At its core, Teflon is used wherever a combination of low friction, chemical inertness, and heat resistance is required. While most famous for creating non-stick surfaces on cookware, its applications extend into critical industrial, medical, and aerospace engineering. Teflon's unique properties make it a go-to material for lining pipes, insulating wires, and coating medical devices.
The true value of Teflon (PTFE) isn't just one of its famous traits, but its rare combination of them. It is simultaneously one of the most slippery, chemically resistant, and heat-tolerant materials available, making it a versatile problem-solver across dozens of industries.

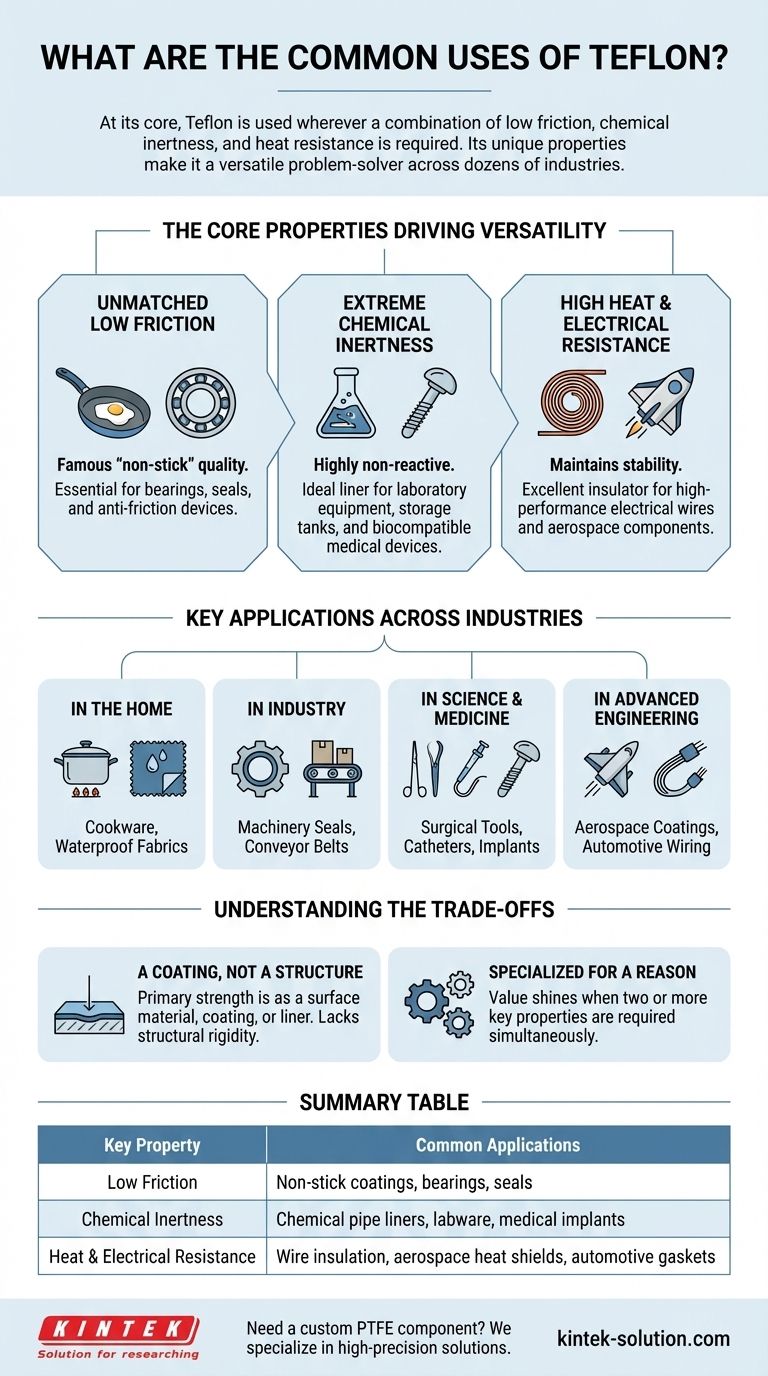
The Core Properties Driving Teflon's Versatility
To understand where Teflon is used, you must first understand why. Its applications are a direct result of three primary characteristics.
