In the world of high-performance thermoplastics, PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) stands out for its remarkable combination of properties. It is a semi-crystalline polymer renowned for its exceptional mechanical strength, robust chemical resistance, and the ability to maintain its integrity at continuous service temperatures as high as 480°F (250°C).
PEEK is the material of choice when standard plastics fail due to extreme heat, aggressive chemicals, or intense mechanical stress. Its selection is a strategic decision, balancing its superior performance against its premium cost and specific chemical vulnerabilities.

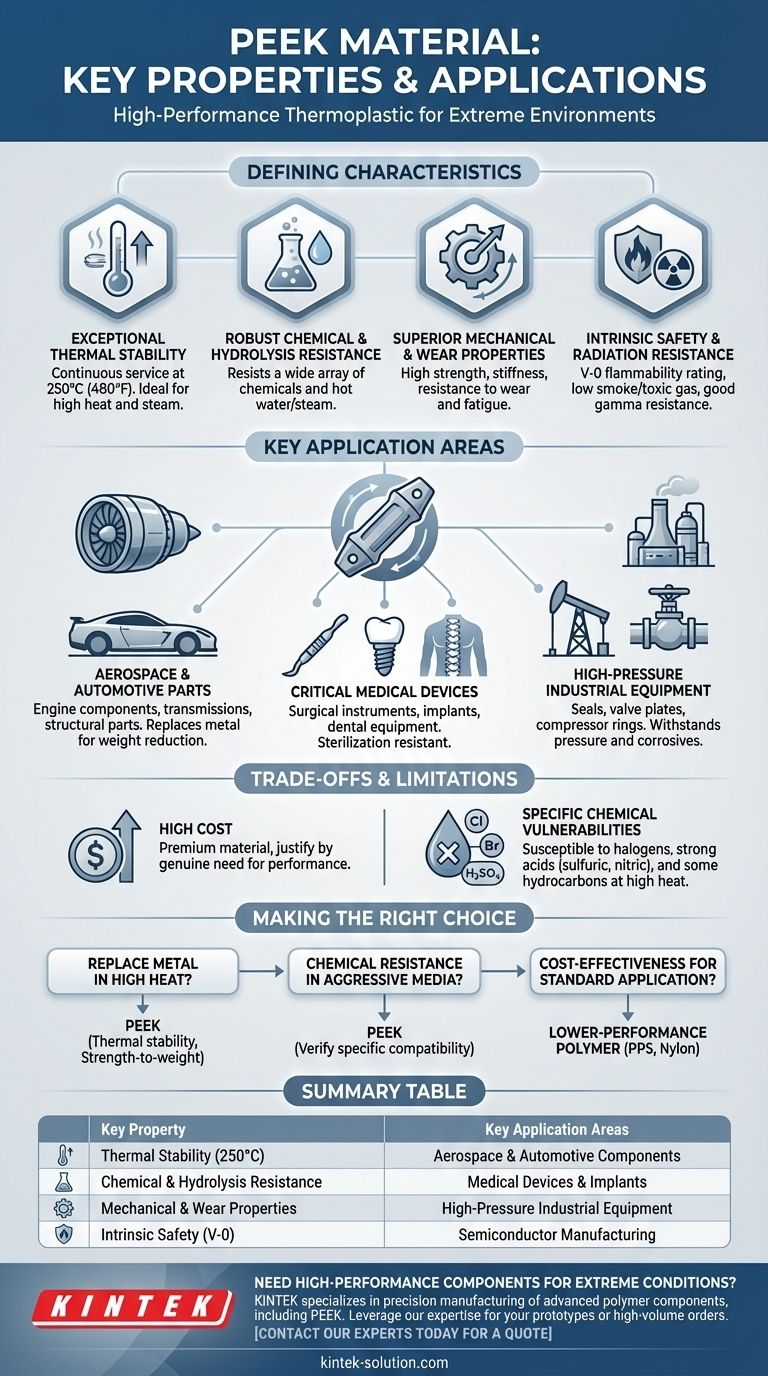
The Defining Characteristics of PEEK
PEEK's value comes from a unique blend of high-end traits that allow it to function in environments where most other polymers would degrade rapidly.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PEEK maintains its excellent mechanical properties, such as stiffness and strength, even at very high temperatures. Its ability to operate continuously at 250°C makes it suitable for applications involving steam, high-temperature fluids, or proximity to heat sources.
