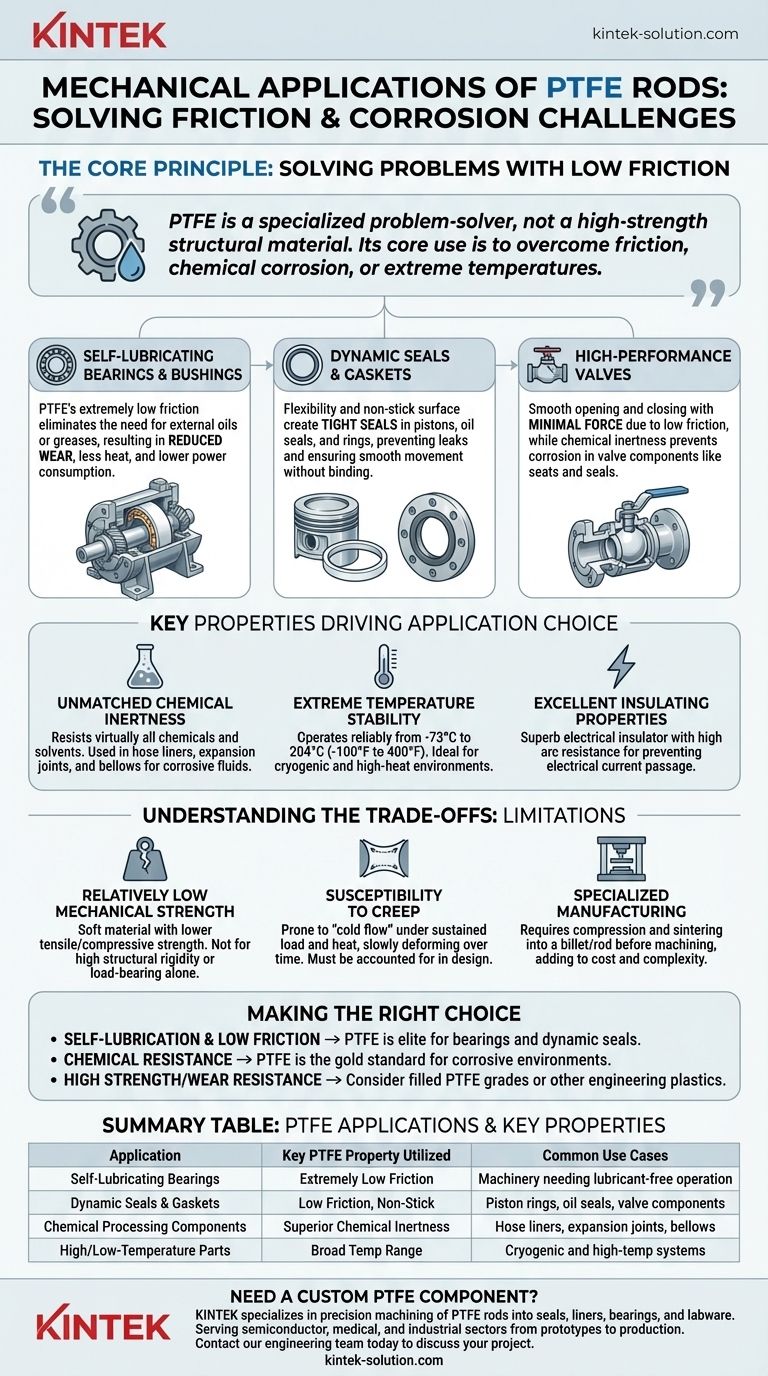
In short, PTFE rods are machined into critical mechanical components like self-lubricating bearings, piston rings, seals, and gaskets. These parts are chosen not for high strength, but for their unique ability to operate with extremely low friction and resist chemical attack in demanding environments where other materials would quickly fail.
The core reason to use PTFE in mechanical applications is to solve problems of friction, chemical corrosion, or extreme temperatures. It is a specialized problem-solver, not a high-strength structural material.
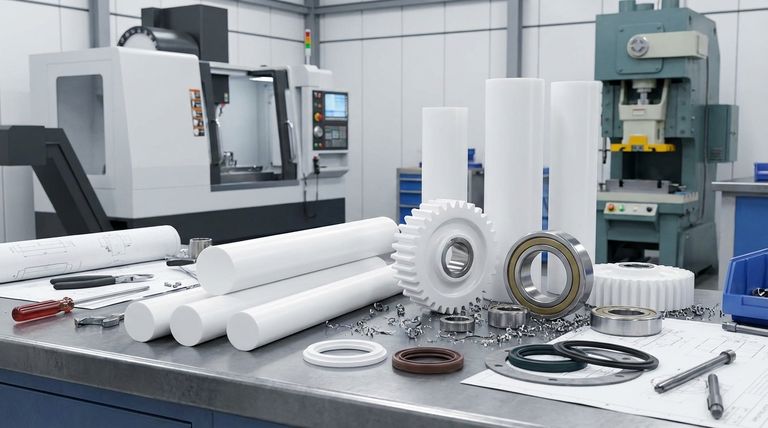

The Core Principle: Solving Problems with Low Friction
The defining characteristic of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is its incredibly low coefficient of friction. This property is the primary driver for its use in dynamic mechanical systems.
