For engineers and designers seeking alternatives to Teflon (PTFE), the primary high-performance option is PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone). PEEK offers significantly higher mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability compared to standard PTFE, making it ideal for more demanding structural applications.
The decision to move away from standard PTFE is rarely about finding a "better" material, but about making a strategic trade-off. You are typically sacrificing some of PTFE's unmatched chemical inertness or low friction to gain significant improvements in mechanical strength, wear resistance, or high-temperature performance with a material like PEEK.
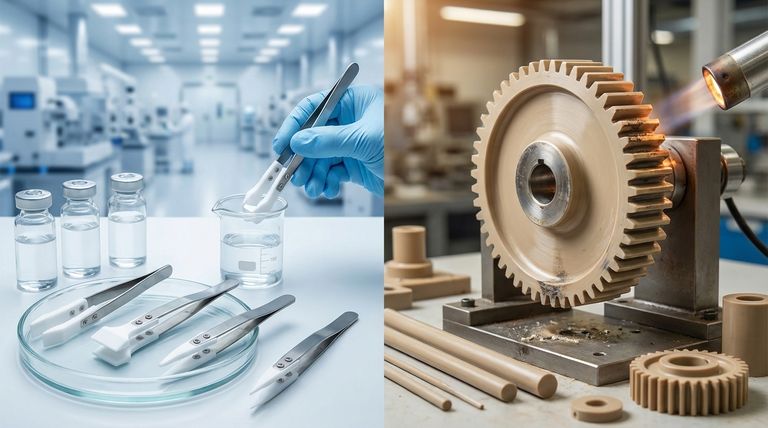

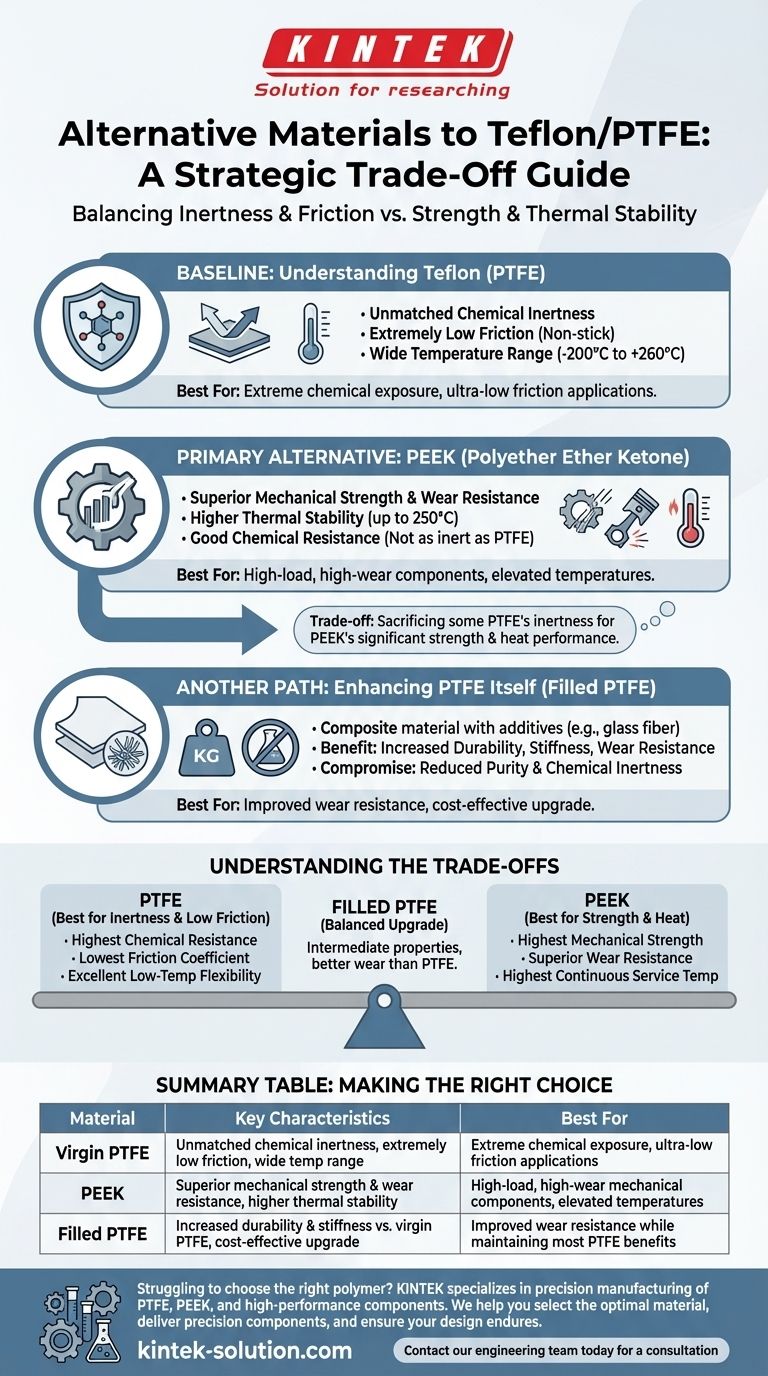
First, A Baseline: Understanding Teflon (PTFE)
To evaluate alternatives, we must first establish the benchmark set by Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known by the brand name Teflon.
### Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is a fluoropolymer thermoplastic renowned for its resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids and alkalis. This makes it the default choice for highly corrosive environments.
### Extremely Low Friction
One of PTFE's most famous properties is its exceptionally low coefficient of friction. This "non-stick" quality is critical in applications requiring smooth, low-resistance movement.
### Wide Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its properties across a broad temperature spectrum, including flexibility at very low temperatures. It also possesses a high melting point and is non-flammable.
The Primary Alternative: PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
When the mechanical limitations of PTFE are a barrier, PEEK is the leading alternative. It is a high-performance thermoplastic that excels where PTFE falls short.
### Superior Mechanical Strength and Wear Resistance
PEEK offers substantially higher tensile strength and rigidity than PTFE. This makes it suitable for components that must bear significant loads or withstand abrasive forces without deforming.
### Higher Thermal Stability
PEEK maintains its mechanical integrity at higher continuous service temperatures, often up to 250°C (482°F). This exceeds the typical operational limits of PTFE, providing a crucial advantage in high-heat applications.
### Good Chemical Resistance
While PEEK has excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, it is not as universally inert as PTFE. Highly concentrated acids can degrade it, a key consideration for material selection.
An Alternative Path: Enhancing PTFE Itself
Before moving to a completely different polymer like PEEK, consider if a modified version of PTFE can meet your needs.
### What is Filled PTFE?
Filled PTFE grades are composite materials. They incorporate additives like glass fiber or carbon into the virgin PTFE matrix to enhance specific properties.
### The Benefit: Increased Durability
These fillers act as a reinforcement, significantly increasing the material's strength, stiffness, and wear resistance compared to standard, unfilled PTFE.
### The Compromise: Reduced Purity and Inertness
The addition of fillers means the material is no longer pure PTFE. This can compromise its overall chemical resistance and disqualifies it from applications requiring the highest levels of material purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Inertness
Choosing the right material is an exercise in balancing competing requirements. There is no single "best" option; only the best fit for a specific application.
### When PTFE is the Unbeatable Choice
If your application's primary challenges are extreme chemical exposure or the need for the lowest possible friction, virgin PTFE's unique properties are almost impossible to replace.
### When PEEK is the Superior Option
For high-load, high-wear mechanical components like bearings, seals, or structural parts operating at elevated temperatures, PEEK's superior strength and thermal stability make it the clear choice.
### When Filled PTFE Hits the Sweet Spot
If you need better wear and deformation resistance than virgin PTFE but don't require the peak performance (or want to avoid the higher cost) of PEEK, a filled PTFE grade offers a balanced, cost-effective upgrade.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the single most critical demand of your project.
- If your primary focus is absolute chemical inertness and ultra-low friction: Virgin PTFE remains the unparalleled industry standard.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength, wear resistance, and high-temperature performance: PEEK is the correct engineering choice.
- If your primary focus is improving the durability of PTFE components on a budget: Filled PTFE provides a practical and effective enhancement.
Choosing the right material ensures your design not only works, but endures.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Unmatched chemical inertness, extremely low friction, wide temperature range | Extreme chemical exposure, ultra-low friction applications |
| PEEK | Superior mechanical strength & wear resistance, higher thermal stability | High-load, high-wear mechanical components, elevated temperatures |
| Filled PTFE | Increased durability & stiffness vs. virgin PTFE, cost-effective upgrade | Improved wear resistance while maintaining most PTFE benefits |
Struggling to choose the right high-performance polymer for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE, PEEK, and other high-performance polymer components. Our experts understand the critical trade-offs between chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability.
We can help you:
- Select the optimal material (PTFE, PEEK, or a filled grade) for your specific needs in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial applications.
- Deliver precision components through custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
- Ensure your design not only works but endures under the most demanding conditions.
Let's discuss your project requirements. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation to find the perfect material solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE that ePTFE gaskets retain? Superior Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What is a PTFE bush and what is its primary use? A Guide to Self-Lubricating Bearings
- What makes Teflon suitable for electrical applications? Unmatched Insulation for Extreme Conditions
- How does PTFE enhance baseball equipment? Unlock Faster Swings and Longer-Lasting Gear
- What factors should engineers consider when selecting PTFE gaskets? Ensure a Perfect Seal for Your Application
- What are the advantages of PTFE rod over other materials? Superior Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What is a PTFE coated O-ring? A Hybrid Seal for Low Friction & Chemical Resistance
- How are PTFE rubber seals constructed? Precision Engineering for High-Performance Sealing



















