When standard seals can no longer handle the pressure, speed, or chemical exposure of your application, you must look to a more advanced solution. A PTFE rotary shaft seal is a high-performance sealing component made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a fluoropolymer renowned for its exceptional properties. These seals are specifically engineered to prevent fluid leakage and contaminant ingress in rotating equipment operating under harsh conditions where traditional elastomeric seals would quickly fail.
PTFE rotary shaft seals are not just an alternative to rubber seals; they are a problem-solving technology. They are designed for the operational extremes of high speed, high temperature, and aggressive chemicals that cause conventional materials to degrade, melt, or wear out prematurely.
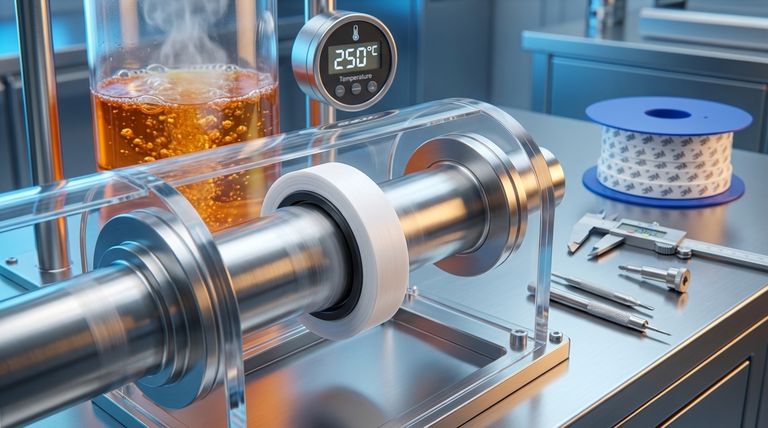

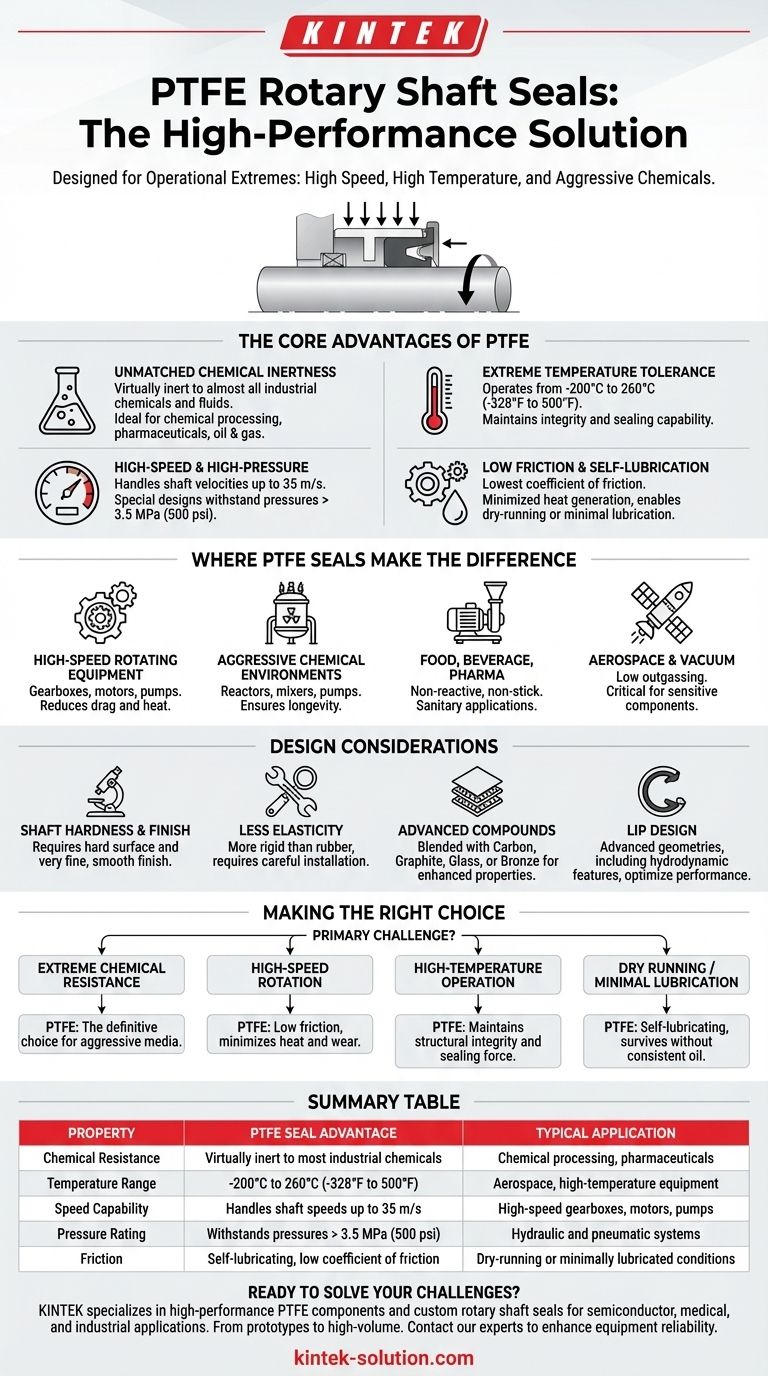
The Core Advantages of PTFE in Sealing
The choice of PTFE is not arbitrary. This material provides a unique combination of properties that make it ideal for the most demanding rotary applications. Understanding these advantages reveals why PTFE seals succeed where others fail.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals and fluids. This makes it the default choice for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and oil and gas, where seals are exposed to aggressive or corrosive media that would destroy standard rubber compounds.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
PTFE seals operate effectively across an exceptionally wide temperature range. They maintain their integrity and sealing capability in conditions from cryogenic temperatures near -200°C (-328°F) up to sustained heat of 260°C (500°F), far exceeding the limits of most elastomers.
