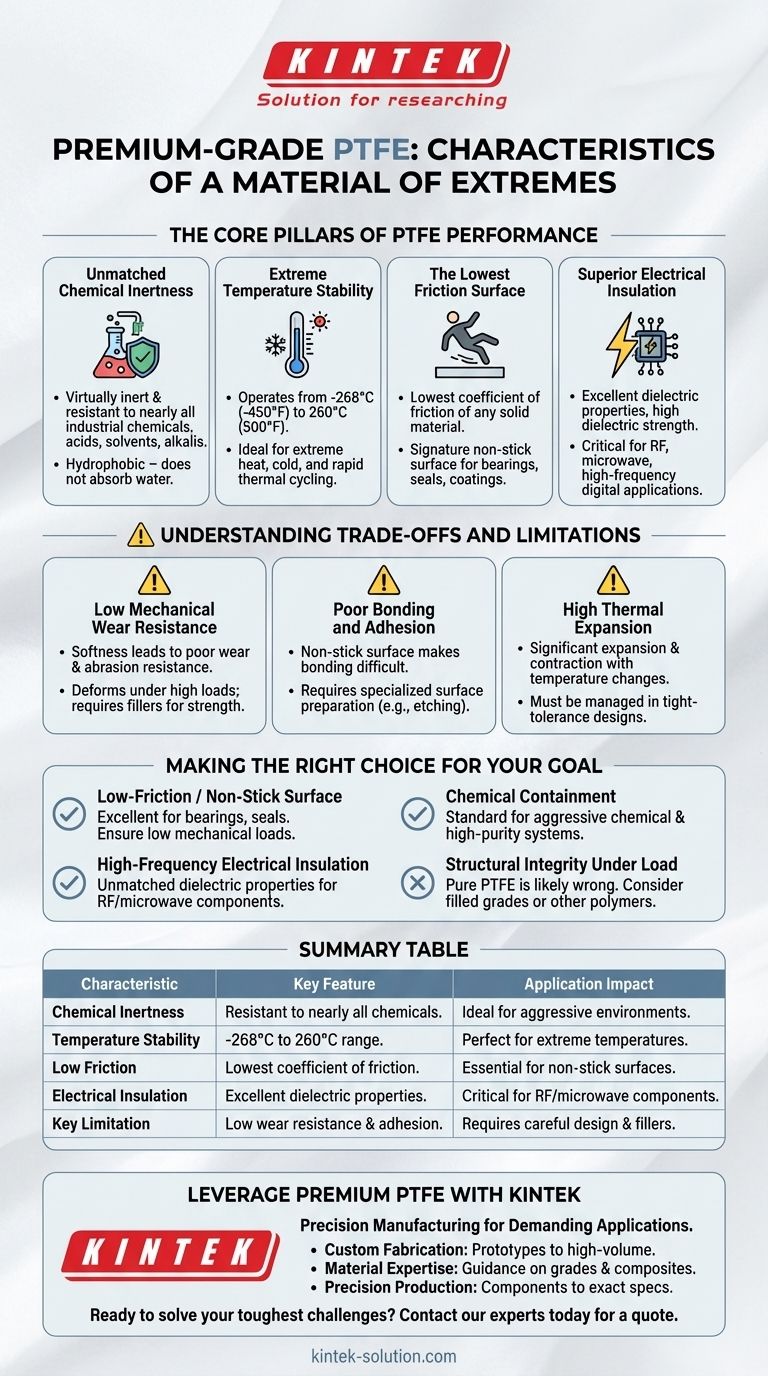
In essence, Premium-Grade Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of extremes. It is defined by its unparalleled chemical inertness, an exceptionally wide operating temperature range, the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid, and outstanding electrical insulation properties.
The key to successfully using PTFE is to understand its dual nature. While it offers world-class performance in chemical, thermal, and low-friction applications, its inherent softness and poor mechanical wear resistance are critical limitations that must be accounted for in any design.
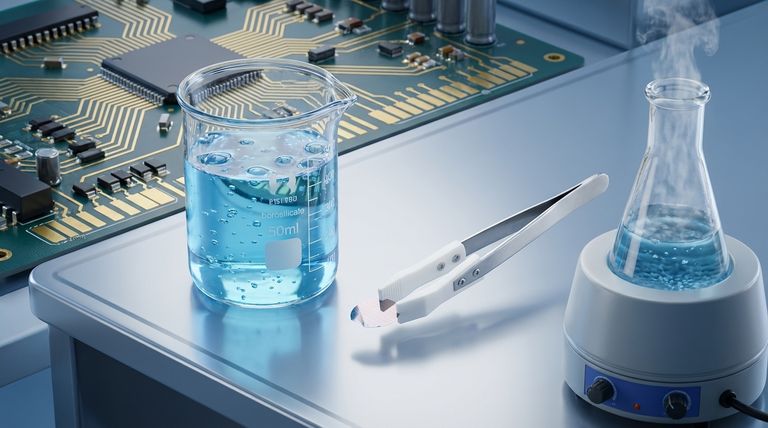

The Core Pillars of PTFE Performance
To properly evaluate PTFE, we must look at its defining characteristics, which make it a go-to material for some of the most demanding engineering challenges.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert and resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, solvents, and alkalis. This remarkable property stems from the strong carbon-fluorine bonds that protect the polymer backbone from chemical attack.
