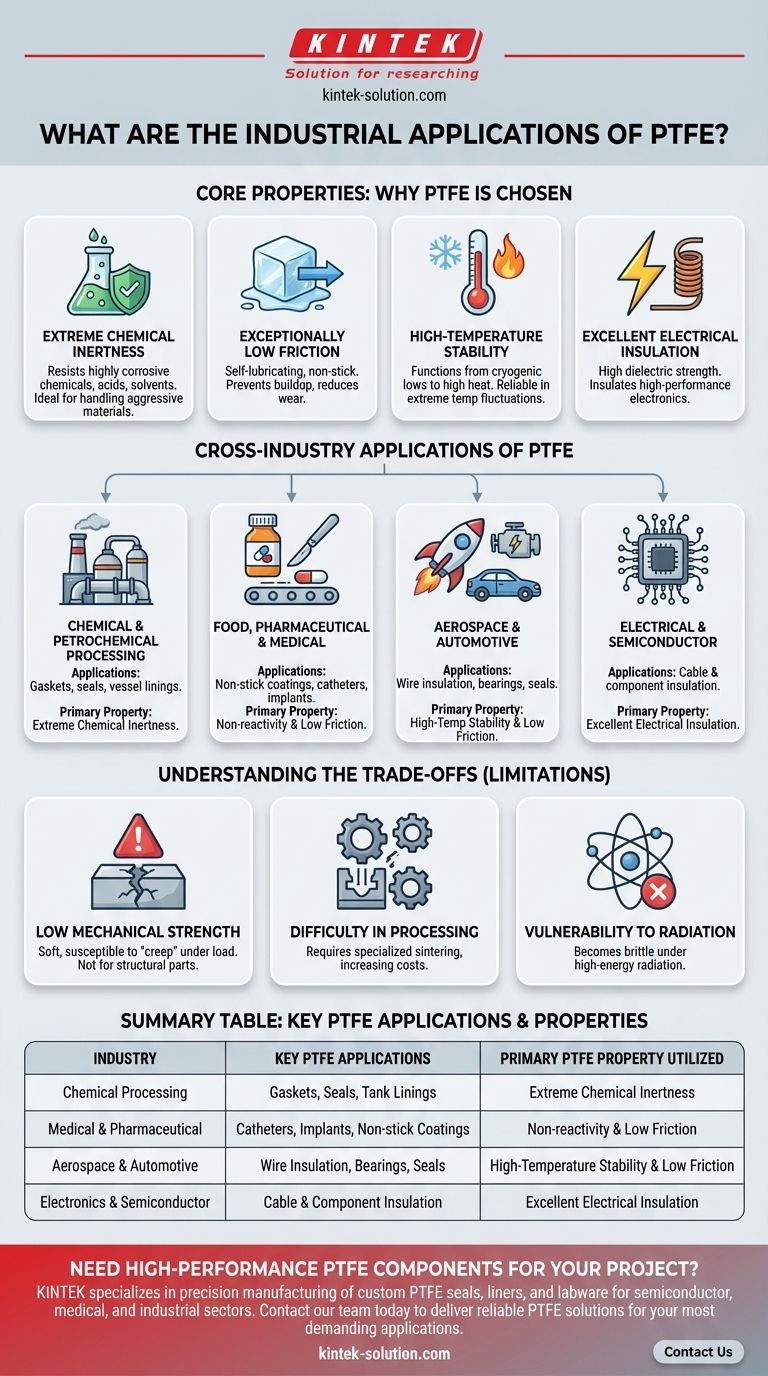
PTFE is one of the most versatile and critical polymers in modern industry, with applications spanning nearly every major sector, including chemical processing, aerospace, medical, and electronics. Its widespread use is due to a unique combination of properties that allow it to perform in extreme environments where other materials would quickly fail.
The immense industrial value of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) stems directly from a trio of core properties: near-total chemical inertness, an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, and high-temperature stability. Understanding these three characteristics is the key to understanding its application in virtually any field.

