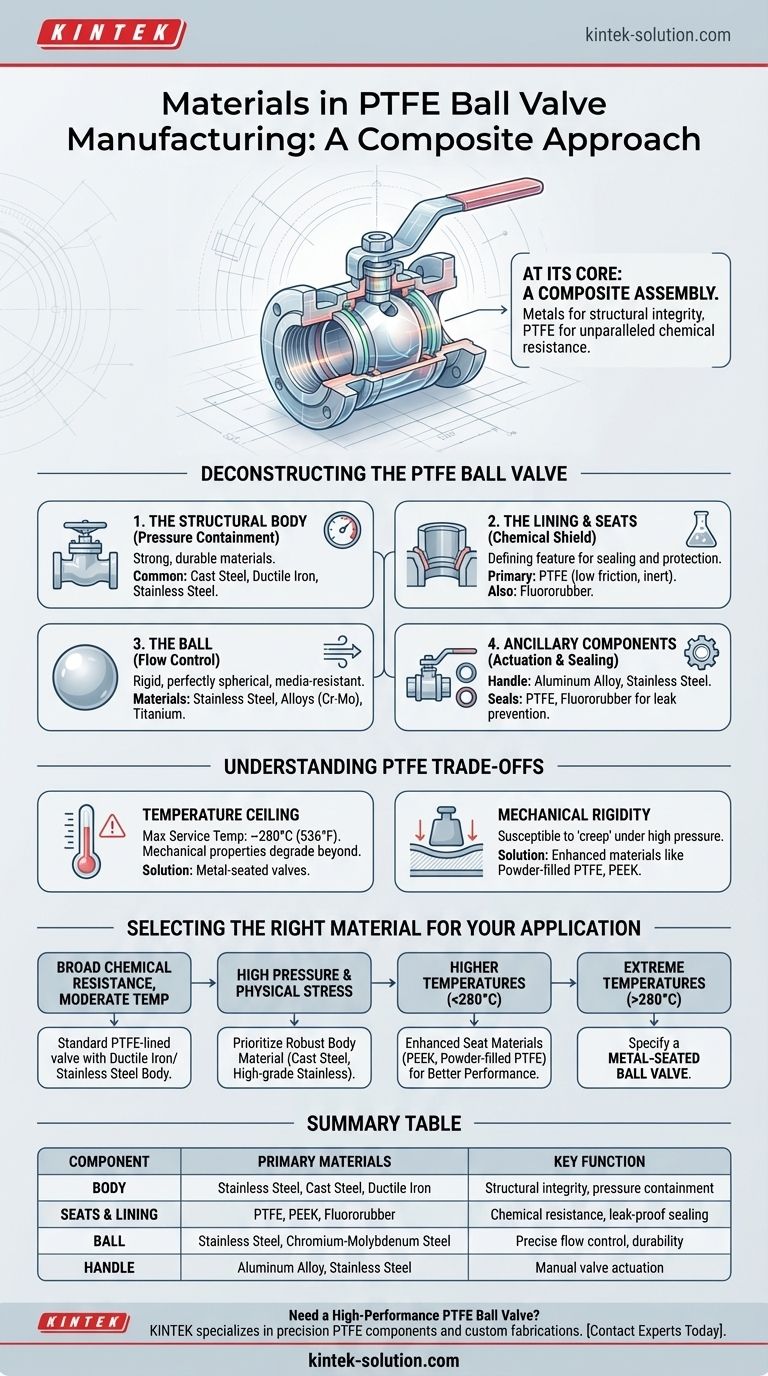
At its core, a PTFE ball valve is a composite assembly, not a component made from a single material. It strategically combines robust metals for structural integrity with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for its unparalleled chemical resistance. The primary materials include a metal body (such as stainless steel or ductile iron), a metal ball, and PTFE for the critical seats and lining that come into contact with the fluid.
The central design principle of a PTFE ball valve is to leverage metal for strength against pressure and external forces, while using PTFE exclusively for the "wetted parts" to create a chemically inert and low-friction barrier against the process media.