Self-Lubricating Bearings and Bushings
PTFE is one of the most effective materials for creating self-lubricating parts. When used for bearings, it allows machine components to slide smoothly against one another without the need for external oils or greases.
This directly results in reduced wear, less heat generation, and lower overall power consumption for the machinery.
Dynamic Seals and Gaskets
PTFE's flexibility and non-stick surface make it ideal for creating dynamic seals. It is frequently machined into piston rings, oil seals, and sealing rings.
These components create a tight seal that prevents leaks while allowing parts to move freely. Because nothing sticks to the surface, the seal is less likely to bind or degrade over time, ensuring a long service life.
High-Performance Valves
In industrial valves, components like seats and seals are often made from PTFE. Its low friction ensures the valve can be opened and closed smoothly with minimal force.
Crucially, its chemical inertness prevents the valve components from being corroded by the fluids passing through them.
Key Properties Driving Application Choice
While low friction is the headline feature, other properties make PTFE uniquely suited for specific mechanical challenges.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it the material of choice for equipment handling corrosive substances.
Applications include hose liners, expansion joints, and bellows used in chemical processing plants where other plastics or metals would be destroyed.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its useful properties across an exceptionally broad temperature range, typically from -73°C to 204°C (-100°F to 400°F).
This allows it to function reliably in both cryogenic applications and high-temperature environments where most other plastics would become brittle or melt.
Excellent Insulating Properties
PTFE is a superb electrical insulator with high arc resistance and a surface that resists tracking. While primarily a mechanical benefit, this is critical when a component must prevent electrical current from passing through it.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Limitations of PTFE
To use PTFE effectively, it is critical to understand its limitations. It is not a universally applicable solution.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
The most significant trade-off is PTFE's mechanical performance. Compared to other engineering plastics like Nylon or PEEK, PTFE is a relatively soft material.
It has lower tensile strength, compressive strength, and hardness. It is not suitable for applications requiring high structural rigidity or load-bearing capacity on its own.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a sustained load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can be prone to "creep" or "cold flow," meaning it will slowly deform over time. This must be accounted for in the design of any load-bearing PTFE component.
Specialized Manufacturing
PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt techniques like injection molding. Instead, it must be compressed and sintered into a billet or rod, which is then machined. This can affect the cost and complexity of producing finished parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on the specific problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is self-lubrication and low friction: PTFE is an elite choice for bearings, slide plates, and dynamic seals where external lubricants are impractical or undesirable.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is the gold standard for sealing, containing, or transferring highly corrosive fluids, especially at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is high structural strength or wear resistance: You should consider filled grades of PTFE or entirely different engineering plastics, as unfilled PTFE is soft and will deform under heavy, sustained loads.
Ultimately, PTFE should be chosen for its unique combination of properties that solve challenges other materials simply cannot address.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key PTFE Property Utilized | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Lubricating Bearings/Bushings | Extremely Low Friction | Machinery requiring operation without external lubricants |
| Dynamic Seals and Gaskets | Low Friction, Non-Stick Surface | Piston rings, oil seals, valve components |
| Chemical Processing Components | Superior Chemical Inertness | Hose liners, expansion joints, bellows |
| High/Low-Temperature Parts | Broad Temperature Range (-73°C to 204°C) | Cryogenic and high-temperature industrial systems |
Need a custom PTFE component to solve a challenging friction or corrosion problem?
KINTEK specializes in precision machining of PTFE rods into critical mechanical parts like seals, liners, bearings, and labware. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, delivering custom solutions from prototypes to high-volume production. Our expertise ensures your components meet exact specifications for performance in demanding environments.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our PTFE fabrication capabilities can benefit your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE mill-type envelope gaskets used for? Seal Critical Flanges in Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- Why are glass-filled PTFE rods used in medical devices? Enhanced Strength and Biocompatibility for Critical Applications
- Can both PTFE and stainless steel impellers be sterilized in an autoclave? Yes, and here's how to choose.
- What are alternative materials to Teflon/PTFE and their characteristics? Explore PEEK & Filled PTFE
- What design considerations are important for PTFE lip seals in extreme temperatures? | Material, Geometry & Energizer
- What makes PTFE an excellent electrical insulator? Superior Performance for High-Frequency & High-Voltage Applications
- What are the key features of spiral PTFE backup rings? Superior Extrusion Protection for High-Pressure Seals
- What are the drawbacks of using PTFE for sealing needs? The Critical Trade-offs in Chemical vs. Mechanical Performance



















