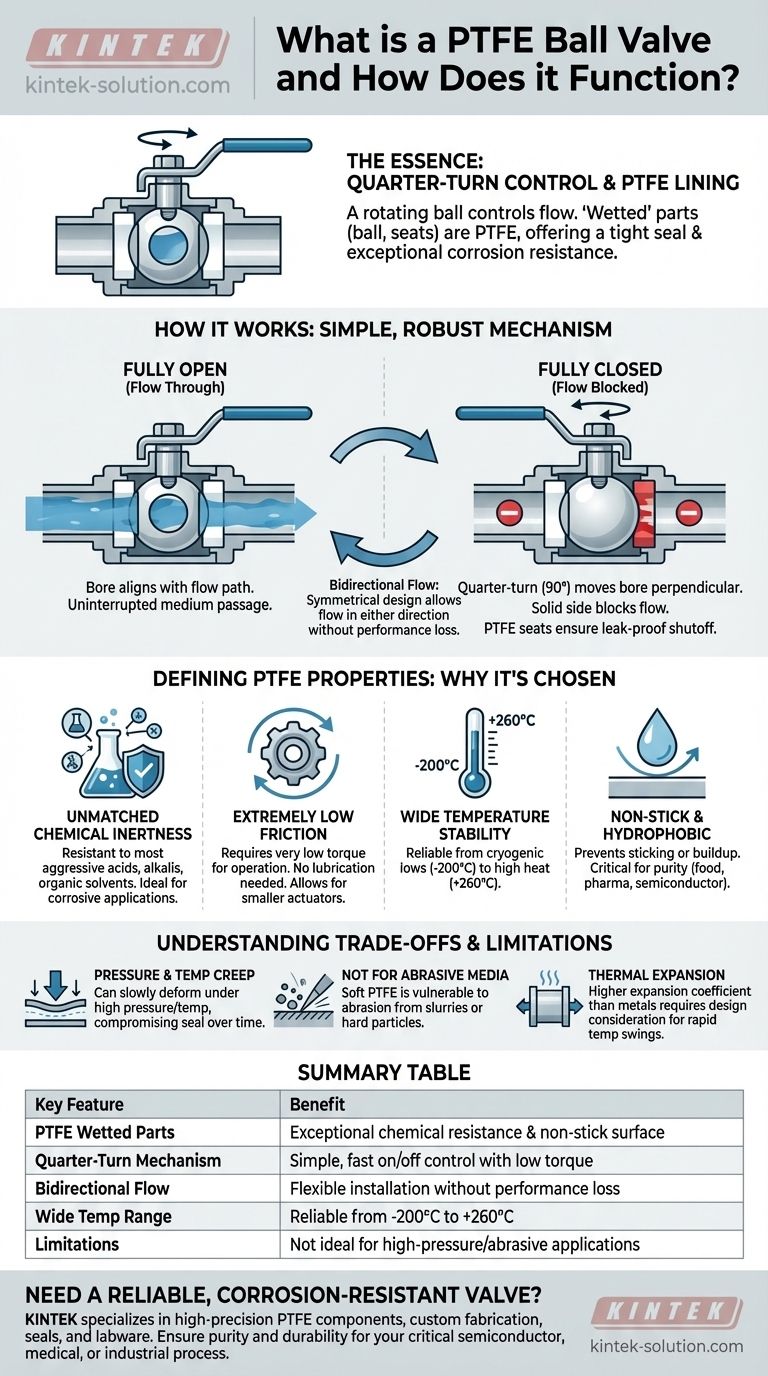
In essence, a PTFE ball valve is a type of quarter-turn valve that uses a rotating ball to control the flow of a fluid or gas. Its defining feature is that all surfaces that come into contact with the process medium—the "wetted" parts—are made from or lined with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the same polymer commonly known as Teflon. This construction provides an exceptionally tight seal and outstanding resistance to chemical corrosion.
The decision to use a PTFE ball valve is driven almost entirely by the unique properties of its core material. Its near-universal chemical inertness and extremely low friction make it the go-to solution for reliably controlling corrosive or high-purity media where other materials would fail.

How a PTFE Ball Valve Works
The valve's operation is based on a simple, robust mechanical principle. Understanding this mechanism clarifies why it is so widely used for on/off flow control.
