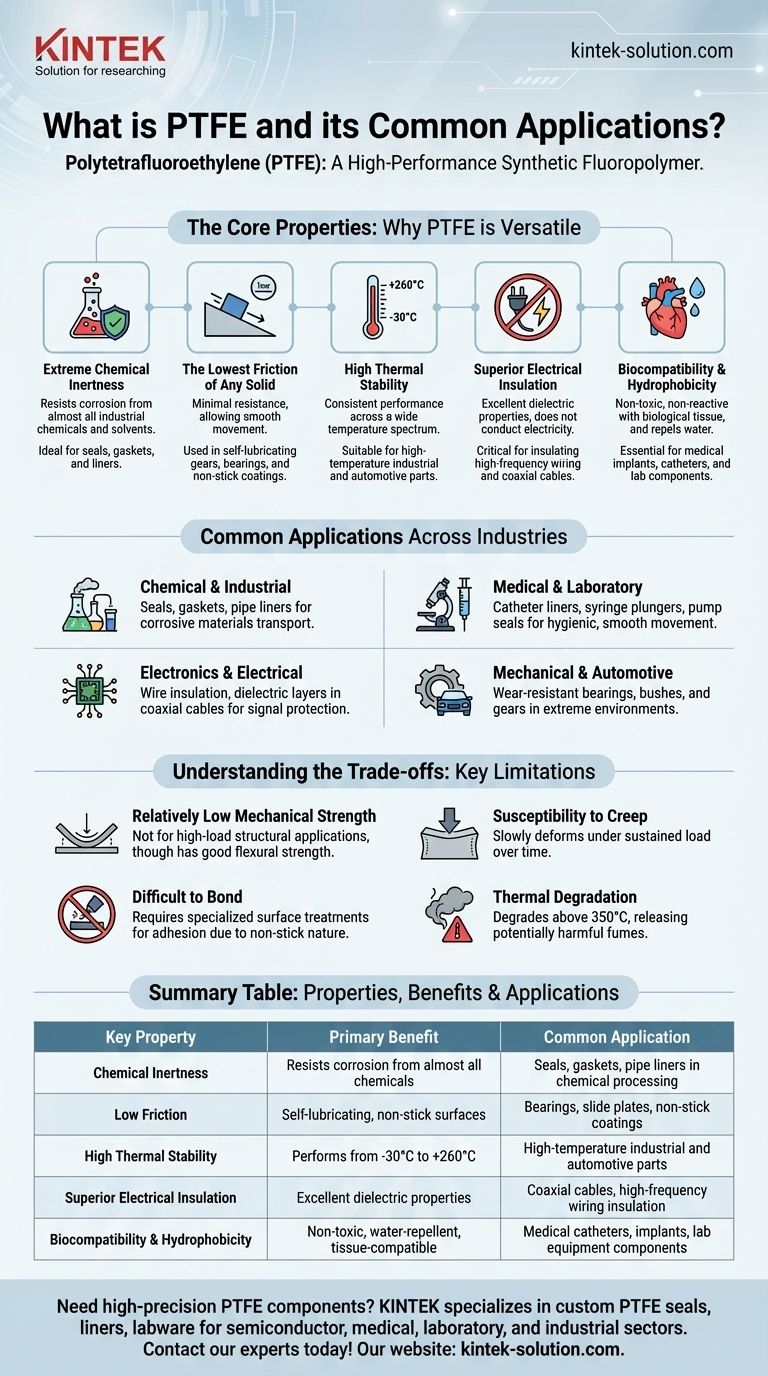
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer, a specialized plastic best known by the brand name Teflon. It is a highly versatile material prized for its extreme chemical resistance, exceptionally low friction, and stability across a wide range of temperatures. While its most common association is with non-stick cookware, its primary value lies in demanding industrial, medical, and electrical applications where other materials would quickly fail.
The true value of PTFE lies not in a single feature, but in its rare combination of properties. Its ability to be simultaneously non-reactive, heat-resistant, and incredibly slippery makes it an indispensable problem-solver in environments where other materials would degrade or seize.

What Makes PTFE So Versatile? The Core Properties
The widespread use of PTFE stems from a unique set of intrinsic characteristics. Understanding these properties is key to understanding its applications.
### Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. Its strong carbon-fluorine bonds make it resistant to corrosion from almost all industrial chemicals and solvents.
This property makes it an ideal material for containers, pipe liners, seals, and gaskets that will be in constant contact with highly reactive substances.
### The Lowest Friction of Any Solid
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This means surfaces can slide against it with minimal resistance.
This "slipperiness" is the reason for its use as a non-stick coating on cookware and as a component in self-lubricating gears, slide plates, and bearings.
### High Thermal Stability
PTFE can perform consistently across a very wide temperature range, typically from -30°C up to a continuous working temperature of +260°C (+500°F).
This allows it to be used in high-temperature industrial processes and automotive engine parts where other plastics would melt or become brittle.
### Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with outstanding dielectric properties. It does not conduct electricity and resists high voltages.
Because of this, it is a critical material for insulating high-frequency wiring and coaxial cables used in computer and telecommunications equipment.
### Biocompatibility and Hydrophobicity
PTFE is non-toxic and does not react with biological tissue, making it highly biocompatible. It is also hydrophobic, meaning it repels water.
These features are essential for medical applications, such as liners for catheters and components for medical implants, where hygiene and compatibility with the human body are critical.
Common Applications Across Industries
Based on its core properties, PTFE has found its way into nearly every technical field.
### In Chemical and Industrial Processing
Its chemical resistance makes PTFE the go-to material for seals, gaskets, O-rings, and ball valves. It is also used to line pipes and tanks that transport or store corrosive materials.
### In Medical and Laboratory Equipment
The combination of low friction and biocompatibility is leveraged in catheter liners, syringe plungers, and pump seals. These components ensure smooth, hygienic movement in delicate instruments.
### In Electronics and Electrical Engineering
Due to its insulating properties, PTFE is used to insulate hookup wires and create the dielectric layer in high-performance coaxial cables, protecting signal integrity.
### In Mechanical and Automotive Systems
The low-friction nature of PTFE is ideal for wear-resistant and self-lubricating components like bearings, bushes, and gears, especially in extreme or abrasive environments where traditional lubricants would fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While PTFE is exceptionally capable, it's important to understand its limitations to use it effectively.
### Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals, PTFE is a soft material. While it has good flexural strength (it can bend without breaking), it is not suitable for high-load structural applications.
### Susceptibility to Creep
Like many polymers, PTFE can slowly deform over time if placed under a constant, sustained load. This must be accounted for in long-term mechanical designs.
### Difficult to Bond
The same non-stick property that makes PTFE useful also makes it very difficult to glue or bond to other surfaces. Specialized surface treatments are often required.
### Thermal Degradation
While it has a high operating temperature, PTFE will begin to degrade at extremely high temperatures (above 350°C), releasing potentially harmful fumes. Its use must be kept within its specified thermal range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is about matching its unique strengths to a specific problem.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in moving parts: PTFE is an unparalleled choice for bearings, slide plates, and low-friction coatings where lubrication is difficult.
- If your primary focus is handling corrosive chemicals: Its chemical inertness makes it the default material for seals, gaskets, and liners in aggressive environments.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its excellent dielectric properties are critical for components like coaxial cables and specialized wiring.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and hygiene: PTFE is essential for medical devices like catheters and implants where non-reactivity with body tissue is paramount.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's unique combination of properties empowers you to solve some of engineering's most demanding material challenges.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from almost all chemicals | Seals, gaskets, pipe liners in chemical processing |
| Low Friction | Self-lubricating, non-stick surfaces | Bearings, slide plates, non-stick coatings |
| High Thermal Stability | Performs from -30°C to +260°C | High-temperature industrial and automotive parts |
| Superior Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Coaxial cables, high-frequency wiring insulation |
| Biocompatibility & Hydrophobicity | Non-toxic, water-repellent, tissue-compatible | Medical catheters, implants, lab equipment components |
Need high-precision PTFE components for your specialized application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and other components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine precision production with custom fabrication capabilities—from rapid prototypes to high-volume production runs—ensuring your components meet the exact demands of your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your most challenging material problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















