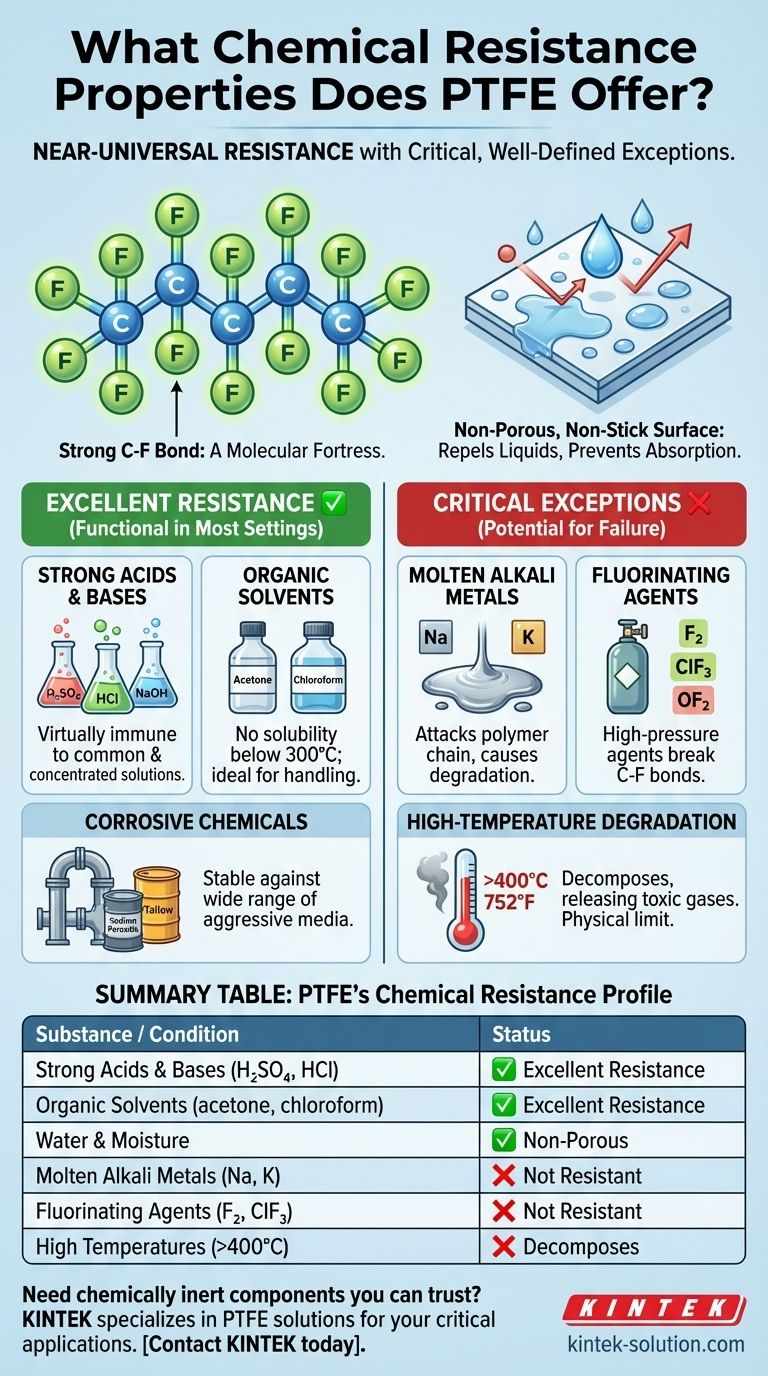
For nearly all practical purposes, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most chemically resistant materials known. It remains stable and unreactive when exposed to a vast spectrum of aggressive chemicals, including concentrated acids, alkalies, and organic solvents. However, its near-universal resistance has a few critical, well-defined exceptions, primarily molten alkali metals and highly reactive fluorinating agents.
The exceptional chemical inertness of PTFE stems from its stable molecular structure. Understanding this allows you to confidently use it for most applications while knowing precisely which niche, hyper-reactive environments to avoid.

The Foundation of PTFE's Inertness
PTFE's remarkable resistance is not an accident; it is a direct result of its unique molecular architecture. This structure creates a material that is fundamentally non-reactive in most situations.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE is a long chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon is completely shielded by a sheath of fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This powerful bond makes the polymer chain exceptionally stable and difficult for other chemicals to attack or break down, creating a kind of chemical fortress at the molecular level.