The Core Mechanism: Quarter-Turn Control
At the heart of the valve is a spherical ball with a hole, or bore, drilled through the center.
When the valve's handle is aligned with the pipe, the bore is also aligned, allowing the medium to flow through uninterrupted. This is the fully open position.
A simple 90-degree (quarter-turn) rotation of the handle turns the ball, moving the bore perpendicular to the flow path. The solid side of the ball now blocks the opening, stopping the flow. This is the fully closed position.
The Role of PTFE Seats
The rotating ball is held in place by two rings called seat rings, which are also made of PTFE.
Because PTFE is a relatively soft and formable material, it creates an exceptionally tight seal against the ball with minimal pressure. This ensures a leak-proof shutoff.
Bidirectional Flow
The symmetrical design of a ball valve allows the process medium to flow through it in either direction without affecting its performance or sealing capability.
The Defining Properties of PTFE
The valve's performance is a direct result of the material it's made from. PTFE offers a combination of characteristics that are difficult to find in any other single material.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is highly resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This makes it an ideal choice for the most corrosive applications where metal valves would quickly degrade.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material known. This means the valve requires very low torque (rotational force) to open and close, allowing for smaller actuators or easy manual operation. It also means no lubrication is ever required.
Wide Temperature Stability
This material performs reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature range, typically from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to high temperatures of +260°C (500°F).
Non-Stick and Hydrophobic Surface
The non-adhesive surface of PTFE prevents process media from sticking to or building up inside the valve. This is critical for applications in the food, pharmaceutical, or semiconductor industries where purity and preventing contamination are paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. Its limitations are just as important to understand as its strengths to ensure proper application.
Pressure and Temperature Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. Under high pressure, especially when combined with high temperatures, the material can slowly deform or "creep." This can eventually compromise the integrity of the seal, making it less suitable for very high-pressure applications compared to metal-seated valves.
Not Suited for Abrasive Media
The softness that creates such a great seal also makes PTFE vulnerable to abrasion. It is a poor choice for controlling slurries or fluids containing hard, abrasive particles, which would quickly wear away the seats and the ball lining, causing the valve to fail.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than the metals typically used for the valve body. In systems that experience wide and rapid temperature swings, this difference must be accounted for in the valve's design to prevent sealing issues.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve hinges on matching its material properties to the demands of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals: The PTFE valve is an excellent, cost-effective choice due to its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is purity and preventing contamination: PTFE's non-stick, hydrophobic nature makes it ideal for applications demanding the highest levels of cleanliness.
- If your application involves high pressure or abrasive slurries: You should consider a valve with harder seat materials, such as a metal-seated ball valve, to ensure durability.
Ultimately, understanding the unique material properties of PTFE is the key to deploying this valve effectively in demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| PTFE Wetted Parts | Exceptional chemical resistance and non-stick surface |
| Quarter-Turn Mechanism | Simple, fast on/off control with low operating torque |
| Bidirectional Flow | Flexible installation without performance loss |
| Wide Temperature Range | Reliable performance from -200°C to +260°C |
| Limitations | Not ideal for high-pressure/abrasive applications |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant valve for your critical process?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom labware. Our expertise in PTFE fabrication ensures you get a valve perfectly suited to handle your aggressive chemicals or high-purity requirements in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision and performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and get a solution that guarantees purity and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What overall benefits does the built-in spring provide to PTFE shaft seals? The Key to Dynamic, Long-Lasting Sealing
- How is Teflon used in the electronics and semiconductor industry? The Key to High-Performance and Purity
- Why is the non-stick surface of PTFE bushings beneficial? For Contamination-Free, Low-Maintenance Performance
- In what types of air compressors are PTFE oil scraper rings commonly used? A Guide to High-Performance Sealing
- What is a PTFE bush and what is its primary use? A Guide to Self-Lubricating Bearings
- What approvals does virgin PTFE have for use in food and pharmaceutical industries? FDA-Approved for Ultimate Purity & Safety
- How does the low friction coefficient of PTFE expansion bellows benefit fluid flow? Reduce Energy Use & Prevent Blockages
- What advantages do PTFE spring-energized seals offer in harsh environments? Unlock Unmatched Reliability



