High-Speed and High-Pressure Capability
Unlike rubber seals that can overheat and wear rapidly at high speeds, PTFE's low friction allows it to handle shaft surface velocities up to 35 m/s. Furthermore, specialized designs can withstand pressures exceeding 3.5 MPa (500 psi), making them suitable for high-performance hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Low Friction and Self-Lubrication
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This self-lubricating characteristic minimizes heat generation, reduces torque requirements, and prevents the stick-slip phenomenon common with other materials. This allows for smooth operation and even enables functionality in dry-running or minimally lubricated conditions.
Where PTFE Seals Make the Difference
The unique properties of PTFE translate directly into superior performance in specific, challenging industries and applications.
High-Speed Rotating Equipment
In equipment like high-speed gearboxes, motors, and pumps, the low friction of PTFE seals reduces parasitic drag and heat buildup. This extends the life of both the seal and the equipment itself while improving efficiency.
Aggressive Chemical Environments
For reactors, mixers, and pumps in the chemical and petrochemical industries, PTFE's chemical inertness is non-negotiable. It ensures seal longevity and prevents process contamination.
Food, Beverage, and Pharmaceutical Processing
Because PTFE is non-reactive and non-stick, it is an ideal material for sanitary applications. It will not contaminate the product stream and can withstand the aggressive cleaning and sterilization protocols common in these industries.
Aerospace and Vacuum Applications
In aerospace, low outgassing is a critical property to prevent contamination of sensitive optical and electronic components in a vacuum. PTFE's stability under vacuum and extreme temperatures makes it essential for many aerospace applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While powerful, PTFE seals are not a universal drop-in replacement for all other seal types. Their successful implementation requires understanding their unique characteristics.
The Importance of Shaft Hardness and Finish
To take full advantage of PTFE's low-friction properties and ensure a long service life, the mating shaft surface must be properly prepared. A hard surface with a very fine, smooth finish is required to prevent abrasion of the PTFE lip.
Less Elasticity than Rubber
PTFE is a more rigid material than traditional elastomers. This means it has less "memory" and is less forgiving of installation errors or significant shaft runout. Careful installation using proper tools is crucial to avoid damaging the sealing lip.
The Role of Advanced Compounds
Pure PTFE can be too soft for some high-pressure or abrasive applications. To enhance its mechanical properties, PTFE is often blended with fillers like carbon, graphite, glass fiber, or bronze. These compounds improve wear resistance, load-bearing capacity, and thermal conductivity.
The Impact of Lip Design
PTFE seal performance can be highly optimized through lip geometry. Advanced designs may include hydrodynamic features that actively pump fluid away from the sealing edge, providing an even higher degree of leakage protection, especially at high speeds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PTFE seal is a decision driven by overcoming the limitations of conventional materials. Use your primary operational challenge as your guide.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: PTFE is the definitive choice for sealing aggressive media where elastomers would dissolve or swell.
- If your primary focus is high-speed rotation: The low-friction nature of PTFE minimizes heat and wear, enabling reliable sealing at speeds that would burn up rubber seals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation: PTFE maintains its structural integrity and sealing force at temperatures that cause elastomers to harden, crack, or melt.
- If your focus is dry running or minimal lubrication: The self-lubricating properties of PTFE make it one of the few materials that can survive and seal effectively without a consistent oil supply.
By matching the distinct capabilities of PTFE to your most difficult sealing challenges, you can dramatically improve equipment reliability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Seal Advantage | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Virtually inert to most industrial chemicals | Chemical processing, pharmaceuticals |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Aerospace, high-temperature equipment |
| Speed Capability | Handles shaft speeds up to 35 m/s | High-speed gearboxes, motors, pumps |
| Pressure Rating | Withstands pressures exceeding 3.5 MPa (500 psi) | Hydraulic and pneumatic systems |
| Friction | Self-lubricating with low coefficient of friction | Dry-running or minimally lubricated conditions |
Ready to solve your most demanding sealing challenges? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom rotary shaft seals designed for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our precision production ensures reliable performance in extreme conditions, from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE sealing solutions can enhance your equipment's reliability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the pressure limitations for PTFE ball valve seats? Understanding the Critical Role of Valve Size
- What are the different types of PTFE lined valves and their key features? Choose the Right Valve for Your Corrosive Process
- What are the key components of Metal-Polymer Bronze Backed PTFE Plain Bearings? A Guide to Their Layered Design
- How do expanded PTFE gaskets perform in terms of sealing performance? Achieve Leak-Free Seals on Challenging Surfaces
- Which industries benefit most from expanded PTFE gaskets? Ensure Purity and Protect Equipment
- Which industries utilize PTFE machined bellows? Solve Critical Challenges in Demanding Environments
- In which industries are PTFE envelope gaskets commonly used? A Guide to Chemical Resistance and Purity
- Why are PTFE coated fasteners used in electronics and telecommunications? Ensure Reliability and Signal Integrity



















