for protecting the substructure.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE sliding elastomeric bearing is a decision to manage large-scale structural movement with engineered precision.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Elastomeric Pad | Supports vertical loads and accommodates rotations. |
| PTFE Sliding Layer | Enables low-friction horizontal movement. |
| Stainless Steel Plate | Provides a smooth, polished surface for the PTFE to slide against. |
| Key Advantage | Decouples large horizontal displacements from the elastomer, reducing substructure forces. |
Need a reliable partner for your critical PTFE components?
The precision and performance of the PTFE sliding surface are paramount to the bearing's success. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom fabrications for the demanding semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We ensure the material integrity and dimensional accuracy required for applications where low friction and durability are non-negotiable.
Let's discuss how our expertise can enhance your next project. Contact our team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PTFE envelope pipe gaskets? Superior Sealing for Harsh Chemical & Pure Processes
- What are the properties of stainless steel-filled PTFE bushings? Achieve Superior Strength & Durability
- Why are cold temperatures challenging for seals and how does PTFE overcome these challenges? Master Cryogenic Sealing
- What are the key features of PTFE lined valves? Maximize Safety and Cut Costs with Corrosion-Resistant Valves
- What are the mechanical applications of PTFE rods? Solve Friction and Corrosion Problems
- What are the benefits of PTFE Industrial and Heavy Wall tubing? Maximize Reliability in Harsh Environments
- What industries are spiral PTFE backup rings ideal for? Achieve Superior Sealing in Extreme Conditions
- What are bearing grades of PTFE used for? Achieve High-Performance, Self-Lubricating Components



