Robust Chemical and Hydrolysis Resistance
This material shows excellent resistance to a wide array of organic and inorganic chemicals. It is also highly resistant to hydrolysis, meaning it will not break down in hot water or steam, a critical feature for medical sterilization and downhole oil and gas equipment.
Superior Mechanical and Wear Properties
PEEK has a high tensile strength and a hard, rigid structure. This results in excellent resistance to wear, creep (the tendency to deform permanently under load), and fatigue, making it ideal for dynamic parts like bearings, seals, and gears.
Intrinsic Safety and Radiation Resistance
With a V-O flammability rating, PEEK generates very low levels of smoke and toxic gas when exposed to flames. It also exhibits good resistance to high doses of gamma radiation without significant degradation of its properties.
Where PEEK Excels: Key Application Areas
PEEK's properties make it an indispensable material in industries where performance and reliability are non-negotiable. It is often used to replace metal components to reduce weight and corrosion.
Demanding Aerospace and Automotive Parts
Its high strength-to-weight ratio and thermal stability are ideal for components inside engines, transmissions, and aircraft structural parts, where reducing weight without sacrificing performance is critical.
Critical Medical Devices
PEEK's chemical inertness and resistance to sterilization methods like autoclaving make it suitable for surgical instruments, dental equipment, and even long-term medical implants.
High-Pressure Industrial Equipment
In the oil & gas and chemical processing industries, PEEK is used for seals, valve plates, and compressor rings that must withstand high pressures, extreme temperatures, and corrosive chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PEEK is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Primary Factor: High Cost
PEEK is one of the more expensive thermoplastics on the market. Its cost must be justified by a genuine need for its high-performance characteristics; it is often overkill for less demanding applications.
Specific Chemical Vulnerabilities
Despite its broad chemical resistance, PEEK can be attacked by certain substances. It is susceptible to halogens (like chlorine and bromine), strong concentrated acids (such as sulfuric and nitric acid), and some specific hydrocarbons, particularly at elevated temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PEEK is a decision driven by the severity of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is replacing metal in high-temperature environments: PEEK's combination of thermal stability and a high strength-to-weight ratio makes it an excellent candidate.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance in aggressive media: PEEK is highly effective, but you must verify its compatibility with any specific halogens or concentrated acids in your process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a standard application: A lower-performance polymer like PPS or Nylon is likely a more appropriate and economical choice.
Ultimately, selecting PEEK is a strategic investment in unparalleled performance where component failure is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Key Application Areas |
|---|---|
| Exceptional Thermal Stability (up to 250°C) | Aerospace & Automotive Components |
| Robust Chemical & Hydrolysis Resistance | Medical Devices & Implants |
| Superior Mechanical & Wear Properties | High-Pressure Industrial Equipment |
| Intrinsic Safety (V-0 Flammability Rating) | Semiconductor Manufacturing |
Need high-performance components that can withstand extreme conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing and custom fabrication of advanced polymer components, including PEEK. Our expertise in creating seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors ensures your critical applications perform reliably.
Let us help you leverage the superior properties of PEEK for your prototypes or high-volume orders. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Shallow Evaporating Dishes for Diverse Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of PTFE-coated O-rings? Understand the risks of wear, flaking, and contamination.
- What machining parameters should be adjusted when working with Teflon? Optimize for Precision & Safety
- Why are PTFE gaskets used in pharmaceutical and food industries? Ensuring Purity, Safety, and Compliance
- What industries commonly use PTFE components? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the key properties of PTFE O-rings? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- How does the low friction coefficient of PTFE expansion bellows benefit fluid flow? Reduce Energy Use & Prevent Blockages
- What are the benefits of glass and MoS2-filled PTFE? Achieve Superior Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the key steps in the manufacturing process of PTFE coated fasteners? Build a Durable, Corrosion-Resistant Shield



















