The most common structural designs for PTFE oil seals are the spring-energized seal, the filled (or modified) PTFE seal, and the multi-lip composite seal. Each design strategically leverages the unique properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to solve specific sealing challenges, such as extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, or high-speed rotation, where traditional rubber seals would fail.
The structural design of a PTFE seal is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It is a deliberate engineering choice to either enhance a specific material property or compensate for one of its inherent limitations, ensuring reliable performance in demanding applications.
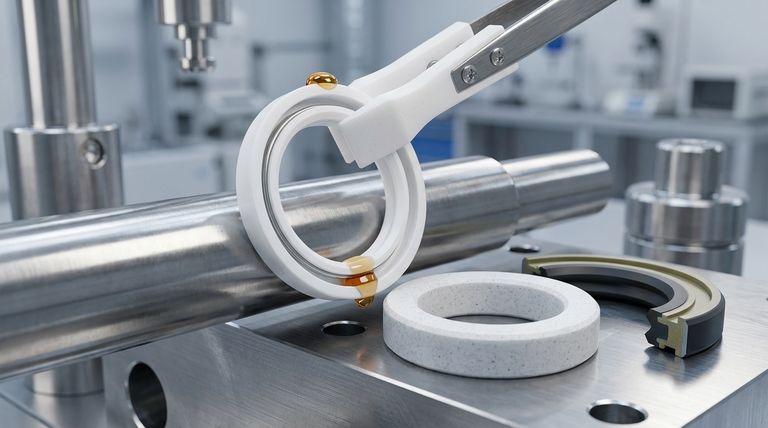

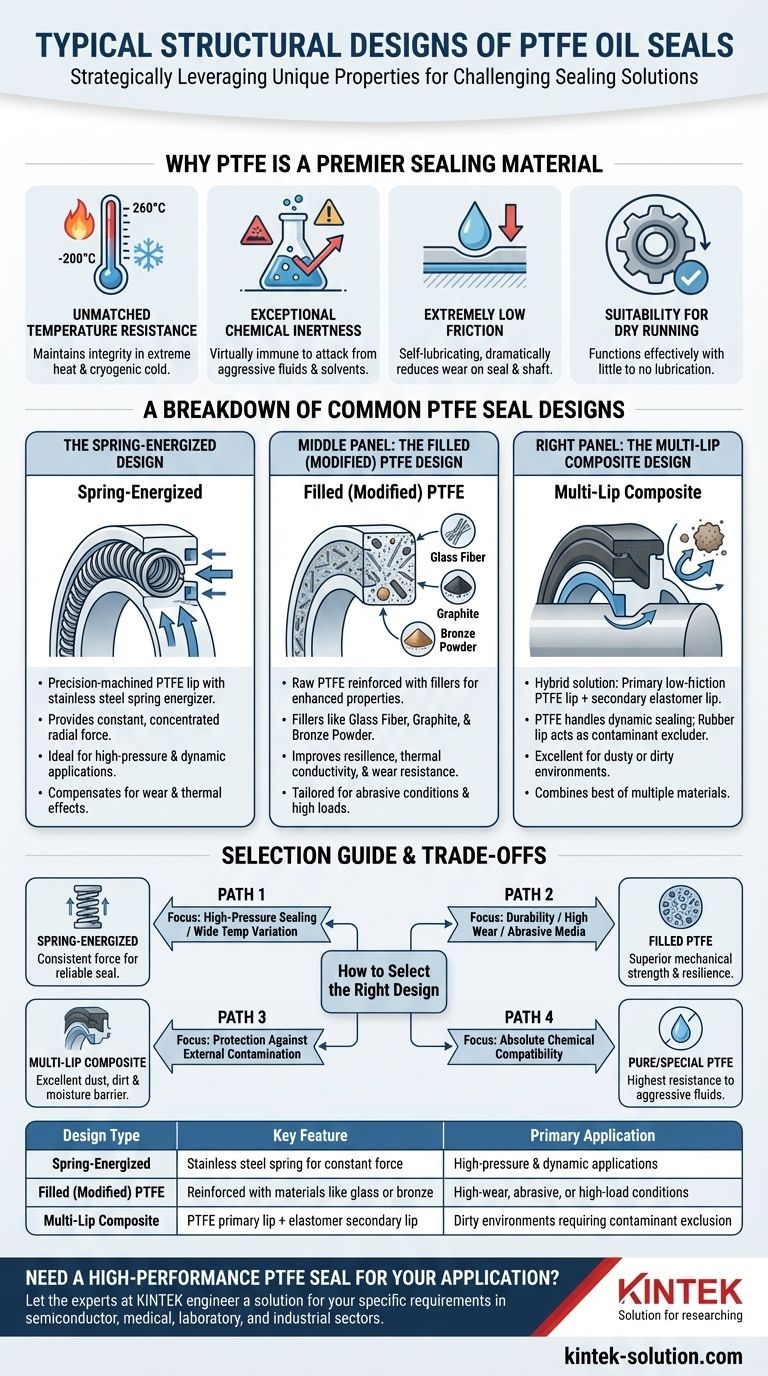
Why PTFE is a Premier Sealing Material
Before dissecting the specific designs, it's crucial to understand why PTFE is chosen. Its core properties make it uniquely suited for challenging environments.