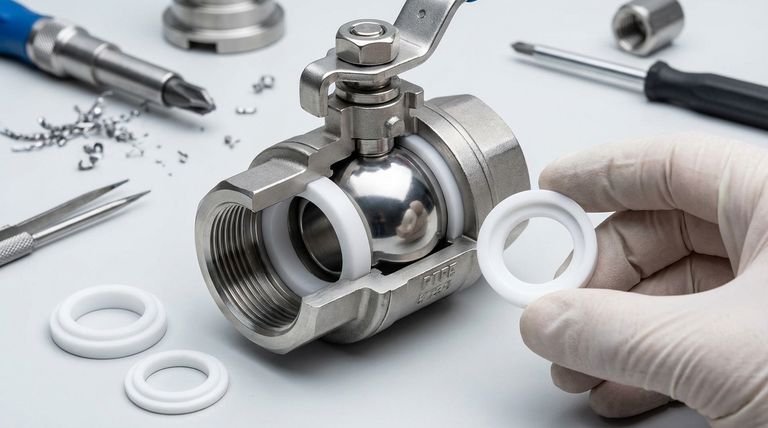

Deconstructing the PTFE Ball Valve: A Component-by-Component Guide
To truly understand the valve, you must look at how different materials are assigned to specific roles based on their unique properties.
The Structural Body: Containing the Pressure
The valve body is the primary pressure-containing structure. It must be strong and durable.
Common materials for the body include cast steel, ductile iron, and stainless steel. The choice depends on the required pressure rating, external environmental corrosion, and cost.
The Lining and Seats: The Chemical Shield
This is the defining feature of a PTFE valve. The seats create the seal around the ball, and a lining may coat the entire interior of the valve body.
PTFE is the default material here due to its near-universal chemical inertness and extremely low coefficient of friction, which allows for low-torque, easy operation. Other fluoroplastics like fluororubber may also be used for seals.
The Ball: The Flow Control Element
The ball is the component that rotates to open or close the flow path. It must be rigid, perfectly spherical, and resistant to the media.
Materials include stainless steel, high-strength alloys like chromium-molybdenum steel, and even titanium alloy for exceptionally aggressive chemical applications. The ball seals against the soft PTFE seats.
The Ancillary Components: Handle and Seals
The handle, used to actuate the valve, is typically made from cast aluminum alloy or stainless steel for durability and corrosion resistance.
Additional seals, such as stem packing, often use PTFE or fluororubber to prevent leaks to the outside environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PTFE
While PTFE is an exceptional material, it is not without its limitations. Understanding these is critical for proper valve selection.
The Temperature Ceiling
Standard PTFE has a maximum service temperature. Beyond approximately 280°C (536°F), its mechanical properties degrade significantly.
For applications exceeding this temperature, a metal-seated ball valve is required, where both the ball and the seat are made of metal.
Mechanical Rigidity
Pure PTFE can be relatively soft and may deform under high pressure or stress, a phenomenon known as "creep."
To counteract this, manufacturers use enhanced materials like powder-filled PTFE, special Nylons, or Polyether-etherketone (PEEK). These offer greater rigidity and can increase the maximum service temperature slightly, bridging the gap between standard PTFE and metal seats.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your choice of valve depends entirely on the demands of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical resistance at moderate temperatures: A standard PTFE-lined valve with a ductile iron or stainless steel body is the ideal and most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is handling high pressure and physical stress: Prioritize a valve with a robust body material like cast steel or a higher-grade stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is operating at higher temperatures (below 280°C): Consider valves using enhanced seat materials like PEEK or powder-filled PTFE for better performance and durability.
- If your primary focus is operating in extreme temperatures (above 280°C): You must specify a metal-seated ball valve, as PTFE is no longer a suitable material for the seats.
By understanding how these materials work together, you can confidently select a valve optimized for both chemical compatibility and mechanical performance.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Materials | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Body | Stainless Steel, Cast Steel, Ductile Iron | Structural integrity, pressure containment |
| Seats & Lining | PTFE, PEEK, Fluororubber | Chemical resistance, leak-proof sealing |
| Ball | Stainless Steel, Chromium-Molybdenum Steel | Precise flow control, durability |
| Handle | Aluminum Alloy, Stainless Steel | Manual valve actuation |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Ball Valve?
Selecting the right materials is critical for your valve's performance, longevity, and safety. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom fabrications for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We help you navigate material trade-offs to deliver a solution perfectly matched to your application's chemical, temperature, and pressure requirements—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Let's engineer your solution together. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for PTFE balls? A Guide to Virgin PTFE vs. Filled Composites
- What makes PTFE balls ideal for chemical applications? Unmatched Inertness for Demanding Environments
- What size range do PTFE balls come in? A Guide from 3mm to 100mm
- What are the tolerances for PTFE balls based on size? Precision vs. Standard Grade Explained
- What are the key features of Teflon balls? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Environments



