Unmatched Low Friction
Teflon, or Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. This is the source of its famous "non-stick" quality.
This property makes it essential for applications where parts must slide against each other with minimal resistance, such as in bearings, seals, and other anti-friction devices.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
Teflon is highly non-reactive and can withstand a vast range of corrosive chemicals. This makes it an ideal material for handling aggressive substances.
You will find it used as a chemically inert liner for laboratory equipment, storage tanks, and industrial pipes. This same inertness makes it biocompatible and safe for use inside the human body.
High Heat and Electrical Resistance
Teflon maintains its stability across a wide range of temperatures and does not conduct electricity, making it an excellent insulator.
This is why it's widely used for insulating high-performance electrical wires and cables, particularly in the automotive and aerospace industries where reliability is critical. Its heat resistance is also vital for aerospace components like heat shields.
Key Applications Across Industries
These core properties unlock a diverse set of uses, from everyday household items to mission-critical components in advanced technology.
In the Home: Beyond the Frying Pan
The most recognizable application is non-stick cookware, including pans and baking sheets. However, its hydrophobic (water-repelling) nature also makes it a key component in producing waterproof, breathable fabrics for outerwear.
In Industry: Machinery and Manufacturing
In industrial settings, Teflon is used to create durable seals, gaskets, and bushings for machinery. Its low-friction surface is also used on components like conveyor belts to ensure smooth operation.
In Science and Medicine: The Biocompatible Choice
Because the human body does not react to it, Teflon is used extensively in medicine. It coats surgical tools and is used to make medical products like catheters, tubes, and even artificial body parts like heart valves or dentures.
In Advanced Engineering: Aerospace and Automotive
The aerospace and automotive industries rely on Teflon for its resilience. It's used in coatings for spacecraft, gaskets for engines, and insulation for critical wiring. It also serves as a liner for fuel tanks and pipes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, Teflon is not a universal solution. Its value is highly specific to its unique combination of properties.
A Coating, Not a Structure
Teflon's primary strength is as a surface material. It is relatively soft and lacks the structural rigidity of metals or other polymers. Therefore, it is almost always used as a coating, liner, or specialized component rather than a primary structural element.
Specialized for a Reason
For applications where only one of its properties is needed, a more cost-effective material might exist. For example, if you only need heat resistance without chemical inertness or low friction, other materials could suffice. Teflon's value shines when two or more of its key properties are required simultaneously.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting Teflon is about matching your primary engineering challenge to one of its core strengths.
- If your primary focus is minimizing friction and wear: Teflon is the ideal choice for non-stick coatings, self-lubricating bearings, and high-performance seals.
- If your primary focus is resisting harsh chemicals or biological interaction: It is the go-to material for lining chemical reactors, creating medical implants, and coating surgical instruments.
- If your primary focus is insulating from heat or electricity: Teflon provides superior performance for high-frequency cables, automotive wiring harnesses, and protective aerospace components.
Ultimately, Teflon's vast range of uses stems directly from its unique and powerful molecular stability.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Common Applications |
|---|---|
| Low Friction | Non-stick coatings, bearings, seals, conveyor belts |
| Chemical Inertness | Chemical pipe liners, labware, medical implants, storage tanks |
| Heat & Electrical Resistance | Wire insulation, aerospace heat shields, automotive gaskets |
Need a custom PTFE component for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise ensures a solution that leverages Teflon's unique properties for your specific challenges.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What makes PTFE versatile for various industrial uses? Discover the Key Properties Driving Its Success
- What is PTFE and what makes it versatile? The Ultimate High-Performance Polymer
- Which industries commonly use PTFE materials? A Guide to High-Performance Polymer Applications
- What are the primary properties of Teflon that make it a 'powerhouse plastic'? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What are the operational temperature and hardness ranges of PTFE? Master its Limits for Your Design
- What are some notable properties of PTFE? Discover the Extreme Performance of Teflon



















