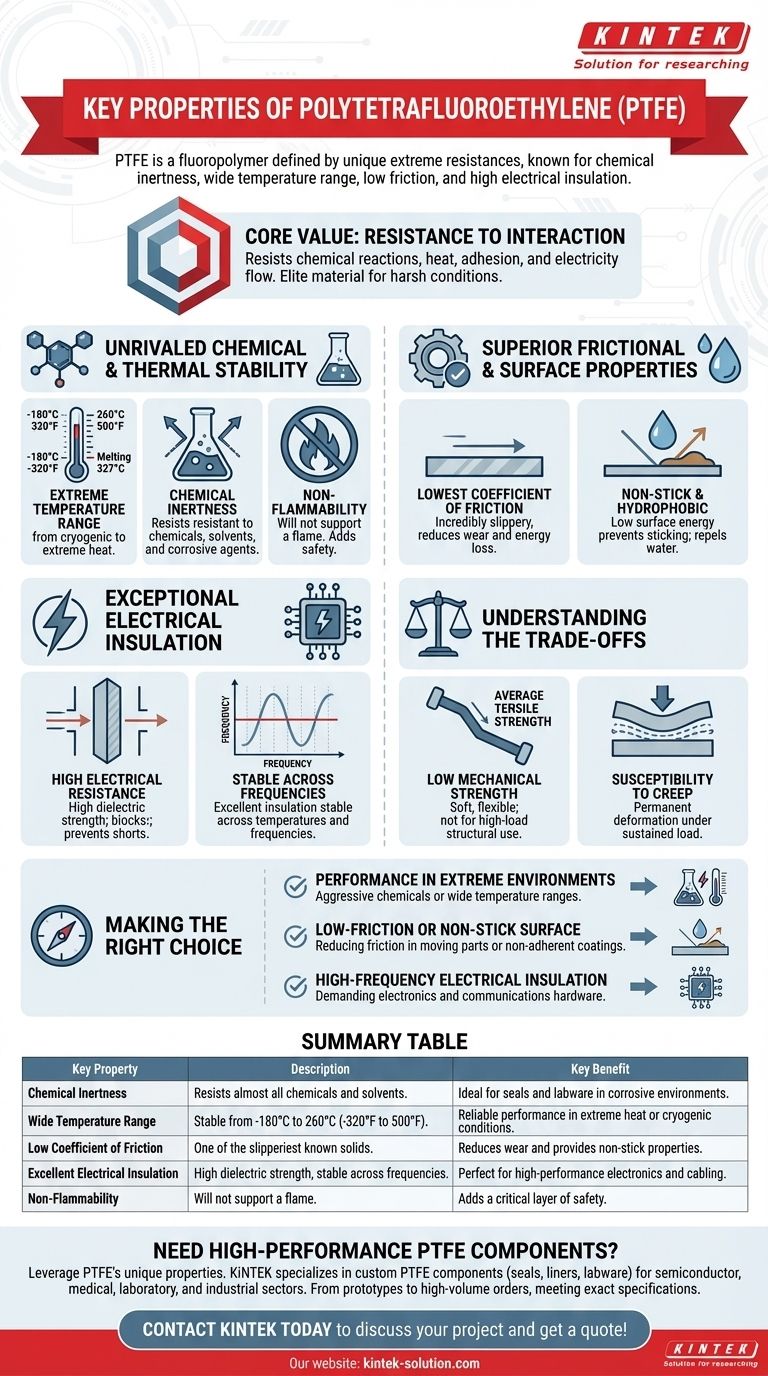
In essence, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer defined by a unique combination of extreme resistances. It is renowned for its exceptional chemical inertness, its ability to function across a vast temperature range, its extremely low coefficient of friction creating a non-stick surface, and its high performance as an electrical insulator.
The core value of PTFE lies in its resistance to interaction. It resists chemical reactions, heat, adhesion, and the flow of electricity, making it an elite material for performance in harsh or specialized conditions where other materials would fail.

Unrivaled Chemical and Thermal Stability
PTFE's molecular structure, consisting of a strong carbon-fluorine bond, is the source of its remarkable stability. This makes it a go-to material for demanding industrial, chemical, and aerospace applications.
### Extreme Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its properties across an exceptionally wide service temperature range. It remains functional and stable from cryogenic temperatures as low as -180°C (-320°F) up to 260°C (500°F), with a melting point around 327°C (620°F).
### Chemical Inertness
This material exhibits outstanding resistance to almost all chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This high degree of chemical stability makes it invaluable for seals, linings, and laboratory equipment that handle reactive substances.
### Non-Flammability
PTFE will not support a flame. This inherent non-flammability adds a critical layer of safety in high-temperature or electrical applications.
Superior Frictional and Surface Properties
The surface characteristics of PTFE are among its most well-known attributes, leading to its widespread use in both consumer and industrial products, most famously under the brand name Teflon.
### Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This creates an incredibly slippery surface that drastically reduces wear and energy loss in mechanical systems.
### Non-Stick and Hydrophobic
Its surface energy is extremely low, which prevents other materials from sticking to it. Furthermore, PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and is non-wetting, as it does not absorb moisture.
Exceptional Electrical Insulation
PTFE's electrical properties are as impressive as its chemical and thermal resistance, making it a first-choice material for high-performance electronics and cabling.
### High Electrical Resistance
It is an outstanding electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. It effectively resists the passage of electric current, preventing shorts and signal interference.
### Stable Across Frequencies
Crucially, PTFE's excellent insulating properties remain stable across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies. This makes it ideal for high-frequency applications like coaxial cables and circuit boards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its resistance properties are elite, PTFE is not a high-strength structural material. Understanding its mechanical limitations is key to using it correctly.
### Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to engineering plastics, PTFE is a soft, flexible material with only average tensile strength. It is not suitable for high-load-bearing structural applications on its own.
### Susceptibility to Creep
Under a sustained load, PTFE can be subject to creep, or permanent deformation. This must be accounted for in the design of components like seals and gaskets.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is about leveraging its extreme properties where they matter most. Its weaknesses in mechanical strength are often offset by its unparalleled performance in other areas.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme environments: PTFE is the ideal choice for applications involving aggressive chemicals or a very wide temperature range.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction or non-stick surface: No material performs better for reducing friction in moving parts or creating a non-adherent coating.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: PTFE's stable dielectric properties make it a superior insulator for demanding electronics and communications hardware.
Ultimately, PTFE is a problem-solving material chosen for its ability to perform reliably where conventional materials cannot.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists almost all chemicals and solvents. | Ideal for seals and labware in corrosive environments. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Stable from -180°C to 260°C (-320°F to 500°F). | Reliable performance in extreme heat or cryogenic conditions. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | One of the slipperiest known solids. | Reduces wear and provides non-stick properties. |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength, stable across frequencies. | Perfect for high-performance electronics and cabling. |
| Non-Flammability | Will not support a flame. | Adds a critical layer of safety. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Leverage the unique properties of PTFE for your most demanding applications. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, thermal stability, and electrical insulation.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















