PTFE oil seals are exceptionally resistant to a wide array of environmental challenges, making them a premier choice for demanding applications. Their unique fluoropolymer composition allows them to withstand extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, moisture, and UV radiation, factors that would cause conventional elastomeric seals to degrade and fail rapidly.
The core reason for PTFE's resilience lies in its inherent chemical inertness and stable molecular structure. This makes it fundamentally non-reactive to most environmental and operational stressors, ensuring long-term sealing integrity where other materials cannot.

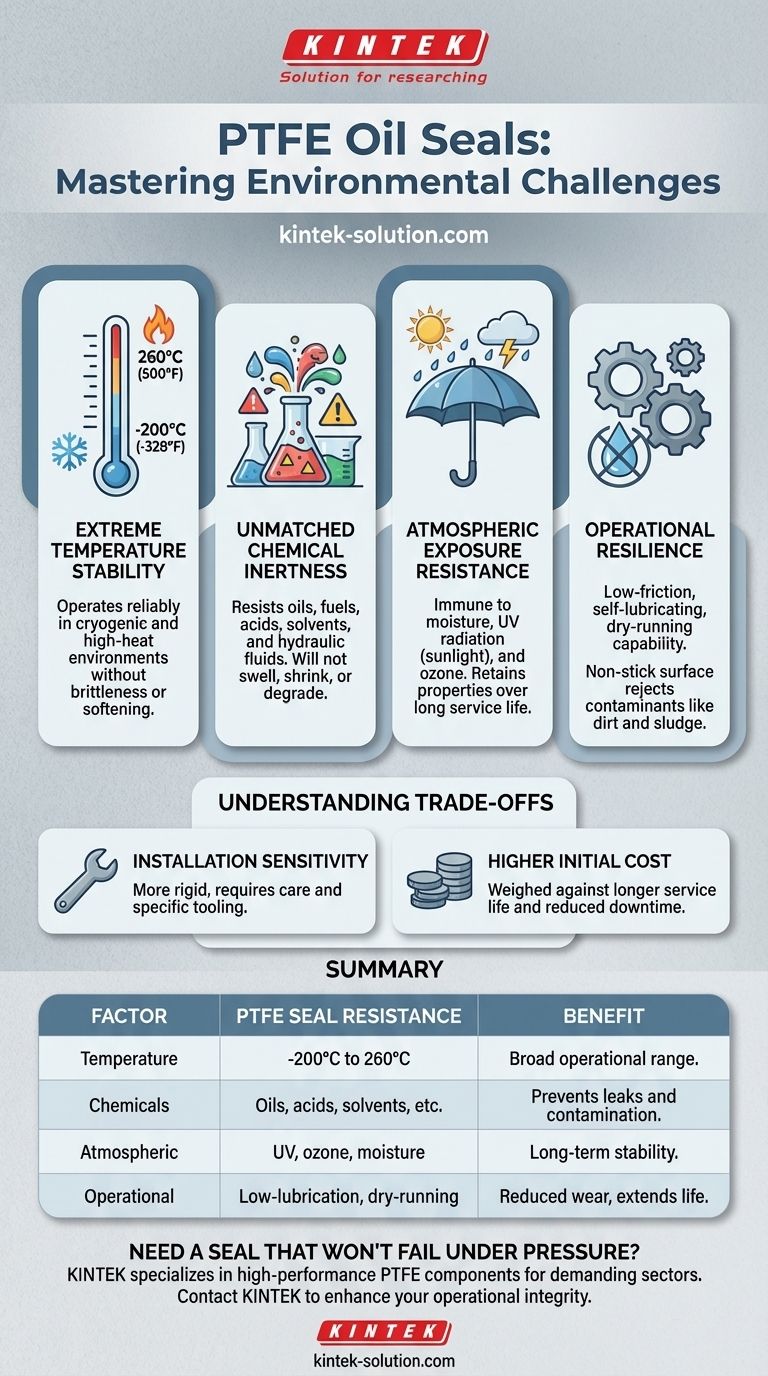
Unpacking PTFE's Environmental Resilience
To understand if a PTFE seal is right for your application, it's essential to examine its specific resistance characteristics. These properties are not merely incremental improvements over other materials; they represent a different class of performance.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE seals operate effectively across an exceptionally broad temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
This stability allows them to function reliably in cryogenic applications as well as in high-heat environments like engine compartments and industrial machinery without becoming brittle or soft.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
One of PTFE's most significant advantages is its resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents.
