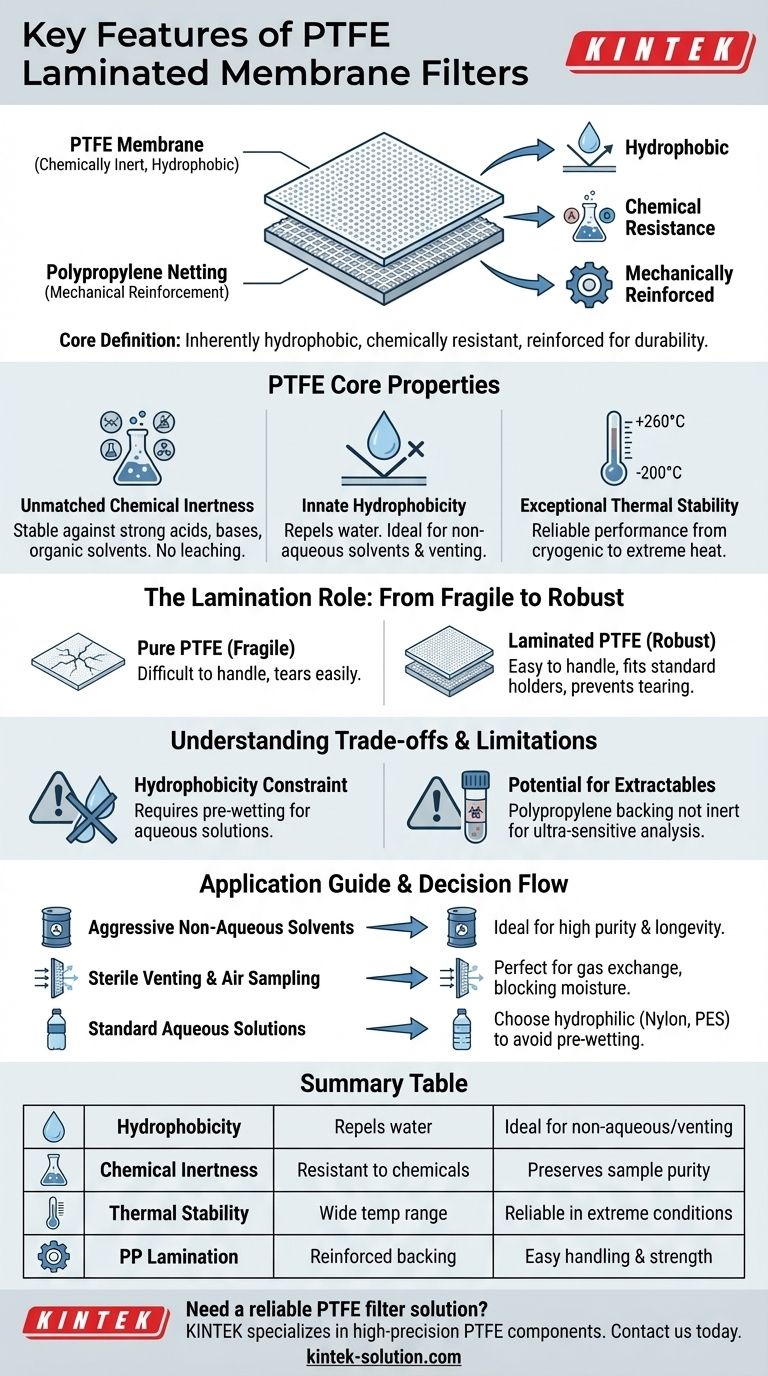
At their core, PTFE laminated membrane filters are defined by three primary features: they are inherently hydrophobic (water-repelling), they possess exceptional chemical resistance to nearly all acids, bases, and solvents, and they are mechanically reinforced with a polypropylene backing. This unique combination makes them highly durable and specialized for applications where water must be excluded.
The central takeaway is that laminating a chemically inert PTFE membrane onto a polypropylene support transforms a fragile material into a robust, easy-to-handle filter. This design makes it the default choice for filtering aggressive non-aqueous solvents, venting, and analytical air sampling.
