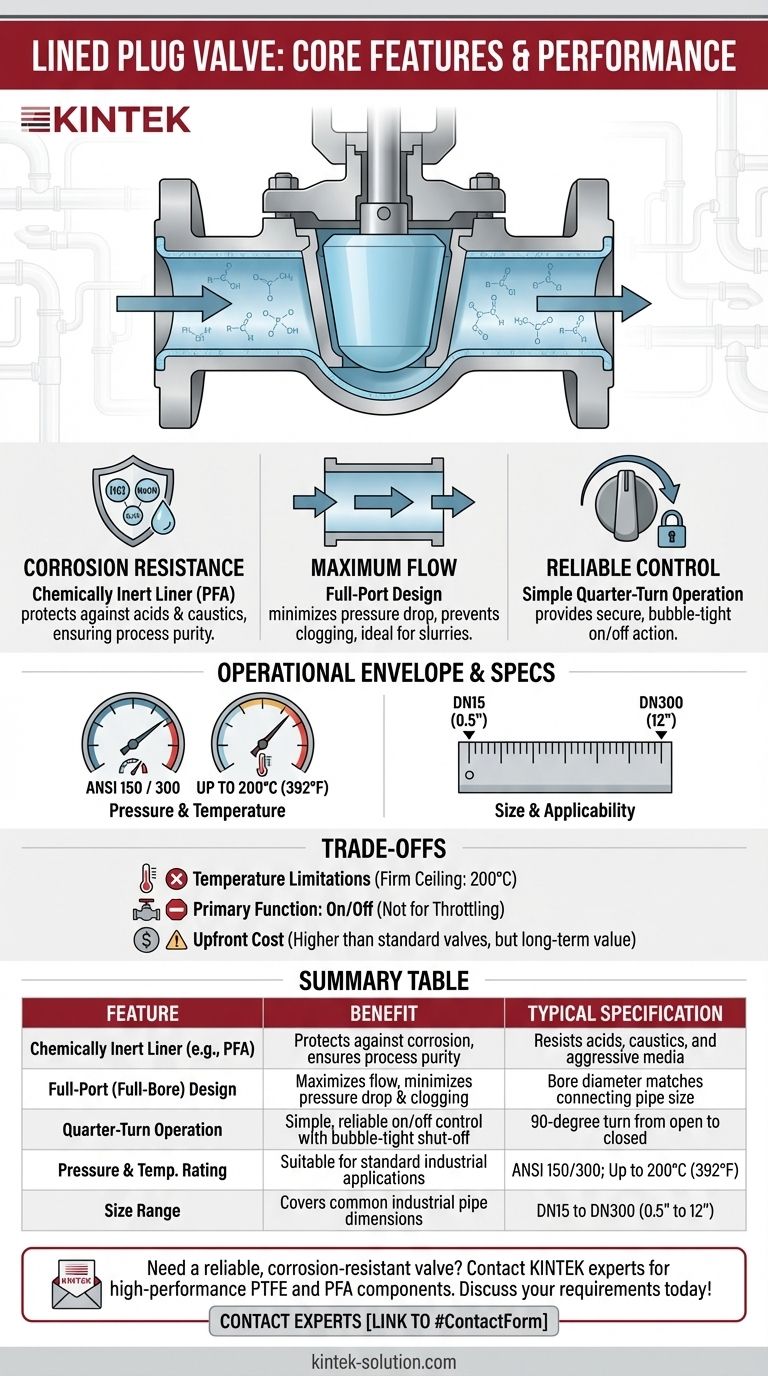
At its core, a Lined Plug Valve combines three critical features. It uses a chemically inert liner to protect against corrosion, a full-port design to ensure maximum, unrestricted flow, and a simple quarter-turn mechanism for reliable on-off control. These elements make it a robust solution for handling aggressive and hazardous fluids where standard valves would quickly fail.
The central purpose of a Lined Plug Valve is not just to control flow, but to provide a secure, corrosion-proof barrier within a piping system. Its value lies in ensuring process purity and operational safety when handling highly reactive or corrosive media.

The Anatomy of Performance
Understanding how a Lined Plug Valve is constructed reveals why it is specified for demanding applications. Each component serves a distinct purpose centered on reliability and chemical resistance.
The Critical Role of the Liner
The defining feature is the thick, non-reactive liner, typically made from materials like PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy). This liner is molded to cover all wetted surfaces of the valve's metallic body and plug.
