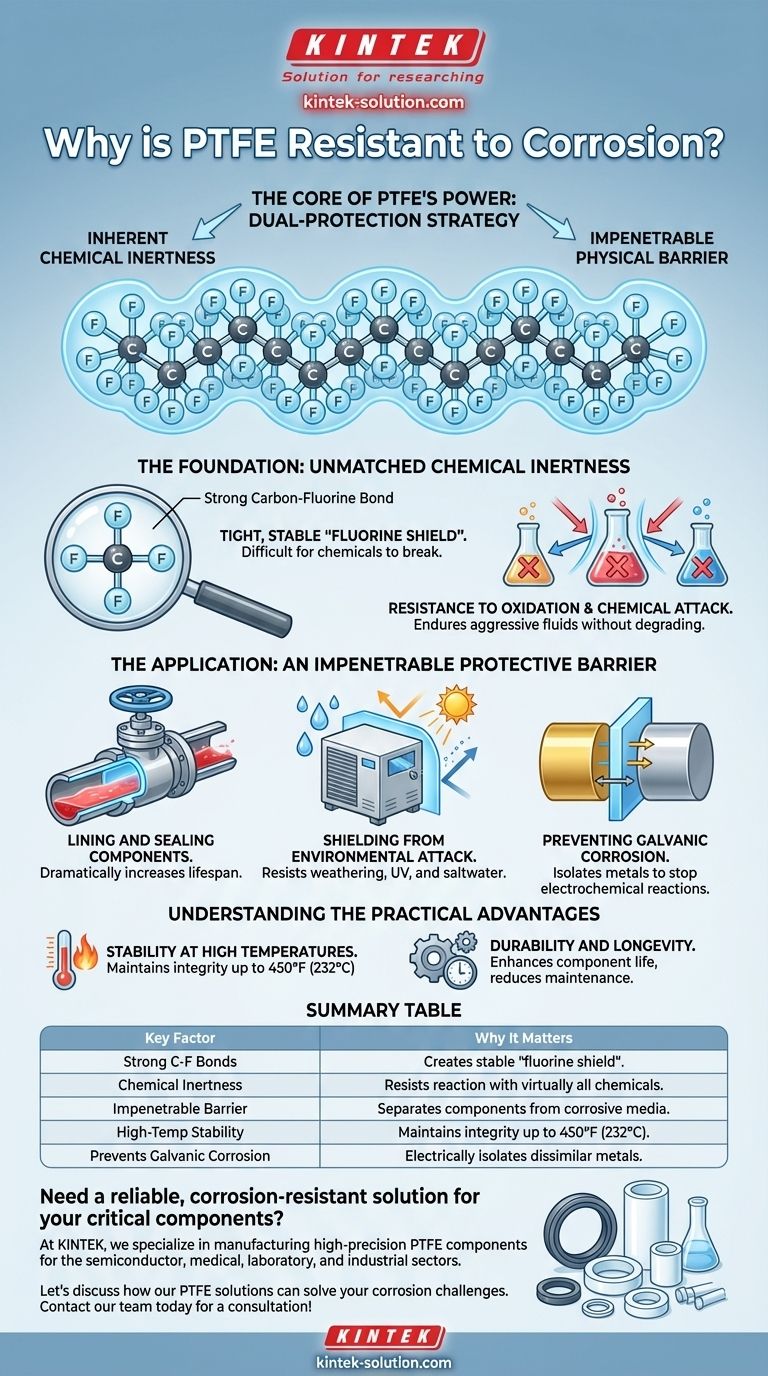
The fundamental reason PTFE is so resistant to corrosion is its unique molecular structure. The exceptionally strong chemical bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms create a molecule that is almost completely inert, refusing to react with even the most aggressive chemicals and environmental factors.
The core of PTFE's power lies in a dual-protection strategy: its inherent chemical inertness makes it virtually unreactive, while its application as a coating or liner creates an impenetrable physical barrier between a corrosive substance and the material you need to protect.

The Foundation: Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not just resistant; for most practical purposes, it is chemically inert. This stability is not an accident but a direct result of its molecular architecture.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between carbon and fluorine atoms is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry. In a PTFE molecule, a long chain of carbon atoms is completely encased by a sheath of fluorine atoms.
This tight, stable "fluorine shield" makes it extremely difficult for other chemicals to break in and react with the carbon backbone.
Resistance to Oxidation and Chemical Attack
This robust structure renders PTFE impervious to oxidation and attack from the vast majority of chemicals.
Unlike metals that rust or plastics that degrade, PTFE can endure continuous exposure to strong acids, alkaline conditions, and corrosive fluids without losing its integrity or plasticity.
The Application: An Impenetrable Protective Barrier
Beyond its inherent properties, the way PTFE is used is central to its role in corrosion prevention. It physically separates vulnerable components from harmful environments.
Lining and Sealing Components
In applications like PTFE-lined butterfly valves or gaskets, the material creates a non-reactive barrier.
The corrosive fluid in a pipe never actually touches the metal valve body; it only contacts the inert PTFE liner, dramatically increasing the operational lifespan of the equipment.
Shielding from Environmental Attack
PTFE's resistance extends beyond industrial chemicals. As a coating, it provides an excellent barrier against environmental factors that cause degradation over time.
It is highly resistant to weathering, UV light, and saltwater, making it essential for protecting outdoor equipment and components in marine environments.
Preventing Galvanic Corrosion
A critical but often overlooked function of PTFE is preventing galvanic corrosion. This occurs when two different metals are in electrical contact in the presence of an electrolyte, causing one to corrode rapidly.
By using a PTFE coating to isolate the metals from each other, this destructive electrochemical reaction is stopped before it can begin.
Understanding the Practical Advantages
The chemical and physical properties of PTFE translate directly into significant real-world benefits, especially in demanding industries like oil and gas or chemical processing.
Stability at High Temperatures
Corrosive processes are often accelerated by heat. PTFE maintains its integrity and protective qualities at continuous service temperatures up to 450°F (232°C).
This thermal stability ensures it remains a reliable barrier even when conditions are hostile in more ways than one.
Durability and Longevity
Because PTFE does not degrade, corrode, or lose its plasticity, it significantly enhances the durability of any component it protects.
This leads to longer service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and more reliable operations in critical systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage PTFE's properties effectively, align your application choice with your primary corrosion challenge.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: Use PTFE as a liner for pipes and valves or as a gasket material for creating chemically inert seals.
- If your primary focus is protecting against environmental exposure: Apply PTFE as a coating to shield components from saltwater, UV radiation, and weathering.
- If your primary focus is preventing galvanic corrosion: Use PTFE coatings or barriers to physically and electrically isolate dissimilar metals from each other.
Ultimately, PTFE provides a complete and lasting solution to corrosion by being fundamentally unreactive to the world around it.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Strong C-F Bonds | Creates a stable "fluorine shield" that is difficult for other chemicals to break. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists reaction with virtually all acids, bases, and solvents. |
| Impenetrable Barrier | As a liner or coating, it physically separates components from corrosive media. |
| High-Temp Stability | Maintains integrity and protection at continuous temperatures up to 450°F (232°C). |
| Prevents Galvanic Corrosion | Electrically isolates dissimilar metals to stop destructive electrochemical reactions. |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant solution for your critical components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your equipment is protected from the most aggressive chemicals and harsh environments, enhancing durability and operational reliability.
Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, we deliver custom fabrication tailored to your exact needs. Let's discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your corrosion challenges. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















