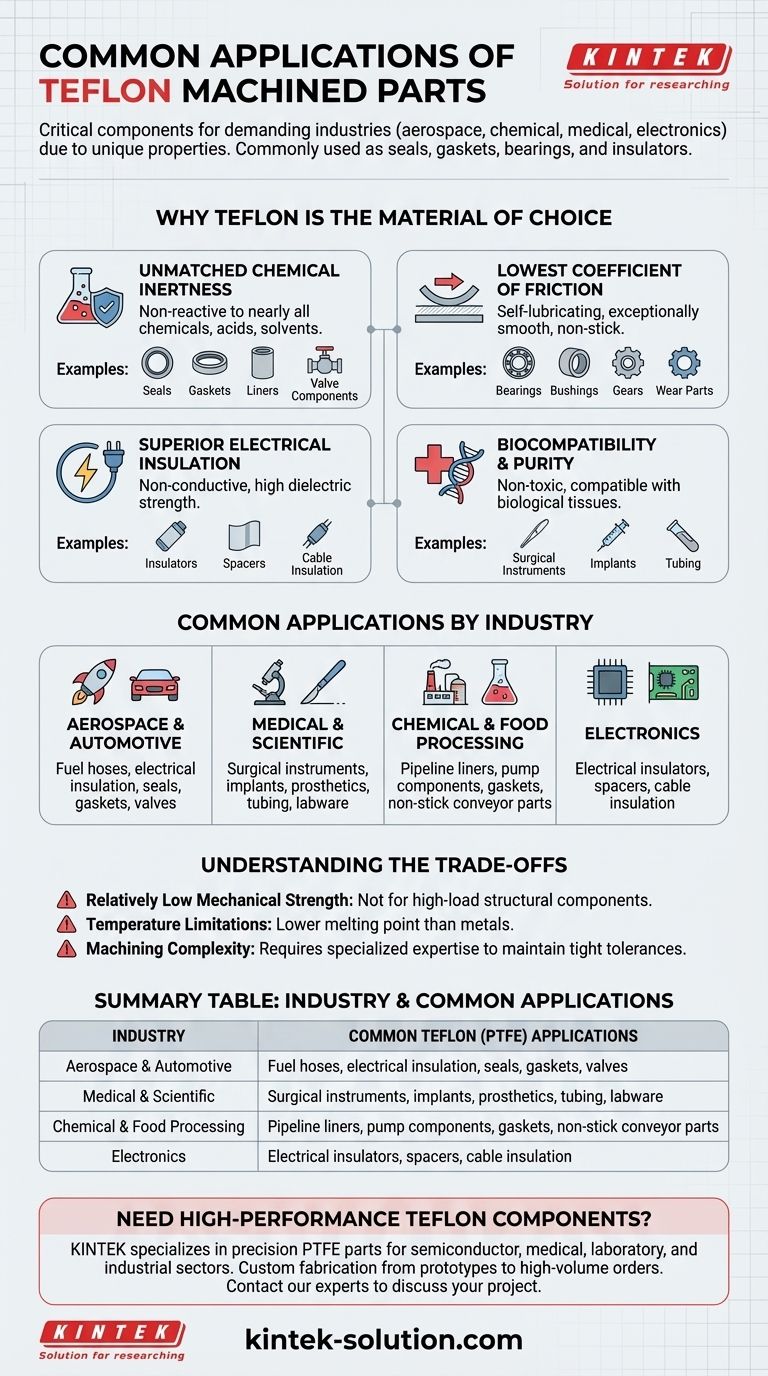
Machined Teflon parts are most commonly used as seals, gaskets, bearings, and electrical insulators. These components are critical in demanding industries like aerospace, chemical processing, medical, and electronics, where standard materials would quickly fail due to corrosion, friction, or electrical conductivity.
The widespread application of machined Teflon (PTFE) isn't arbitrary; it's a direct result of its unique combination of properties. Engineers turn to Teflon when they need a material that is simultaneously chemically inert, exceptionally low-friction, and a superb electrical insulator.