This design completely isolates the process fluid from the structural metal parts. The result is exceptional corrosion resistance against acids, caustics, and other aggressive chemicals, preventing both valve degradation and fluid contamination.
The Full-Port Design Advantage
A full-port (or full-bore) design means the valve's internal diameter matches the connecting pipe's diameter.
This creates a straight, unobstructed flow path when the valve is open. This minimizes turbulence and pressure drop, making it highly efficient and ideal for handling viscous liquids or slurries that could clog a reduced-port valve.
Simple and Robust Quarter-Turn Operation
Lined Plug Valves operate with a simple 90-degree turn to move from fully open to fully closed. The plug rotates within the lined body, and the liner itself often acts as the primary sealing surface.
This mechanism is mechanically simple, which enhances reliability and service life. It also allows for quick and clear on-off action, leaving no ambiguity about the valve's position.
Defining the Operational Envelope
A valve's specifications define its suitability for a given industrial process. The pressure, temperature, and size ratings dictate the boundaries for safe and effective operation.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
These valves are commonly available in ANSI 150 and ANSI 300 pressure classes, making them suitable for a wide range of standard industrial piping systems.
The temperature rating, often up to 200°C (392°F), is typically limited by the specific liner material. The PFA liner's thermal stability is what allows for reliable performance at elevated temperatures that would degrade other polymers.
Size and Applicability
The typical size range from DN15 to DN300 (approximately 0.5" to 12") covers the most common pipe dimensions found in chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and water treatment plants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, Lined Plug Valves are a specialized solution. Acknowledging their limitations is key to proper application.
Temperature Limitations
While a 200°C rating is high for a lined valve, it is a firm ceiling set by the polymer liner. For applications requiring significantly higher temperatures, an all-metal or ceramic-lined valve might be necessary.
Primary Function is On/Off Control
The plug valve design excels at providing a tight, bubble-free seal in the fully closed position. It is not designed for throttling or precise flow modulation, as sustained partial-open positions can lead to uneven wear on the plug and liner.
Upfront Cost
The specialized materials and manufacturing process required to apply a void-free liner make these valves more expensive upfront than standard, unlined metal valves. However, this cost is often justified by a vastly extended service life and reduced maintenance in corrosive environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting a Lined Plug Valve should be a decision driven by the specific demands of your process fluid and operational goals.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: The chemically inert PFA liner provides unparalleled protection for the valve's metal body, ensuring process purity and long-term asset integrity.
- If your primary focus is maximum flow efficiency: The full-port design ensures minimal pressure drop, making it ideal for high-volume processes or challenging media like slurries.
- If your primary focus is reliable, bubble-tight shut-off: The simple quarter-turn mechanism combined with the liner's sealing properties offers a secure and dependable seal for critical isolation needs.
By understanding these core features, you can confidently specify a Lined Plug Valve for your most demanding fluid handling challenges.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Typical Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Chemically Inert Liner (e.g., PFA) | Protects against corrosion, ensures process purity | Resists acids, caustics, and aggressive media |
| Full-Port (Full-Bore) Design | Maximizes flow, minimizes pressure drop and clogging | Bore diameter matches connecting pipe size |
| Quarter-Turn Operation | Simple, reliable on/off control with bubble-tight shut-off | 90-degree turn from open to closed |
| Pressure & Temperature Rating | Suitable for standard industrial applications | ANSI 150/300; Up to 200°C (392°F) |
| Size Range | Covers common industrial pipe dimensions | DN15 to DN300 (0.5" to 12") |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant valve for your critical process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE and PFA components, including seals, liners, and custom labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a solution perfectly tailored to handle your aggressive fluids safely and efficiently.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our lined valve solutions can enhance your system's integrity and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What technical services are provided for PTFE product development? A Guide from Concept to Component
- What are the key considerations for PTFE lined butterfly valve installation? Protect Your Liner for a Leak-Proof Seal
- Why are PTFE reducing flanges considered cost-effective? Maximize Uptime and Minimize Costs
- What are the installation methods for PTFE slide bearings? Bolting, Welding & Mortar Embedment
- What materials are used in the manufacturing of PTFE ball valves? Optimize for Chemical Resistance & Performance
- What are PTFE lined valves and what is their primary purpose? Achieve Superior Corrosion Resistance
- How is PTFE used in ball valves and Y strainers? Essential for Leak-Proof Seals & Chemical Resistance
- Why is virgin PTFE particularly suitable for food and medical applications? Ensuring Purity and Safety



