This includes aggressive fluids such as oils, fuels, acids, and hydraulic fluids. The seal's material will not swell, shrink, or break down when exposed to these substances, preventing leaks and contamination.
Resistance to Atmospheric Exposure
PTFE is virtually immune to degradation from common atmospheric and environmental factors.
It does not absorb moisture and is unaffected by long-term exposure to UV radiation (sunlight) and ozone. Unlike many rubber compounds, PTFE does not suffer from degradation due to aging, meaning it retains its properties over a very long service life.
Key Operational Properties in Harsh Environments
Beyond passive resistance, a PTFE seal's active properties contribute directly to its survival and performance in difficult operational settings.
Low-Friction and Dry-Running Capability
The material has an extremely low coefficient of friction, often described as self-lubricating. This is critical in applications with no-oil or low-oil conditions.
Even after a prolonged shutdown, a PTFE seal can restart without damage, as its low-friction nature prevents stick-slip wear and reduces heat generation at the sealing lip.
Non-Stick Surface for Contaminant Rejection
PTFE's non-stick properties prevent contaminants like dirt, dust, and sludge from adhering to the seal's surface.
This ensures the sealing lip remains clean and effective, preventing abrasive particles from being drawn into the sealing area, which would otherwise accelerate wear and cause failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its strengths are significant, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation.
Installation Sensitivity
PTFE is a more rigid material than traditional elastomers like nitrile or FKM. This means it has less elasticity and "memory."
As a result, installation requires greater care and often specific tooling to avoid nicking or permanently deforming the sealing lip. It is less forgiving of shaft imperfections or installation errors.
Higher Initial Cost
The advanced manufacturing process and raw material costs make PTFE seals more expensive than their standard rubber counterparts.
This higher upfront cost must be weighed against the benefits of longer service life, reduced downtime, and reliability in environments where a conventional seal would fail prematurely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal material is a critical engineering decision. Your primary operational challenge should guide your choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature or chemical exposure: PTFE is the definitive choice due to its inert fluoropolymer structure, which provides unmatched resistance.
- If your primary focus is outdoor use or long-term stability: PTFE's inherent immunity to UV, ozone, and aging makes it ideal for applications with prolonged environmental exposure.
- If you are dealing with low-lubrication or high-speed conditions: PTFE's self-lubricating, low-friction properties are critical for preventing wear and extending service life where traditional seals would fail from heat.
Ultimately, selecting a PTFE seal is a strategic decision for any application where operational reliability cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Factor | PTFE Seal Resistance |
|---|---|
| Temperature | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Chemicals | Oils, fuels, acids, solvents, hydraulic fluids |
| Atmospheric Exposure | UV radiation, ozone, moisture |
| Operational Stress | Low-lubrication, dry-running, contaminant rejection |
Need a seal that won't fail under pressure?
Your application demands reliability. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication services, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensure you get a sealing solution built to withstand your specific environmental challenges.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our PTFE expertise can enhance your operational integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries benefit from PTFE and PFA lined check valves? Ensure Safety and Purity in Harsh Processes
- Why is UV resistance important for PTFE Teflon washers? Ensure Long-Term Reliability in Outdoor and Harsh Environments
- How should one choose between virgin and glass-filled Teflon balls? A Guide to Material Selection
- How are PTFE Bellows manufactured? A Guide to Precision Thermal Forming
- Why is ePTFE a good choice for fragile or damaged flanges? Protect Your Flanges with Low-Stress Sealing
- What are the uses of PTFE coatings in the semiconductor and electronics industries? Ensure Purity & Reliability
- Why is mineral-filled PTFE used in medical and food industries? | Superior Durability Meets FDA-Compliant Safety
- What is the Shore hardness and compression strength of PTFE? A Guide to Its Mechanical Limits



