Why Teflon is the Material of Choice
The value of machined Teflon, technically known as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), lies in its core characteristics. Understanding these properties explains its role in so many critical applications.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Teflon is non-reactive to nearly all chemicals, acids, and solvents. This makes it an ideal material for components that will be exposed to harsh or corrosive substances.
This property is why it's a primary choice for seals, gaskets, liners, and valve components in the chemical processing and aerospace industries.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. It is inherently self-lubricating and provides an exceptionally smooth, non-stick surface.
This is the key reason it's used for bearings, bushings, gears, and wear parts, where reducing friction and preventing wear is paramount.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Teflon does not conduct electricity and has high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand high voltages without breaking down.
This makes it essential for electrical insulators, spacers, and cable insulation, particularly in sensitive electronics and aerospace components where signal integrity is crucial.
Biocompatibility and Purity
PTFE is non-toxic and biocompatible, meaning it can be used in direct contact with biological tissues without causing an adverse reaction.
This purity is critical for applications in medical equipment, such as surgical instruments, implants, and tubing, as well as for parts used in food processing machinery.
Common Applications by Industry
While the properties are the "why," seeing the applications by industry provides a practical context for where Teflon excels.
In Aerospace and Automotive
Components in these sectors must withstand extreme conditions. Teflon is used for fuel hoses, electrical wire insulation, surface protection coatings, valves, seals, and gaskets.
In Medical and Scientific Fields
Purity and non-reactivity are non-negotiable. Teflon is machined into parts for surgical instruments, implants, prosthetics, tubing, and non-reactive laboratory equipment.
In Chemical and Food Processing
Handling corrosive materials or ensuring food safety is the primary goal. Here, Teflon is used for pipeline liners, pump components, gaskets, non-stick conveyor parts, and seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging where Teflon may not be the best fit.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals or other engineering plastics, Teflon is relatively soft. It is not suitable for high-load structural components and can be susceptible to "creep" under constant pressure.
Temperature Limitations
While resistant to a wide range of temperatures, PTFE has a lower melting point than metals. It is not intended for extremely high-temperature applications where structural integrity is required.
Machining Complexity
The softness that contributes to its excellent sealing properties can also make it challenging to machine to extremely tight tolerances. This requires specialized expertise to prevent deformation during manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary challenge will determine if machined Teflon is the correct solution.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: Teflon is the industry standard for seals, gaskets, and valve components in corrosive environments.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: It is the ideal choice for self-lubricating bearings, bushings, and low-wear sliding parts.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Teflon is a superior material for insulators and connectors in sensitive electronic systems.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility: It is a go-to material for components used in medical devices and food-grade machinery.
Ultimately, choosing machined Teflon is a decision to prioritize performance and reliability in environments where other materials simply cannot perform.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Common Teflon (PTFE) Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace & Automotive | Fuel hoses, electrical insulation, seals, gaskets, valves |
| Medical & Scientific | Surgical instruments, implants, labware, biocompatible tubing |
| Chemical & Food Processing | Pipeline liners, pump components, non-stick conveyor parts |
| Electronics | Electrical insulators, spacers, cable insulation |
Need high-performance Teflon components for your critical application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision machining of PTFE parts like seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine expert material knowledge with custom fabrication capabilities—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to deliver components that meet your exact specifications for chemical resistance, low friction, and electrical insulation.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What post-machining processes can improve PTFE surface finishes? Achieve a Flawless Finish for Your Components
- What are the main disadvantages of virgin PTFE products in fluid sealing applications? Overcoming Creep and Cold Flow
- What is the disadvantage of using glass as a filler in PTFE? The Critical Trade-off for Wear Resistance
- Why is chip clearance important in PTFE machining? Prevent Clogging and Ensure Precision
- How do expanded PTFE gaskets perform in terms of sealing performance? Achieve Leak-Free Seals on Challenging Surfaces
- In which industries are PTFE mill-type envelope gaskets applied? Ensure Leak-Free Sealing in Demanding Environments
- How are Teflon sheets used in Direct-to-Garment (DTG) printing? Achieve a Professional, Durable Finish
- Why are PTFE bushes suitable for high-temperature environments? Unlock Superior Heat & Chemical Resistance



















