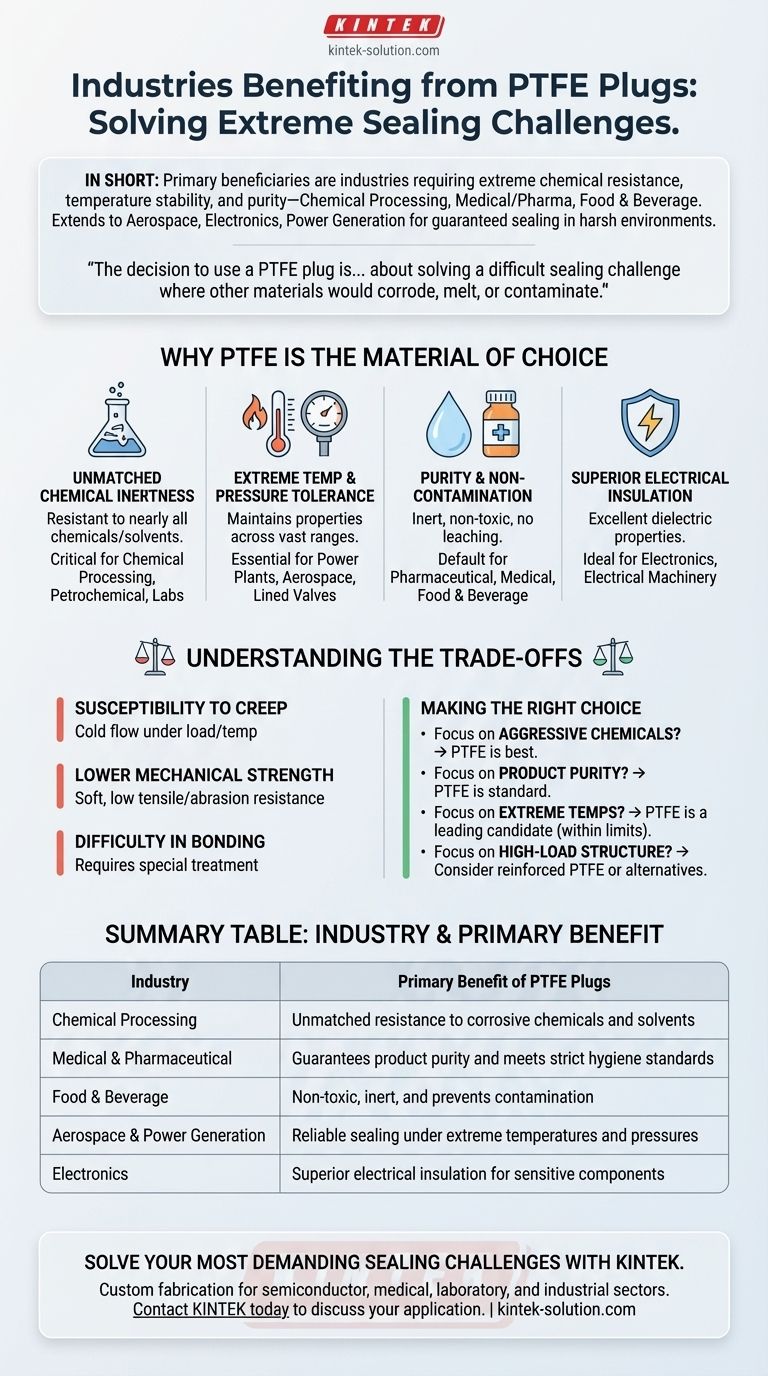
In short, industries that require extreme chemical resistance, temperature stability, and purity—such as chemical processing, medical and pharmaceutical, and food and beverage—are the primary beneficiaries of PTFE plugs. Their use extends to any application where sealing must be guaranteed in a harsh or highly sensitive environment, including aerospace, electronics, and power generation.
The decision to use a PTFE plug is rarely about simply filling a hole. It is about solving a difficult sealing challenge where other materials would corrode, melt, or contaminate the system. Understanding PTFE's unique properties is key to knowing when it is not just a good choice, but the only choice.

