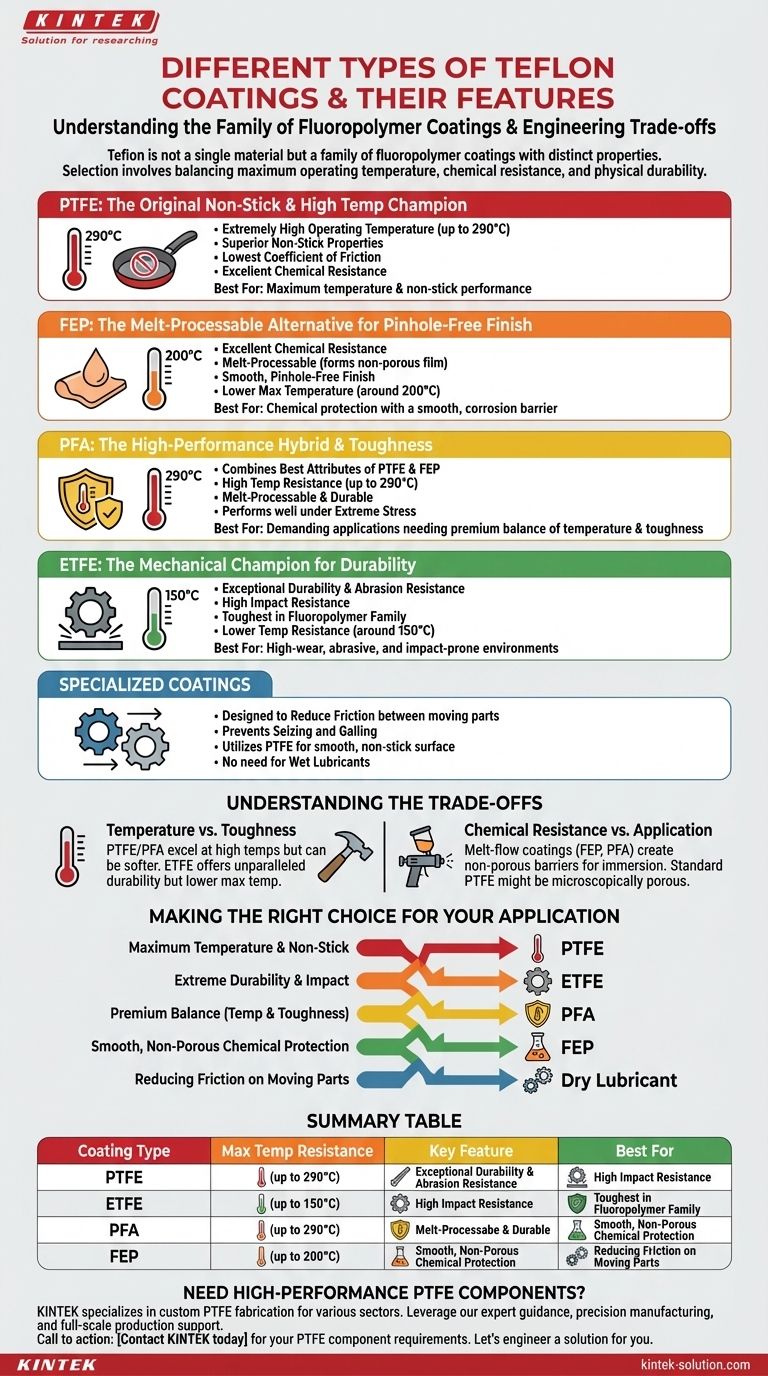
At its core, Teflon is not a single material but a family of fluoropolymer coatings, each engineered with a distinct set of properties. The most common types are PTFE, FEP, PFA, and ETFE, which primarily differ in their temperature resistance, chemical durability, and mechanical toughness. Specialized versions like dry lubricant coatings are also available for specific mechanical applications.
The critical insight is that selecting a Teflon coating is not about finding the "best" one, but about understanding the engineering trade-offs. Your choice hinges on balancing three key factors: the maximum operating temperature, the required chemical resistance, and the need for physical durability.

