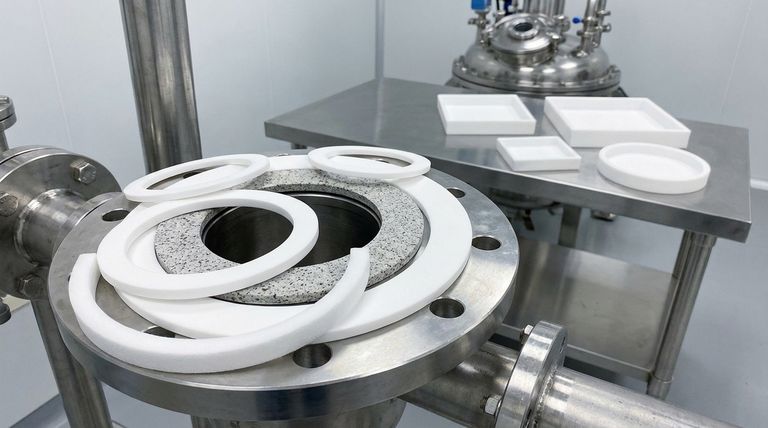
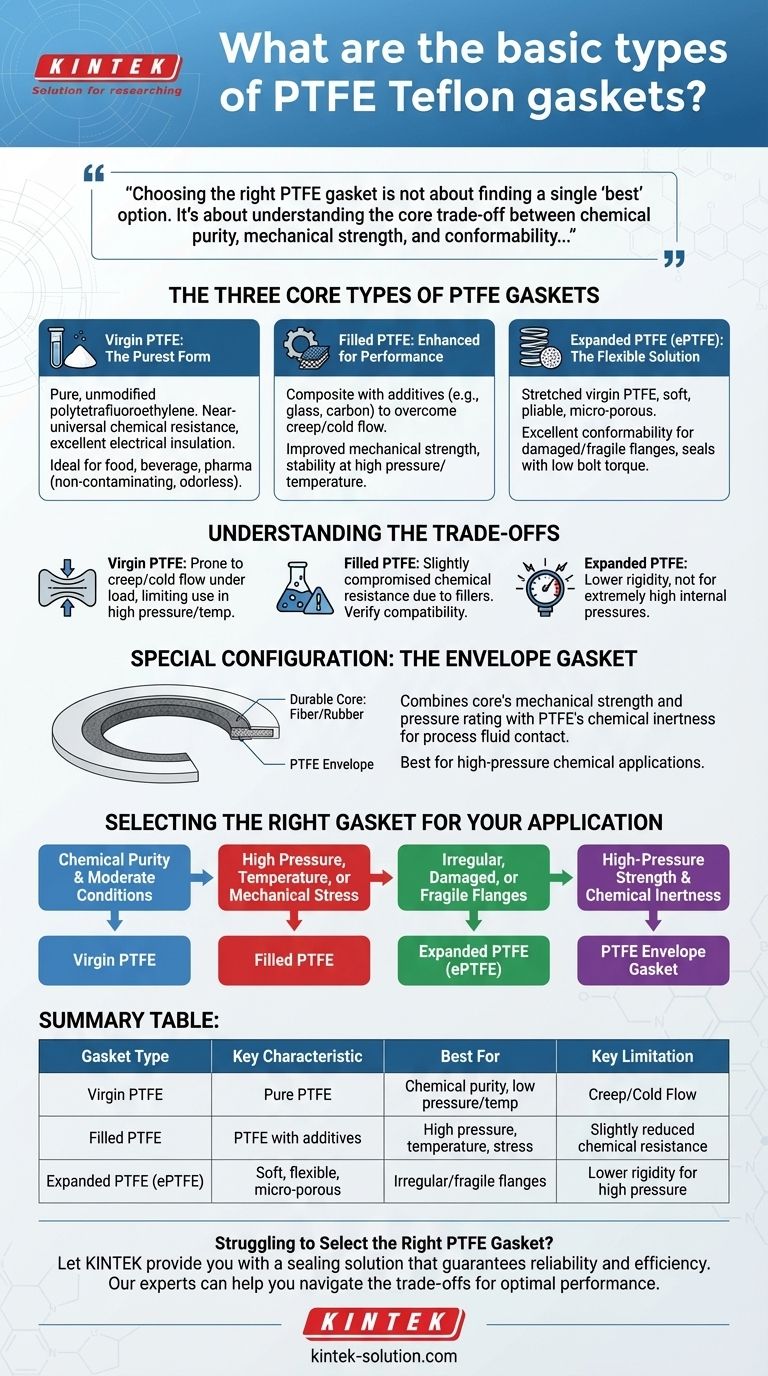
In essence, there are three fundamental types of PTFE Teflon gaskets. These are Virgin PTFE, which is pure polytetrafluoroethylene; Filled PTFE, which is a composite material enhanced with additives like glass or carbon; and Expanded PTFE (ePTFE), a soft, flexible form created by physically altering virgin material. Each type is engineered to solve a different sealing challenge.
Choosing the right PTFE gasket is not about finding a single "best" option. It's about understanding the core trade-off between chemical purity, mechanical strength, and conformability to match the gasket's properties to your specific operational demands.

