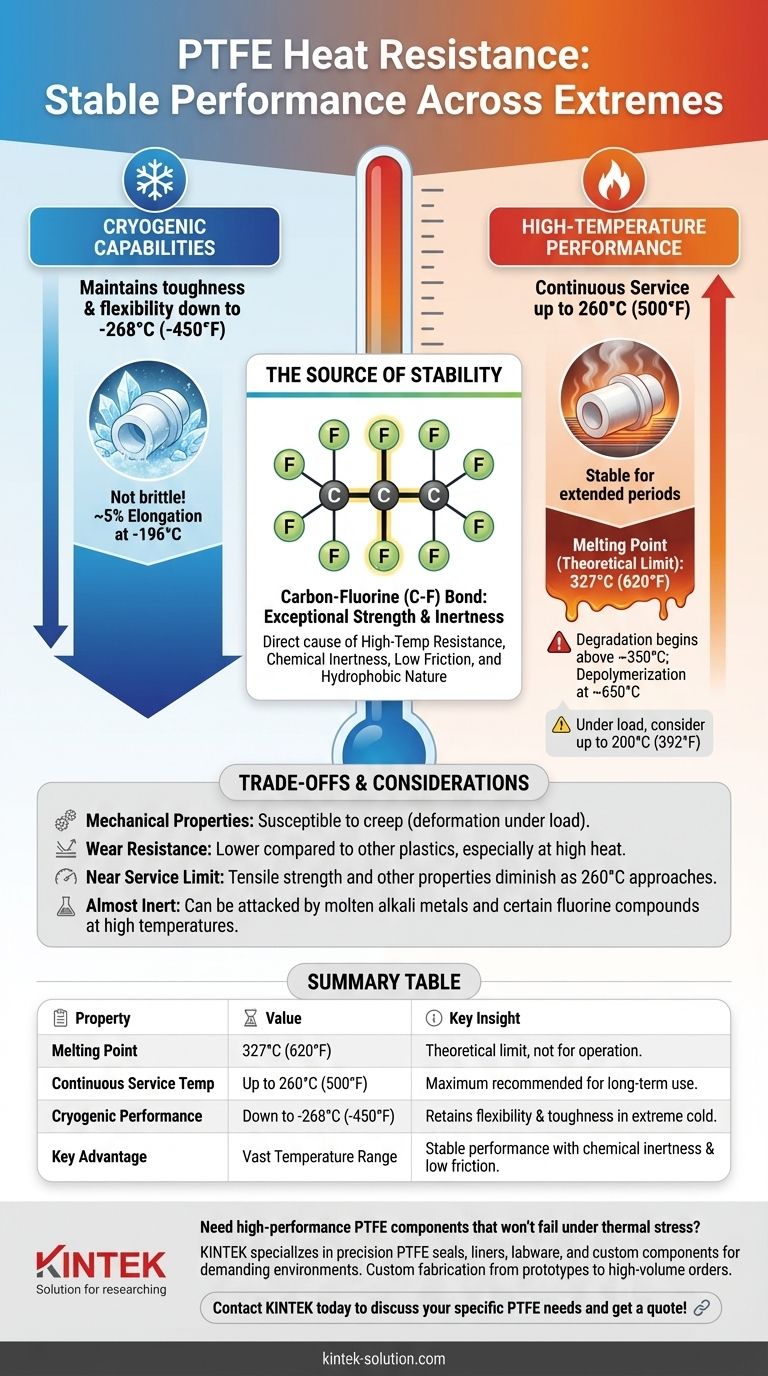
The key heat resistance property of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is its exceptionally wide and stable operating temperature range. It has a high melting point of approximately 327°C (620°F) and a continuous service temperature of up to 260°C (500°F). Crucially, it also retains its essential properties like toughness and flexibility at cryogenic temperatures as low as -268°C (-450°F).
PTFE's value is not just its resistance to high heat, but its ability to maintain its unique combination of chemical inertness, low friction, and mechanical toughness across an enormous spectrum of temperatures, from extreme heat to deep cold.