The Core Fluoropolymer Coatings: A Comparative Look
To make an informed decision, you must understand the fundamental differences between the main types of Teflon. Each was developed to solve a specific set of industrial challenges.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): The Original Non-Stick
PTFE is the original and most widely recognized Teflon coating. It is known for having one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid.
Its primary features are an extremely high operating temperature (up to 290°C) and superior non-stick properties. It is also highly stable and resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals.
FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene): The Melt-Processable Alternative
FEP offers excellent chemical resistance similar to PTFE but has a lower maximum operating temperature of around 200°C.
Unlike PTFE, FEP is melt-processable, which allows it to flow during baking to form a non-porous film. This makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring a very smooth, pinhole-free finish and excellent corrosion protection.
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy): The High-Performance Hybrid
PFA effectively combines the best attributes of both PTFE and FEP. It offers the high-temperature resistance of PTFE while also being melt-processable like FEP.
This makes PFA an exceptionally tough and durable coating that performs well under extreme thermal and mechanical stress, though it is often a more premium option.
ETFE (Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene): The Mechanical Champion
ETFE is the toughest coating in the fluoropolymer family. Marketed under brand names like Tefzel, its defining feature is exceptional durability and impact resistance.
While its temperature resistance is lower (around 150°C), its mechanical strength makes it ideal for abrasive or high-wear environments where other coatings might fail.
Specialized and Application-Specific Coatings
Beyond the primary types, certain formulations are optimized for a single, critical function.
Dry Lubricant Coatings
These coatings are specifically designed to reduce friction between moving parts.
They utilize PTFE as a key ingredient, creating a smooth, non-stick surface that prevents seizing and galling in mechanical components without the need for wet lubricants like oil or grease.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "do-it-all" Teflon coating. Choosing the correct one requires acknowledging the inherent compromises between different properties.
Temperature vs. Toughness
A common trade-off exists between high-temperature resistance and mechanical toughness. PTFE and PFA excel at high temperatures but can be softer materials.
Conversely, ETFE offers unparalleled physical durability and abrasion resistance but has a significantly lower maximum service temperature.
Chemical Resistance vs. Application Method
All major fluoropolymers offer excellent chemical resistance. However, the application process can affect the final film's integrity.
Melt-flow coatings like FEP and PFA create a non-porous barrier ideal for total chemical immersion, whereas standard PTFE coatings might be microscopically porous unless applied in multiple layers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the single most critical performance demand of your project.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and non-stick performance: PTFE is the industry standard and most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and impact resistance: ETFE provides the best mechanical toughness in the Teflon family.
- If you need a premium balance of high temperature and toughness: PFA offers a hybrid solution for the most demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is a smooth, non-porous film for chemical protection: FEP's melt-flow properties provide an excellent corrosion barrier at moderate temperatures.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction on moving mechanical parts: A specialized dry lubricant coating is engineered specifically for this purpose.
Ultimately, aligning the unique strengths of each coating with your specific operational needs is the key to a successful application.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Max Temp Resistance | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | Up to 290°C | Superior non-stick, excellent chemical resistance | Maximum temperature & non-stick performance |
| FEP | Up to 200°C | Melt-processable for a smooth, non-porous film | Chemical protection with a pinhole-free finish |
| PFA | Up to 290°C | Combines high temp resistance with toughness | Demanding applications needing a premium balance |
| ETFE | Up to 150°C | Exceptional durability and abrasion resistance | High-wear, abrasive environments |
| Dry Lubricant | Varies | Lowers friction between moving parts | Reducing seizing and galling in mechanical components |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Selecting the right fluoropolymer is just the first step. You need a manufacturing partner who understands the critical balance of material properties and precision production.
KINTEK specializes in custom PTFE fabrication for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We deliver the superior chemical resistance, non-stick performance, and durability your application demands.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Leverage our deep material science knowledge to select the optimal coating or material for your specific needs.
- Precision Manufacturing: From complex seals and liners to custom labware, we ensure every component meets exact specifications.
- Full-Scale Production: We support your project from initial prototypes to high-volume orders with consistent quality.
Let's engineer a solution for you. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE component requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















