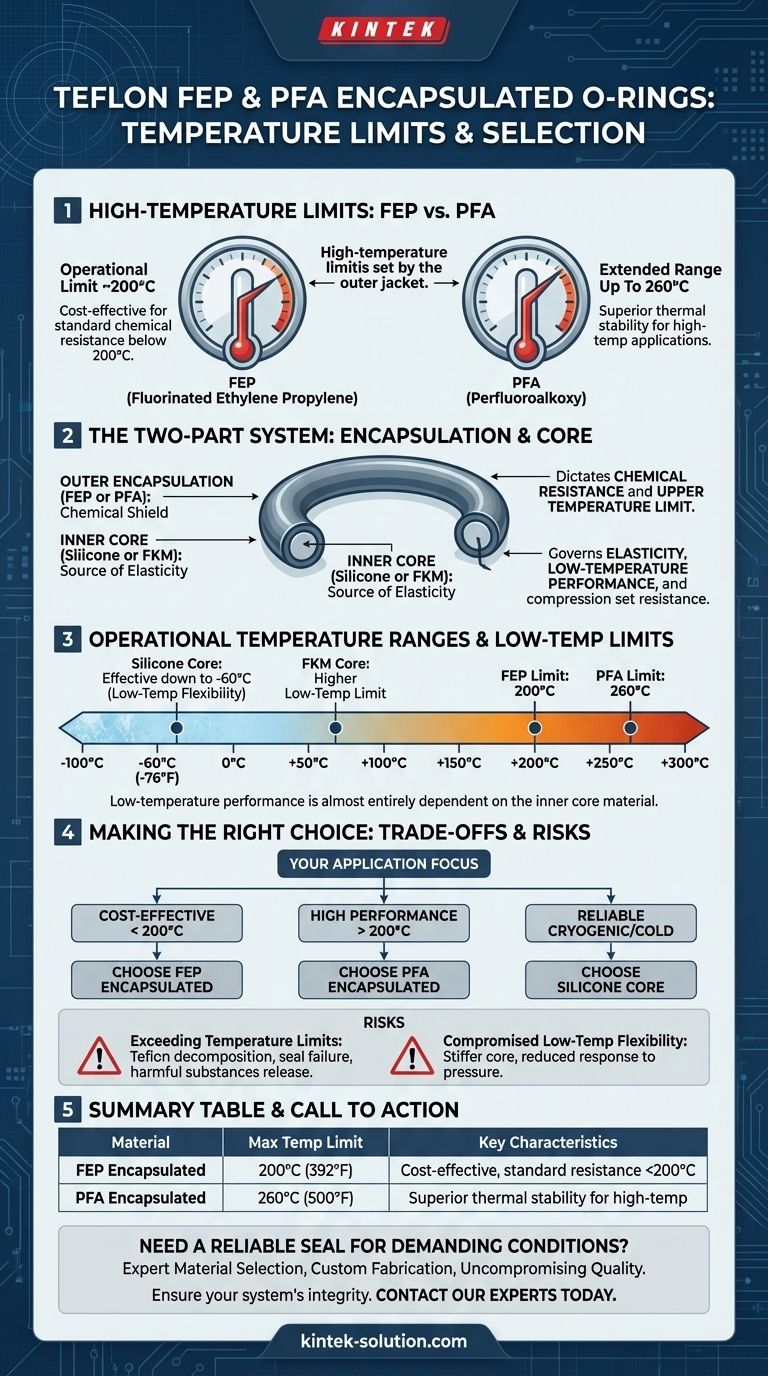
For Teflon encapsulated O-rings, the specific temperature limits are dictated by the outer material. FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) encapsulated O-rings have an operational temperature limit of approximately 200°C (392°F). For more demanding applications, PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) encapsulated O-rings offer a higher limit, withstanding temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
While the outer Teflon layer dictates chemical resistance and the upper temperature limit, the inner core material—typically silicone or FKM (Viton®)—governs the O-ring's elasticity and its low-temperature performance.