Why PTFE Is the Material of Choice: The Core Properties
Before listing applications, it's essential to understand why this material is so frequently specified by engineers. Its utility is not based on a single feature but on the powerful combination of several.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. It resists degradation from highly corrosive chemicals, acids, solvents, and oxidizing agents.
This property makes it indispensable for handling and storing aggressive materials without risk of corrosion or contamination.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, a quality often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This makes it naturally "non-stick" and self-lubricating.
This lubricity is crucial for applications that require smooth movement, reduced wear, and prevention of material buildup.
High-Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its properties across a very wide temperature range, from cryogenic lows to high-heat environments.
This allows it to function reliably in applications like jet engines, high-temperature industrial processes, and aerospace systems where temperature fluctuations are extreme.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand a strong electric field without breaking down.
This makes it a first-choice material for insulating high-performance wiring and sensitive electronic components.
A Cross-Industry Breakdown of PTFE Applications
With an understanding of its properties, the specific industrial uses of PTFE become clear and logical.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
This sector relies on PTFE's chemical resistance. It is used for gaskets, seals, and linings for vessels, tanks, pipes, and valves. This prevents corrosion and ensures the purity of the processed chemicals.
Food, Pharmaceutical, and Medical
In these fields, non-reactivity and non-stick properties are critical. PTFE is used for non-stick coatings on food processing equipment, conveyor belt rollers, and medical devices like catheters, surgical instruments, and implants.
Aerospace and Automotive
High-temperature stability and low friction are key. PTFE is used for wire and cable insulation, low-friction bearings, seals, and gaskets in engines and other critical systems that must perform under stress.
Electrical and Semiconductor Manufacturing
The material's excellent insulating properties are paramount here. It is used extensively as a high-performance insulator for wiring, cables, and electronic components, especially in high-frequency applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. Acknowledging PTFE's limitations is crucial for proper engineering and application.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to "creep," meaning it can deform over time when under a sustained load. It is not suitable as a primary structural component.
Difficulty in Processing
Unlike many thermoplastics, PTFE cannot be easily melt-processed or injection-molded. It requires specialized manufacturing techniques like sintering, which can increase production costs.
Vulnerability to Radiation
High-energy radiation can break down the polymer chains in PTFE, causing it to become brittle and lose its mechanical properties. This makes it unsuitable for certain nuclear or high-radiation environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application will determine if PTFE is the optimal material.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: PTFE is an unparalleled choice for lining vessels, pipes, and valves that handle aggressive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: Its self-lubricating and non-stick properties make it ideal for low-wear bearings, seals, and industrial coatings.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature electrical insulation: Its thermal stability and dielectric strength are critical for aerospace, defense, and high-performance electronics.
Ultimately, PTFE's value lies in its unique ability to provide reliable performance in extreme chemical, thermal, and electrical environments.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key PTFE Applications | Primary PTFE Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Gaskets, Seals, Tank Linings | Extreme Chemical Inertness |
| Medical & Pharmaceutical | Catheters, Implants, Non-stick Coatings | Non-reactivity & Low Friction |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Wire Insulation, Bearings, Seals | High-Temperature Stability & Low Friction |
| Electronics & Semiconductor | Cable & Component Insulation | Excellent Electrical Insulation |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Project?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards for chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can deliver reliable PTFE solutions for your most demanding applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of Teflon coatings and their features? Choose the Right Fluoropolymer for Your Application
- Why is PTFE resistant to corrosion? Discover the Secret to Unmatched Chemical Inertness
- What are the temperature resistance properties of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cold Performance
- What are the four basic types of Teflon and their key differences? Select the Right Fluoropolymer for Your Application
- What is the melting point of PTFE? Master Its Thermal Limits for Better Performance
- What are some alternative names for PTFE? Unlocking the Versatility of Teflon and TFE
- What are some unique applications of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick Pans to Medical & Aerospace
- What are the benefits of PTFE's chemical resistance? Achieve Unmatched Reliability in Corrosive Environments



















