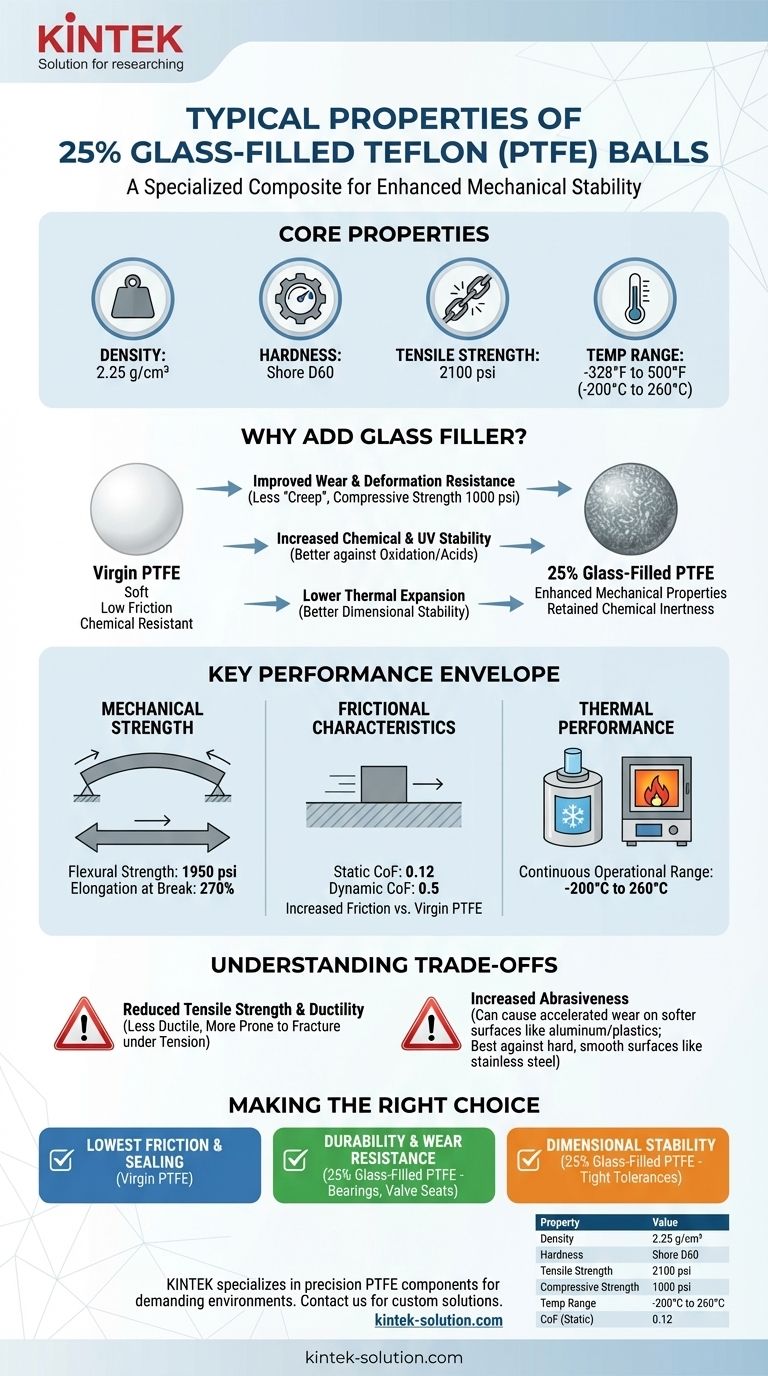
As a specialized composite material, 25% glass-filled Teflon (PTFE) balls have a density of 2.25 g/cm³, a Shore D60 hardness, and a tensile strength of 2100 psi. They are engineered to operate across an exceptionally wide temperature range, from -328°F to 500°F (-200°C to 260°C). These properties represent a significant modification from virgin Teflon, tailored for applications requiring enhanced mechanical stability.
The core purpose of adding glass fibers to Teflon is to dramatically improve its mechanical properties—specifically its resistance to wear, compression, and deformation under load—while retaining Teflon's inherent chemical inertness and thermal stability.

Why Add Glass Filler to Teflon?
Virgin Teflon is known for its exceptional chemical resistance and extremely low friction, but it is a relatively soft material. Adding a 25% glass filler is an engineering solution to overcome its mechanical limitations.
The Primary Enhancement: Wear and Deformation Resistance
Glass fibers act as a reinforcement within the PTFE matrix. This dramatically increases the material's compressive strength (1000 psi) and hardness (Shore D60).
The result is a material that is far less prone to "creep" or deform under a sustained load. This makes it superior for applications like valve seats, bearings, and seals that operate under pressure.
Improved Chemical and Environmental Stability
While retaining the broad chemical inertness of virgin PTFE, the glass filler adds improved resistance to oxidation and acids.
Furthermore, glass-filled PTFE has high resistance to UV light, making it more suitable for applications with environmental exposure compared to its unfilled counterpart.
Lower Thermal Expansion
A significant benefit of the glass filler is a lower coefficient of thermal expansion.
This means the material will expand and contract less with temperature changes, providing better dimensional stability in components where tight tolerances are critical.
Core Properties of 25% Glass-Filled Teflon
These specifications define the material's performance envelope and are critical for proper application design.
Mechanical Strength
The material's strength profile is a balance of properties. It has a tensile strength of 2100 psi and a flexural strength of 1950 psi.
Its elongation at break is 270%, indicating that while it is much stiffer than virgin PTFE, it still retains a degree of flexibility.
Frictional Characteristics
The reported static coefficient of friction is 0.12, while the dynamic coefficient is 0.5.
The static value is relatively low, but it's important to note that adding fillers to PTFE typically increases friction compared to the virgin material.
Thermal Performance
This composite has an outstanding operational temperature range.
It can function continuously at temperatures as high as 500°F (260°C) and remains effective at cryogenic temperatures as low as -328°F (-200°C).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a glass-filled composite involves accepting specific compromises in exchange for enhanced durability. Understanding these trade-offs is key to avoiding material misapplication.
Reduced Tensile Strength and Ductility
While compressive strength is boosted, the glass fibers can reduce the material's ultimate tensile strength compared to high-grade virgin PTFE.
The filler disrupts the polymer matrix, making it less ductile and more prone to fracture under pure tension than the unfilled version.
Increased Abrasiveness
The glass fibers that provide reinforcement are inherently abrasive.
This is a critical consideration for design. A 25% glass-filled Teflon ball can cause accelerated wear on softer mating surfaces, such as aluminum or other plastics. It performs best against hard, smooth surfaces like stainless steel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material selection should be driven by the most critical demand of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction and sealing against soft surfaces: Virgin PTFE is the superior choice for its self-lubricating properties and non-abrasive nature.
- If your primary focus is durability and wear resistance under load: 25% glass-filled PTFE is the clear winner for components like bearings, valve seats, and structural parts.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability across a wide temperature range: The lower thermal expansion of glass-filled PTFE makes it ideal for maintaining tight tolerances.
Ultimately, selecting 25% glass-filled Teflon is a deliberate engineering decision to enhance mechanical durability while retaining the exceptional thermal and chemical stability of the base polymer.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.25 g/cm³ |
| Hardness | Shore D60 |
| Tensile Strength | 2100 psi |
| Compressive Strength | 1000 psi |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 260°C |
| Coefficient of Friction (Static) | 0.12 |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored for demanding environments? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine expert material knowledge with custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to deliver solutions that enhance your product's durability and performance. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your specific application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