Unmatched Temperature Resistance
PTFE maintains its integrity and performance across an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This makes it ideal for applications involving extreme heat or cryogenic cold.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
This material is virtually immune to attack from most chemicals, including aggressive oils, acids, solvents, and industrial fluids. This ensures the seal will not degrade or swell when exposed to harsh media.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This self-lubricating property dramatically reduces wear on both the seal and the rotating shaft, extending the operational life of the entire system.
Suitability for Dry Running
Because of its low-friction nature, PTFE seals can often operate with little to no lubrication. They can function effectively even after a prolonged shutdown and immediate restart, where the oil film might be absent.
A Breakdown of Common PTFE Seal Designs
Each structural design modifies the basic PTFE ring to optimize its performance for specific operational demands.
The Spring-Energized Design
This construction features a precision-machined PTFE lip and a stainless steel spring energizer. The spring provides a constant, concentrated radial force on the sealing lip.
This force ensures a tight seal even under low pressure, compensates for material wear over time, and accommodates thermal expansion and contraction. It is the go-to design for high-pressure and dynamic applications.
The Filled (Modified) PTFE Design
In this design, the raw PTFE material is reinforced with fillers to enhance specific mechanical properties. The base PTFE is a relatively soft material, and fillers improve its resilience.
Common fillers include glass fiber for increased rigidity, graphite for better thermal conductivity and wear resistance, and bronze powder for improved strength and resistance to creep. This design tailors the seal material itself to withstand abrasive conditions or high loads.
The Multi-Lip Composite Design
This is a hybrid solution that combines the best of multiple materials. It typically features a primary sealing lip made of low-friction PTFE and a secondary, auxiliary lip made from a more traditional elastomer like rubber.
The PTFE lip handles the dynamic sealing against the shaft, while the rubber lip acts as a dustproof or contaminant excluder. This design is ideal for protecting machinery in dirty or dusty environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PTFE seals are not without their considerations. Understanding these limitations is key to successful implementation.
Limited Elasticity
Unlike rubber, PTFE is not naturally elastic. It does not "bounce back" to its original shape as readily. This is precisely why designs often incorporate springs or other energizers to provide a consistent sealing force.
Higher Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes more than most metals. Seal and hardware design must account for this differential expansion to maintain proper sealing force and prevent failure.
Manufacturing Complexity
Producing high-performance PTFE seals involves precision processes like molding, extrusion, curing, and CNC machining. This complexity can result in a higher cost compared to standard elastomeric seals.
How to Select the Right Design
Choosing the correct seal structure is critical for ensuring long-term reliability in your specific application.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing or wide temperature variation: The spring-energized design provides the consistent force needed to maintain a reliable seal under these conditions.
- If your primary focus is durability against high wear or abrasive media: A filled PTFE seal with a reinforcement like glass fiber or bronze offers superior mechanical strength.
- If your primary focus is protecting against external contamination: The multi-lip composite design offers an excellent barrier against dust, dirt, and moisture.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical compatibility: A seal made from pure or specially formulated PTFE will provide the highest level of resistance to aggressive fluids.
Ultimately, selecting the correct PTFE seal design transforms a potential point of failure into a component of exceptional reliability.
Summary Table:
| Design Type | Key Feature | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Spring-Energized | Stainless steel spring for constant force | High-pressure & dynamic applications |
| Filled (Modified) PTFE | Reinforced with materials like glass or bronze | High-wear, abrasive, or high-load conditions |
| Multi-Lip Composite | PTFE primary lip + elastomer secondary lip | Dirty environments requiring contaminant exclusion |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal for Your Application?
Choosing the right structural design is critical for reliability in demanding environments. The experts at KINTEK specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can help you:
- Select the optimal design (spring-energized, filled, or multi-lip) for your specific temperature, pressure, and chemical requirements.
- Provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring a perfect fit and function.
- Leverage our material expertise to enhance seal life and performance in your equipment.
Let's engineer a solution for you. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE rotary shaft seals and what are they designed for? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What makes PTFE gaskets resistant to chemical corrosion? The Molecular Fortress Explained
- Why are PTFE and PEEK suitable for backup rings? Ensure Seal Integrity in Extreme Conditions
- What are machined PTFE parts made of? The Power of Pure Carbon and Fluorine
- In which industries are PTFE bellow mechanical seals commonly used? The Ultimate Solution for Corrosive Fluids
- What are the steps involved in the PTFE lining process? A Guide to Durable Chemical Resistance
- Why are PTFE lined pipes considered essential for certain industries? Unmatched Corrosion Resistance & Purity
- What are critical installation practices for PTFE O-rings? Avoid Leaks and Ensure a Perfect Seal



