The Two-Part System: Encapsulation and Core
To properly select an encapsulated O-ring, you must understand its construction. It is a composite seal made of two distinct components, each with a specific function.
The Outer Encapsulation: Your Chemical Shield
The seamless outer layer of Teflon (FEP or PFA) is the component in direct contact with the process media.
Its primary role is to provide exceptional chemical resistance against a wide array of corrosive fluids, from aggressive acids to aromatic solvents. This encapsulation is what makes these O-rings ideal for harsh chemical environments.
The Inner Core: The Source of Elasticity
Unlike solid Teflon, which has poor elastic memory, an encapsulated O-ring uses a flexible inner core to provide the physical force needed to maintain a seal.
This core is typically made from silicone or FKM (Viton®). The choice of core material is critical for the seal's overall temperature range and compression set resistance.
Operational Temperature Ranges Explained
The effective service temperature of the O-ring is a combination of the limits of both the encapsulation and the core.
High-Temperature Limits: FEP vs. PFA
The upper temperature limit is set by the outer jacket material.
- FEP Encapsulation: Reliably operates up to 200°C (392°F).
- PFA Encapsulation: Provides an extended range, safely operating up to 260°C (500°F).
Choosing the correct encapsulation is a straightforward decision based on the maximum temperature of your application.
Low-Temperature Limits: The Core's Role
The low-temperature performance is almost entirely dependent on the inner core material.
A silicone core allows the O-ring to remain effective down to approximately -60°C (-76°F). An FKM core typically has a higher low-temperature limit.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Selecting the wrong material or exceeding its operational limits can lead to seal failure and compromise system safety.
The Risk of Exceeding Temperature Limits
Exposing these O-rings to temperatures beyond their stated maximums, especially direct flame, can cause the Teflon to decompose.
This decomposition not only destroys the seal but can also release harmful substances into your system. It is a critical failure mode that must be avoided.
Compromised Flexibility at Low Temperatures
Even within the specified range, as temperatures drop, the energizing core will become stiffer.
This can reduce the seal's ability to respond to pressure or surface fluctuations, particularly in dynamic applications or systems with significant thermal cycling. Always verify the core material is suited for your minimum operating temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct encapsulated O-ring requires matching the material properties to your specific operational conditions.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in applications consistently below 200°C (392°F): An FEP encapsulated O-ring is the appropriate and standard choice.
- If your primary focus is performance in applications that will exceed 200°C (392°F): You must specify a PFA encapsulated O-ring to ensure thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is reliable sealing in cryogenic or very cold environments: Ensure you select an O-ring with a silicone core for its superior low-temperature flexibility.
Ultimately, a precise understanding of your application's full temperature range is essential for ensuring long-term seal integrity and system reliability.
Summary Table:
| Material | Maximum Temperature Limit | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| FEP Encapsulated | 200°C (392°F) | Cost-effective for standard chemical resistance below 200°C. |
| PFA Encapsulated | 260°C (500°F) | Superior thermal stability for high-temperature applications. |
Need a Reliable Seal for Demanding Conditions?
Choosing the right encapsulated O-ring is critical for the safety and performance of your equipment in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including custom FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance to ensure your seals withstand specific temperature and chemical challenges.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototype to high-volume production, tailored to your exact specifications.
- Uncompromising Quality: Precision-engineered components for maximum reliability and longevity.
Ensure your system's integrity. Contact our experts today for a consultation on your custom sealing solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How do PTFE balls contribute to reduced maintenance costs? Extend Component Life and Cut Downtime
- What are the key chemical properties of PTFE balls? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- Why are PTFE balls particularly suitable for high-performance applications? Key Properties & Selection Guide
- What factors determine the different grades of PTFE balls available? Select the Right Grade for Your Application
- How do the chemical properties of PTFE balls influence their performance? Unmatched Durability in Harsh Environments



















