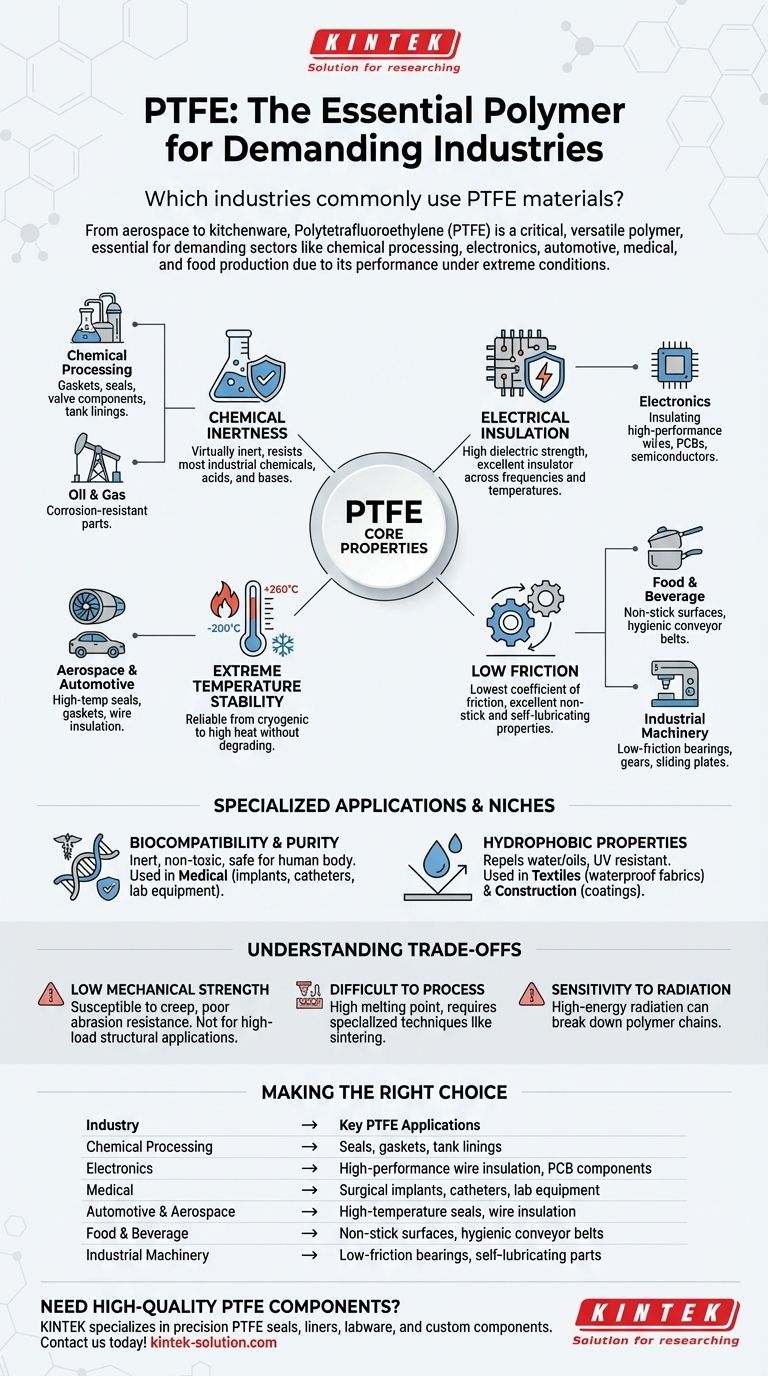
From aerospace to kitchenware, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the most versatile and widely used polymers in modern engineering. Its unique properties make it a critical material in demanding sectors such as chemical processing, electronics, automotive, medical, and food production, where performance under extreme conditions is non-negotiable.
PTFE’s value comes from its rare combination of near-total chemical inertness, extreme temperature stability, excellent electrical insulation, and an incredibly low coefficient of friction. This unique profile makes it a default problem-solver for a vast range of industrial challenges.

Why PTFE Is Critical in Demanding Industries
The widespread adoption of PTFE is not accidental. It solves specific, critical problems that other materials cannot. Its utility is best understood by examining its core properties and how they map directly to industrial needs.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert, meaning it does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, and bases. This makes it an invaluable material for handling corrosive substances.
This property is fundamental to its use in the chemical processing and oil & gas industries for applications like gaskets, seals, valve components, and tank linings.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE has an exceptionally high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, making it one of the best electrical insulators known. It maintains these properties across a wide range of frequencies and temperatures.
This is why the electronics industry relies heavily on PTFE for insulating high-performance wires, cables, and components in printed circuit boards (PCBs) and semiconductors.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE performs reliably across a massive temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). It does not become brittle in cryogenic conditions or degrade in high heat.
This thermal stability is crucial for the aerospace and automotive sectors, where it is used for seals, gaskets, and wire insulation in jet engines and other high-temperature environments.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, a property famously used for non-stick coatings. This "slipperiness" is also vital for industrial machinery.
The food and beverage industry uses it for non-stick cookware and hygienic conveyor belt surfaces. In manufacturing, it is used for low-friction bearings, gears, and sliding plates that require no external lubrication.
Specialized Applications and Niches
Beyond the major industrial sectors, PTFE’s other unique characteristics have allowed it to fill critical niches.
Biocompatibility and Purity
Because PTFE is inert and non-toxic, it is highly biocompatible and does not trigger immune responses. This makes it safe for use inside the human body.
The medical and pharmaceutical industries use medical-grade PTFE for surgical implants, catheters, syringes, and laboratory equipment where purity and non-reactivity are essential.
Hydrophobic Properties
PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and oils. It is also resistant to UV radiation and weathering.
This quality is the basis for high-performance waterproof and breathable fabrics used in the textile industry. It is also used in construction for protective coatings and plumbing applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While PTFE offers exceptional performance, it comes with limitations that are critical to understand.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to creep (slow deformation under load) and has poor abrasion resistance compared to other engineering plastics. It is not suitable for high-load structural applications on its own.
Difficult to Process
PTFE's high melting point and high melt viscosity make it difficult to process using conventional methods like injection molding. It typically requires specialized techniques like compression molding and sintering.
Sensitivity to Radiation
High-energy radiation can break down the polymer chains in PTFE, causing it to become brittle and lose its mechanical properties. This limits its use in certain nuclear and space applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a material requires matching its properties to your primary goal. Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE is the right solution.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is the industry benchmark for seals, linings, and components in chemically aggressive environments.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Its outstanding dielectric properties make it a top choice for high-frequency and high-temperature wiring and electronics.
- If your primary focus is low friction: It is the gold standard for creating non-stick surfaces and self-lubricating mechanical parts.
- If your primary focus is structural strength: You should consider alternative polymers or look into reinforced PTFE grades that include fillers like glass or carbon to improve mechanical properties.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's distinct profile of strengths and weaknesses is the key to leveraging its power in the right industrial context.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key PTFE Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Seals, gaskets, tank linings for corrosive substances |
| Electronics | High-performance wire insulation, PCB components |
| Medical | Surgical implants, catheters, lab equipment |
| Automotive & Aerospace | High-temperature seals, wire insulation |
| Food & Beverage | Non-stick surfaces, hygienic conveyor belts |
| Industrial Machinery | Low-friction bearings, self-lubricating parts |
Need high-quality PTFE components for your industry? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver solutions that meet your exact specifications. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments



