It is also hydrophobic, meaning it does not absorb water, ensuring its properties remain stable even in humid environments.
Extreme Temperature Stability
This material maintains its properties across an incredibly broad temperature spectrum. It remains functional and flexible at cryogenic temperatures as low as -268°C (-450°F) and can operate continuously at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
This stability makes it ideal for applications involving extreme heat, cold, or rapid thermal cycling.
The Lowest Friction Surface
PTFE has the lowest known coefficient of friction of any solid material, which is why it is often cited as being more slippery than wet ice on wet ice.
This results in its signature non-stick surface, critical for applications like low-friction bearings, seals, and non-stick coatings.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an exceptional electrical insulator with outstanding dielectric properties. It maintains high dielectric strength and low power loss, even at high frequencies.
This makes it an indispensable material for high-performance cables, connectors, and printed circuit boards, especially in microwave and RF applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. The same properties that make PTFE exceptional in some areas create significant drawbacks in others. Acknowledging these trade-offs is crucial for successful implementation.
Low Mechanical Wear Resistance
The primary trade-off for PTFE's extremely low friction is its softness and poor resistance to wear and abrasion. In high-load or abrasive conditions, pure PTFE will deform and wear away quickly.
For this reason, it is often reinforced with fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze to improve its mechanical strength and wear characteristics.
Poor Bonding and Adhesion
PTFE's non-stick, low-energy surface makes it extremely difficult to bond to other materials using conventional adhesives.
Attaching PTFE to other components requires specialized surface preparation, such as chemical etching, to create a bondable surface. This adds complexity and cost to the manufacturing process.
High Thermal Expansion
Compared to metals and many other polymers, PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes, a factor that must be carefully managed in designs with tight tolerances.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE requires aligning its unique profile with the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction, non-stick surface: PTFE is an excellent choice for bearings, seals, and coatings, but you must ensure the application involves low mechanical loads to avoid rapid wear.
- If your primary focus is chemical containment: Its near-total chemical inertness makes it the standard for lining pipes, valves, and vessels in aggressive chemical or high-purity environments.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: Its superior dielectric properties are unmatched for components in RF, microwave, and high-speed digital circuits.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under load: Pure PTFE is almost certainly the wrong choice; consider a filled PTFE grade or a different high-performance polymer altogether.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE effectively depends on designing around its strengths while mitigating its inherent weaknesses.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Key Feature | Application Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resistant to nearly all chemicals and solvents. | Ideal for aggressive chemical environments and high-purity systems. |
| Temperature Stability | Operates from -268°C to 260°C (-450°F to 500°F). | Perfect for extreme heat, cryogenics, and thermal cycling. |
| Low Friction | Lowest coefficient of friction of any solid. | Essential for non-stick surfaces, bearings, and seals. |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties, even at high frequencies. | Critical for RF, microwave, and high-speed digital components. |
| Key Limitation | Low mechanical wear resistance and poor adhesion. | Requires careful design, often needs filler reinforcement. |
Leverage Premium PTFE for Your Most Demanding Applications
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components. Whether you need custom seals, liners, or labware for the semiconductor, medical, or industrial sectors, our expertise ensures your designs capitalize on PTFE's strengths while mitigating its limitations.
We provide:
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production.
- Material Expertise: Guidance on selecting the right PTFE grade or composite for your specific load, chemical, and temperature requirements.
- Precision Production: Components manufactured to your exact specifications for reliable performance.
Ready to solve your toughest engineering challenges? Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE Teflon washers? Unlock Superior Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- Which industries benefit from Teflon machined parts? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the advantages of polyester-filled PTFE? A Guide to Superior Wear & Load Performance
- How are PTFE rods utilized in electronic and electrical applications? Unlock Superior Performance & Reliability
- Why is compatibility with equipment crucial when selecting PTFE packing? Avoid Costly Failures & Downtime
- What is PTFE packing and what are its primary characteristics? Master Sealing for Extreme Conditions
- What are the main industries that utilize PTFE lined valves? Ensure Safety and Purity in Critical Processes
- What industries commonly use PTFE rotary shaft seals? The Ultimate Guide for Extreme Conditions



