The Three Core Types of PTFE Gaskets
The differences between the main PTFE gasket types stem from their composition and manufacturing process. Each one excels in a different environment.
Virgin PTFE: The Purest Form
Virgin PTFE is the original, unmodified material. It is celebrated for its near-universal chemical resistance, extremely low coefficient of friction, and excellent electrical insulation properties.
Because it contains no additives, it is the ideal choice for applications where purity is critical, such as in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. It is non-contaminating and odorless.
Filled PTFE: Enhanced for Performance
Filled PTFE is a composite created by adding a filler material to virgin PTFE during manufacturing. Common fillers include glass, carbon, and graphite.
These fillers are added to overcome the primary weakness of virgin PTFE: creep, or cold flow. Fillers dramatically improve the gasket's mechanical strength, stability under load, and resistance to deformation at high temperatures. This makes it suitable for higher pressure and temperature applications.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE): The Flexible Solution
Expanded PTFE is made by stretching virgin PTFE under specific conditions, creating a soft, pliable, and micro-porous material. It retains the exceptional chemical resistance of virgin PTFE.
Its key advantage is conformability. ePTFE is extremely effective at sealing flanges that are worn, damaged, uneven, or fragile (like glass-lined or plastic flanges). It can create a tight seal with very low bolt torque, preventing damage to sensitive equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. Understanding the inherent limitations of each PTFE type is crucial for preventing seal failure.
The Weakness of Virgin PTFE: Creep and Cold Flow
The biggest drawback of virgin PTFE is its tendency to creep or "cold flow." When compressed in a flange, especially under heat, the material can slowly deform and squeeze out, leading to a loss of bolt load and potential leaks.
This characteristic limits its use to lower pressure and temperature applications where mechanical stress is not the primary concern.
The Compromise of Filled PTFE: Chemical Resistance
While fillers significantly enhance mechanical properties, they can slightly compromise the universal chemical resistance of pure PTFE. The filler material itself may be vulnerable to certain aggressive chemicals that virgin PTFE would easily resist.
You must always verify that both the PTFE and the specific filler are compatible with the media being sealed.
The Limitation of Expanded PTFE: High-Pressure Rigidity
Expanded PTFE's softness is its greatest strength but also its limitation. It does not have the rigidity or blowout resistance of a solid filled PTFE gasket.
It is designed for creating a seal on imperfect surfaces, not for containing extremely high internal pressures where a more robust, solid gasket is required.
Special Configuration: The Envelope Gasket
Beyond the three core material types, you will also encounter different structural designs, most notably the PTFE envelope gasket.
The Best of Both Worlds
An envelope gasket consists of a durable core material (such as compressed fiber or rubber) wrapped in a thin "envelope" of PTFE.
This design cleverly combines the superior mechanical strength, pressure rating, and resilience of the core with the chemical inertness of the PTFE, which is the only material that touches the process fluid. It is an excellent solution for high-pressure chemical applications.
Selecting the Right Gasket for Your Application
Use your primary operational challenge to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and moderate conditions: Virgin PTFE is your most cost-effective and suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is handling high pressure, temperature, or mechanical stress: Filled PTFE provides the necessary strength and resistance to creep.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular, damaged, or fragile flanges: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) offers the required conformability and seals with low bolt load.
- If your primary focus is combining high-pressure strength with chemical inertness: A PTFE envelope gasket leverages the best properties of multiple materials.
Ultimately, a successful seal depends on correctly matching the gasket material's capabilities to the demands of your system.
Summary Table:
| Gasket Type | Key Characteristic | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Pure, unmodified PTFE | Chemical purity, low pressure/temperature | Prone to creep/cold flow |
| Filled PTFE | PTFE with additives (glass, carbon) | High pressure, temperature, mechanical stress | Slightly reduced chemical resistance |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Soft, flexible, micro-porous | Irregular, damaged, or fragile flanges | Lower rigidity for high-pressure containment |
Struggling to Select the Right PTFE Gasket?
Choosing the wrong gasket material can lead to leaks, contamination, and costly downtime. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between Virgin, Filled, and Expanded PTFE to ensure you get a gasket that delivers optimal performance, longevity, and chemical compatibility for your specific application—whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order.
Let us provide you with a sealing solution that guarantees reliability and efficiency.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let's solve your sealing challenge together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What future advancements are expected for PTFE oil seals? From Smart Seals to 3D Printing
- What are PTFE slide bearings and what is their primary function in construction? Manage Structural Movement Safely
- What are the key properties of PTFE envelope gaskets? Ensure Reliable Sealing in Demanding Environments
- What is the thermal shock resistance of PTFE lined pipes? Engineered for Extreme Temperature Cycling
- How can deformation of PTFE during machining be minimized? Master Precision with Sharp Tools & Thermal Control
- How do PTFE components compare to metal components? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- How are PTFE lip seals used in the aerospace industry? Ensure Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- In which industries or applications are Teflon (PTFE) balls commonly used? Essential for Harsh Environments



















