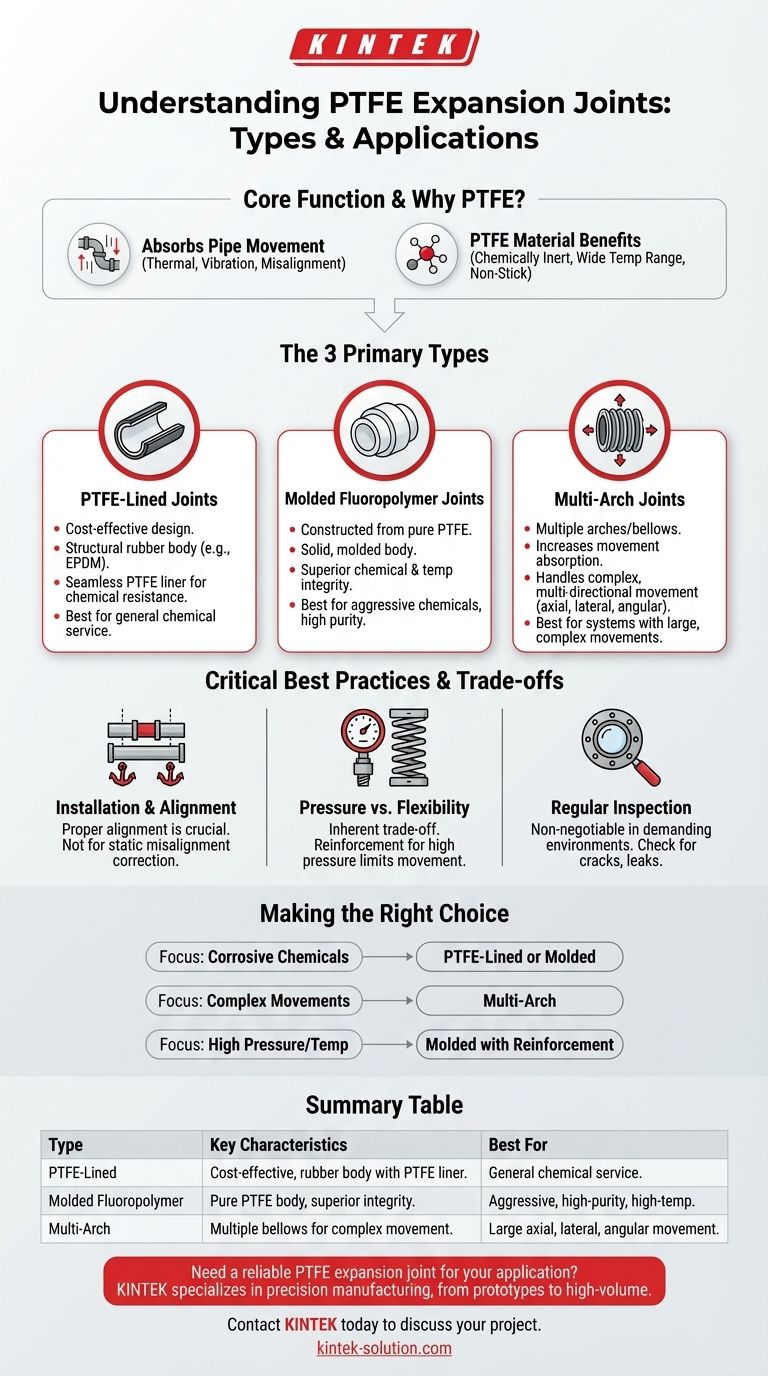
At its core, there are three primary types of PTFE expansion joints. These are PTFE-lined joints, which offer excellent chemical resistance for the wetted surfaces; molded fluoropolymer joints, known for superior temperature and chemical integrity throughout; and multi-arch joints, which are specifically designed to absorb complex, multi-directional pipe movements.
The critical insight is that selecting the right PTFE expansion joint is not about choosing a "type" in isolation. It is about matching the specific construction of the joint—the liner, the body, and the number of arches—to the precise demands of your system's chemical environment, temperature, pressure, and movement.

Understanding the Core Function
Before diving into the types, it's essential to understand the problem these components solve. Industrial piping systems are not static; they expand and contract with temperature changes, vibrate from machinery, and can suffer from minor misalignments.
What an Expansion Joint Does
A PTFE expansion joint, or compensator, is a flexible connector designed to absorb these movements. Its primary job is to prevent stress on the piping, pumps, and vessels, which could otherwise lead to premature failure and costly downtime.