A Non-Reactive, Impermeable Surface
PTFE has an ultra-low surface energy, which is why it is famous for its non-stick properties. This same characteristic means that corrosive liquids have a difficult time "wetting" the surface to initiate a chemical reaction.
Furthermore, PTFE is non-porous and does not absorb water, preventing corrosive agents from seeping into the material and causing degradation from within.
Broad Spectrum of Resistance: What PTFE Excels Against
In most industrial and laboratory settings, PTFE is considered functionally inert. Its resistance covers the vast majority of chemicals used in processing.
Strong Acids and Bases
PTFE is virtually immune to all common and concentrated acids. It can be boiled in concentrated sulfuric, nitric, or hydrochloric acid without any change in its properties. It is also resistant to most alkalies and bases.
Organic Solvents
Finding a solvent that can dissolve PTFE at room temperature is practically impossible. It shows no solubility in known solvents below 300°C (572°F), making it an ideal choice for handling chemicals like acetone and chloroform.
Corrosive Industrial Chemicals
The material remains stable when exposed to a wide range of other aggressive media, including sodium peroxide, tallow, and various corrosive chemicals common in oil and gas, pharmaceutical, and chemical processing industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical Exceptions
No material is perfect. While PTFE's list of resistances is long, its weaknesses are specific and absolute. Ignoring them can lead to catastrophic failure.
Molten Alkali Metals
Liquid or molten alkali metals, such as sodium and potassium, are highly reactive and have the ability to attack the PTFE polymer chain, causing it to degrade.
Elemental Fluorine and Related Compounds
Ironically, the element that gives PTFE its stability can also be its undoing. High-pressure gaseous fluorine, chlorine trifluoride, and oxygen difluoride are among the few substances potent enough to chemically break the C-F bonds.
High-Temperature Degradation
This is a physical limitation, not a chemical one. While PTFE has a high melting point of 327°C (621°F), it will begin to decompose at approximately 400°C (752°F). This process releases toxic fluorocarbon gases and must be avoided.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using this knowledge allows you to select materials with confidence, ensuring safety and equipment longevity.
- If your primary focus is general chemical processing (acids, solvents, bases): PTFE is an industry-standard choice that provides unparalleled and reliable protection against corrosion.
- If you are working with molten alkali metals or high-pressure fluorinating agents: You must seek an alternative material, as PTFE is known to fail in these specific, highly reactive environments.
- If your application involves temperatures approaching its physical limits: Carefully evaluate the maximum operating temperature to ensure you remain well below PTFE's 400°C decomposition point.
Ultimately, PTFE's chemical resistance makes it a premier problem-solving material for the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| PTFE's Chemical Resistance Profile | Status |
|---|---|
| Strong Acids & Bases (e.g., H₂SO₄, HCl, NaOH) | ✅ Excellent Resistance |
| Organic Solvents (e.g., acetone, chloroform) | ✅ Excellent Resistance |
| Water & Moisture | ✅ Non-Porous, Non-Absorbent |
| Molten Alkali Metals (e.g., sodium, potassium) | ❌ Not Resistant |
| Fluorinating Agents (e.g., F₂, ClF₃) | ❌ Not Resistant |
| High Temperatures (Above 400°C / 752°F) | ❌ Decomposes |
Need chemically inert components you can trust?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment is protected against the harshest chemicals, from acids to solvents.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision and durability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the safety and longevity of your critical applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Is PTFE recommended for abrasive applications? A Guide to PTFE's Strengths and Weaknesses
- What are the non-stick properties of PTFE impellers? Achieve Purity & Prevent Buildup in Critical Mixing
- What are the key features of PTFE ball valves? Superior Chemical Resistance & Reliable Flow Control
- What are the main differences between solid Teflon O-rings and Teflon encapsulated O-rings? Choose the Right Seal for Harsh Environments
- What are the basic types of PTFE Teflon gaskets? Choose the Right Seal for Your Application
- What is the significance of PTFE's chemical inertness in instrumentation systems? Ensure Unmatched System Integrity and Accuracy
- How do PTFE bellows differ from pusher seals? Unlock Superior Reliability for Demanding Applications
- What are some application examples of PTFE O-ring seals in mechanical equipment? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges



