Why PTFE Is the Material of Choice
The widespread adoption of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) plugs and seals is a direct result of a unique combination of material properties. Industries don't choose PTFE by chance; they choose it to solve specific, often extreme, operational challenges.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is famously resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it indispensable in environments where corrosive materials are handled.
This property is critical in chemical processing, petrochemical plants, and laboratories. A PTFE plug ensures the integrity of the seal and prevents both the plug from degrading and the chemical from being contaminated.
Extreme Temperature & Pressure Tolerance
PTFE maintains its properties across a vast temperature range and can be engineered for high-pressure applications, especially in lined valves and expansion joints.
This is why it is heavily used in power plants for handling high-pressure steam and in aerospace for reliable sealing in components exposed to fluctuating temperatures and aggressive fuels.
Purity and Non-Contamination
As an inert and non-toxic material, PTFE does not leach chemicals or impart flavors. It meets the stringent hygiene and safety standards required for sensitive applications.
This makes it a default choice in pharmaceutical, medical, and food and beverage manufacturing. PTFE plugs and seals ensure that the final product, whether a medication or a food item, remains pure.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE has excellent dielectric properties, meaning it does not conduct electricity. This makes it an ideal insulator.
In the electronics and electrical machinery industries, PTFE is used to insulate sensitive components, preventing short circuits and ensuring reliable performance in enclosures and connectors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, PTFE is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is crucial for proper application and avoiding failure.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform or "creep." This can be a concern in high-load, static sealing applications.
This means that for high-pressure structural seals, the plug's design and môi trường's constraints must be carefully evaluated. Reinforced PTFE grades can help mitigate this.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or other engineering plastics, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
It is not suitable for applications requiring high structural rigidity or where it will be subjected to significant physical wear, unless it is a component within a more robust assembly.
Difficulty in Bonding
PTFE's low-friction, non-stick surface makes it very difficult to bond to other materials using conventional adhesives.
Joining PTFE to other substrates requires special surface treatments, such as chemical etching, which adds complexity and cost to the manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your industry and application dictate whether PTFE is the correct material. Use these guidelines to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE is almost certainly your best and safest choice due to its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is maintaining product purity: PTFE is the industry standard for medical, food, and pharmaceutical applications where non-toxicity is critical.
- If your primary focus is sealing in extreme temperatures: PTFE is a leading candidate, but you must operate within its specified temperature range and consider its mechanical properties under load.
- If your primary focus is a high-load structural component: Standard PTFE is likely unsuitable; you should explore reinforced PTFE grades or alternative materials like PEEK or metal.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is an engineering decision to leverage its exceptional properties for environments where common materials inevitably fail.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Benefit of PTFE Plugs |
|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Unmatched resistance to corrosive chemicals and solvents |
| Medical & Pharmaceutical | Guarantees product purity and meets strict hygiene standards |
| Food & Beverage | Non-toxic, inert, and prevents contamination |
| Aerospace & Power Generation | Reliable sealing under extreme temperatures and pressures |
| Electronics | Superior electrical insulation for sensitive components |
Solve your most demanding sealing challenges with KINTEK's precision PTFE components.
Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get the exact PTFE seals, liners, labware, and plugs you need—from prototypes to high-volume orders—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes Teflon suitable for use in bearings and similar applications? Discover Its Low-Friction, Chemical-Resistant Advantages
- Why are PTFE fasteners used in applications requiring electrical insulation? Ensure Reliable, Non-Conductive Performance
- What type of thermoplastic is Teflon and what are its inherent properties? | A Guide to PTFE's Unique Strengths
- How should PTFE-lined valves be maintained for optimal performance? Ensure Long-Term Reliability & Prevent Costly Downtime
- What are the key benefits of Teflon bushes for industrial applications? Reduce Friction and Maintenance
- What are the key properties of PTFE and nylon in bushings and thrust washers? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What environmental factors do PTFE bellows resist? Superior Chemical and Thermal Resilience for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of PTFE bushes? Achieve Maintenance-Free, High-Performance Operation



