Why PTFE is the Material of Choice
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer with a unique combination of properties. It is nearly universally inert, meaning it can handle highly corrosive chemicals without degrading. It also offers a wide operating temperature range and excellent non-stick properties, making it ideal for the demanding environments found in chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing plants.
A Breakdown of PTFE Expansion Joint Types
While there are many variations, most designs fall into a few key categories based on their construction and intended function.
PTFE-Lined Expansion Joints
This is a very common and cost-effective design. It consists of a structural body, often made of an elastomer like EPDM or butyl rubber, with a seamless PTFE liner on all surfaces that come into contact with the system media.
The liner provides the necessary chemical resistance, while the rubber body provides the structural strength and flexibility to handle pressure and movement.
Molded Fluoropolymer Expansion Joints
This type is constructed from pure or high-grade fluoropolymers like PTFE, not just lined with it. The entire body of the joint is a solid, molded piece of PTFE or a similar material.
This construction offers the ultimate in chemical and temperature resistance throughout the entire component, making it suitable for the most aggressive and high-purity applications where any contamination is unacceptable.
Multi-Arch Expansion Joints
The flexibility of an expansion joint comes from its "arch" or bellow. A standard joint may have a single arch.
Multi-arch designs feature two or more arches, which significantly increases the amount of movement they can absorb. They are specifically engineered for systems with large or complex movements, including simultaneous axial (compression/extension), lateral (side-to-side), and angular (bending) motion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
Choosing a joint is only the first step. Proper application and maintenance are critical for ensuring system reliability and safety.
Installation and Alignment are Critical
The most common cause of premature expansion joint failure is improper installation. Pipes must be properly aligned and anchored according to manufacturer guidelines. An expansion joint is designed to absorb system movements, not to correct for significant, static pipe misalignment.
Pressure vs. Flexibility
There is an inherent trade-off between a joint's pressure rating and its flexibility. To handle higher pressures, joints often require reinforcement, such as metal rings, which can limit their range of movement. You must select a joint that meets the pressure requirements without sacrificing the necessary flexibility.
Regular Inspection is Non-Negotiable
In demanding environments, especially those with high pressure or aggressive chemicals, regular visual inspections are essential. Look for any signs of cracking, blistering, material degradation, or leakage around the flanges to prevent catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection should be driven by the specific needs of your system. Use these points as a guide to focus your decision.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals: Prioritize a PTFE-lined or a solid molded fluoropolymer joint to ensure material compatibility with the process media.
- If your primary focus is accommodating large or complex pipe movements: A multi-arch design is the correct solution, as it is engineered for high levels of axial, lateral, and angular deflection.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure or high-temperature service: Look for joints with reinforcement features and verify that the material's temperature rating is well above your system's operating maximum.
Ultimately, a well-chosen expansion joint is a critical investment in the integrity and longevity of your entire piping system.
Summary Table:
| Type of PTFE Expansion Joint | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE-Lined | Cost-effective; structural rubber body with PTFE liner for chemical resistance. | General chemical service with standard movement. |
| Molded Fluoropolymer | Entirely molded from PTFE; superior chemical/temperature integrity. | Aggressive chemicals, high-purity, and high-temperature applications. |
| Multi-Arch | Multiple arches (bellows) to absorb complex, multi-directional movements. | Systems with large axial, lateral, and angular pipe movements. |
Need a reliable PTFE expansion joint for your semiconductor, medical, or industrial application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom expansion joints. We ensure your joint is perfectly matched to your system's chemical, temperature, pressure, and movement requirements—from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a solution that protects your piping system's integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of unreinforced PTFE laminates? Navigating Manufacturing Challenges for High-Frequency Performance
- What are the two main types of specialty PTFE washers and their characteristics? Choose the Right Washer for Your Application
- What temperature limits should be considered for Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings? Ensure Seal Integrity in High-Temp Applications
- In which industries are PTFE lined ball valves commonly used? Master Corrosive & High-Purity Fluid Control
- What is PTFE and what are its common applications? Discover the Versatile High-Performance Polymer
- What are the key benefits of PTFE oil seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the advantages of PTFE balls over metals or alloys? Superior Chemical & Friction Resistance
- What are the typical structural designs of PTFE oil seals? A Guide to Spring-Energized, Filled, and Multi-Lip Seals



