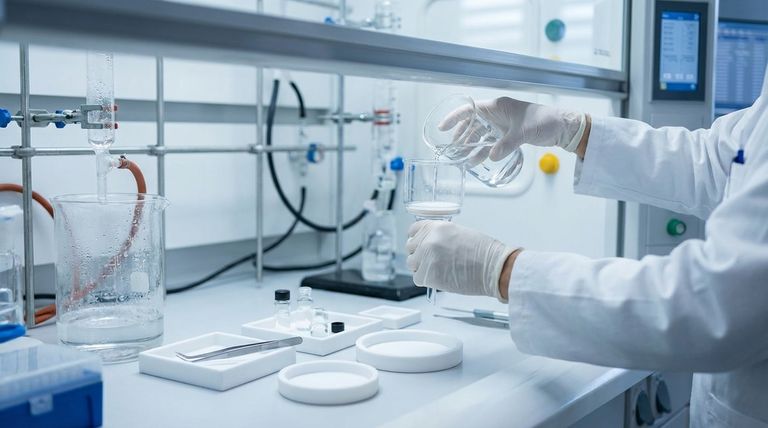

The Core Properties of PTFE Membranes
To understand why these filters are used, we must first look at the intrinsic properties of the Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) material itself.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant polymers known. It remains stable when exposed to a vast range of aggressive chemicals, including strong acids, bases, and organic solvents.
This inertness is critical for high-purity applications. It ensures that the filter itself does not degrade, break down, or leach contaminants into the filtrate, preserving the integrity of your sample.
Innate Hydrophobicity
The term hydrophobic means the membrane naturally repels water. Water will not readily pass through the filter pores.
This property is the primary reason PTFE filters are used for filtering non-aqueous solvents, as it prevents the filter from becoming saturated with atmospheric or trace water. It also makes them ideal for venting applications, where air or gas can pass through while blocking moisture or aqueous aerosols.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE can withstand an extremely wide temperature range, performing reliably from cryogenic temperatures (–200°C) up to very high heat (+260°C / 500°F).
This thermal resilience allows the filters to be used in processes involving extreme temperatures without losing their structural or chemical integrity.
The Role of the Lamination
While PTFE provides the chemical performance, the lamination provides the necessary physical durability for practical use.
Reinforcement with Polypropylene Netting
A pure PTFE membrane can be delicate and difficult to handle. To overcome this, it is laminated onto a polypropylene netting.
This backing provides significant mechanical strength and stiffness to the filter, preventing it from tearing or deforming during installation or under pressure.
Practical Handling Benefits
The added reinforcement makes the filters much easier to work with. They can be conveniently placed in standard disc filter holders without specialized tools or techniques, streamlining laboratory and industrial processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, these filters are not universally applicable. Understanding their limitations is key to using them correctly.
Hydrophobicity as a Limitation
The filter's greatest strength is also its main constraint. Because PTFE is hydrophobic, it will not allow water or aqueous solutions to pass through without significant pressure.
To filter a water-based solution, the membrane must first be pre-wetted with a low-surface-tension solvent, such as methanol or isopropanol. This adds an extra step to the process and introduces another chemical that may not be desirable.
Potential for Extractables
While the PTFE layer is extremely inert, the polypropylene support material is not. For highly sensitive analytical work, you must consider whether your solvent could potentially extract trace contaminants from the polypropylene backing.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing the right filter depends entirely on the nature of your fluid and your ultimate goal.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive, non-aqueous solvents: This is the ideal application for a PTFE laminated membrane, ensuring high purity and filter longevity.
- If your primary focus is sterile venting or air sampling: The hydrophobic nature of PTFE makes it perfect for allowing gas exchange while blocking water and microbial contaminants.
- If your primary focus is filtering standard aqueous (water-based) solutions: You should choose a different, naturally hydrophilic membrane material (like nylon, PES, or PVDF) to avoid the extra pre-wetting step.
Ultimately, a PTFE laminated membrane filter is a specialized tool engineered for performance under demanding chemical and environmental conditions.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobicity | Naturally repels water | Ideal for non-aqueous solvents and venting applications |
| Chemical Inertness | Resistant to acids, bases, and solvents | Preserves sample purity and filter integrity |
| Thermal Stability | Operates from -200°C to +260°C | Reliable performance in extreme temperatures |
| Polypropylene Lamination | Reinforced backing for mechanical strength | Easy handling and installation, prevents tearing |
Need a reliable PTFE filter solution for your demanding applications?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including laminated membrane filters, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your filters deliver unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical durability—whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our custom PTFE solutions can enhance your process efficiency and product purity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE perform in terms of chemical resistance? The Ultimate Guide to Inert Sealing & Lining
- What are some common applications of PTFE based on its electrical properties? | High-Frequency & High-Voltage Solutions
- What are the key heat resistance properties of PTFE? Master Extreme Temperature Applications
- What are some common fillers used with PTFE and their benefits? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- What are the key properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)? Unlock Extreme Performance
- What are the dielectric properties of PTFE? The Ultimate Insulator for Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE used in industrial applications? Solve Extreme Chemical, Thermal & Friction Challenges
- What are some common applications of PTFE? Harnessing the Power of a Versatile Polymer



