Deconstructing High-Temperature Performance
PTFE is renowned for its stability under thermal stress, a characteristic that sets it apart from most other polymers. Understanding its specific temperature limits is critical for proper application.
The Melting Point: A Theoretical Limit
The official melting point of PTFE is 327°C (620°F). This is the temperature at which the material transitions from a solid to a viscous liquid.
However, this is not a practical operating temperature. Well before reaching this point, the material begins to lose its structural integrity and mechanical properties.
The Continuous Service Temperature: The Practical Limit
The most important figure for engineering applications is the continuous service temperature, which for PTFE is 260°C (500°F).
This is the maximum temperature at which PTFE can operate for extended periods without significant degradation of its core properties. For optimal performance, especially under mechanical load, a slightly lower range up to 200°C (392°F) is often recommended.
Degradation and Depolymerization
Above its service limit, PTFE's properties will decline. While it is nonflammable, it is not recommended for use above 350°C.
At extremely high temperatures, around 650°C (1200°F), PTFE begins to depolymerize, breaking down its molecular structure.
Unpacking its Cryogenic Capabilities
PTFE's thermal stability extends to extreme cold, where many other materials become brittle and fail.
Performance at Extreme Cold
PTFE maintains its useful properties at temperatures as low as -196°C (-320°F) and in some cases down to -268°C (-450°F).
Retaining Mechanical Toughness
Unlike other plastics that shatter at low temperatures, PTFE retains a notable degree of flexibility and toughness.
For example, it can still demonstrate around 5% elongation at -196°C, proving it does not become completely brittle and can withstand mechanical stress in cryogenic environments.
The Source of PTFE's Stability
PTFE's remarkable thermal and chemical properties are not accidental; they are a direct result of its unique molecular structure.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The backbone of the PTFE molecule consists of carbon atoms completely shielded by a sheath of fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This exceptional bond strength makes the molecule highly stable and non-reactive, requiring a massive amount of energy to disrupt.
A Cascade of Benefits
This molecular stability is the root cause of PTFE's most famous traits. The C-F bond is directly responsible for its:
- High-temperature resistance
- Extreme chemical inertness (resisting nearly all acids, bases, and solvents)
- Hydrophobic (water-repelling) nature
- Incredibly low coefficient of friction
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its thermal and chemical properties are elite, PTFE is not the ideal choice for every situation. Its limitations must be considered.
Mechanical Properties Under Load
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to creep (deformation under sustained load) and has lower wear resistance compared to other engineering plastics, especially at elevated temperatures.
Performance Nears the Limit
As temperatures approach the 260°C service limit, its tensile strength, wear resistance, and other mechanical properties will diminish. Design calculations must account for this performance drop in high-heat applications.
Nothing is Truly Inert
While PTFE is virtually impervious to almost all chemicals, it can be attacked by a few rare substances, such as molten alkali metals and certain fluorine compounds at high temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on its unique profile.
- If your primary focus is continuous high-temperature operation: PTFE is a premier choice for applications requiring stability and inertness up to 260°C (500°F).
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: PTFE is one of the few polymers that retains mechanical toughness and avoids brittleness at temperatures approaching absolute zero.
- If your primary focus is combined thermal and chemical stress: PTFE is unparalleled in its ability to handle aggressive chemical environments across its entire vast operating temperature range.
Ultimately, PTFE provides unwavering reliability in thermal environments where most other materials would quickly fail.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 327°C (620°F) | Theoretical limit, not for operation. |
| Continuous Service Temp | Up to 260°C (500°F) | Maximum recommended temperature for long-term use. |
| Cryogenic Performance | Down to -268°C (-450°F) | Retains flexibility and toughness in extreme cold. |
| Key Advantage | Stable performance across a vast temperature range while maintaining chemical inertness and a low friction coefficient. |
Need high-performance PTFE components that won't fail under thermal stress?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. Our expertise ensures your parts deliver reliable performance in the most demanding environments, from semiconductor processing to medical and laboratory applications.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing the material integrity and precise specifications your project requires.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific PTFE needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















