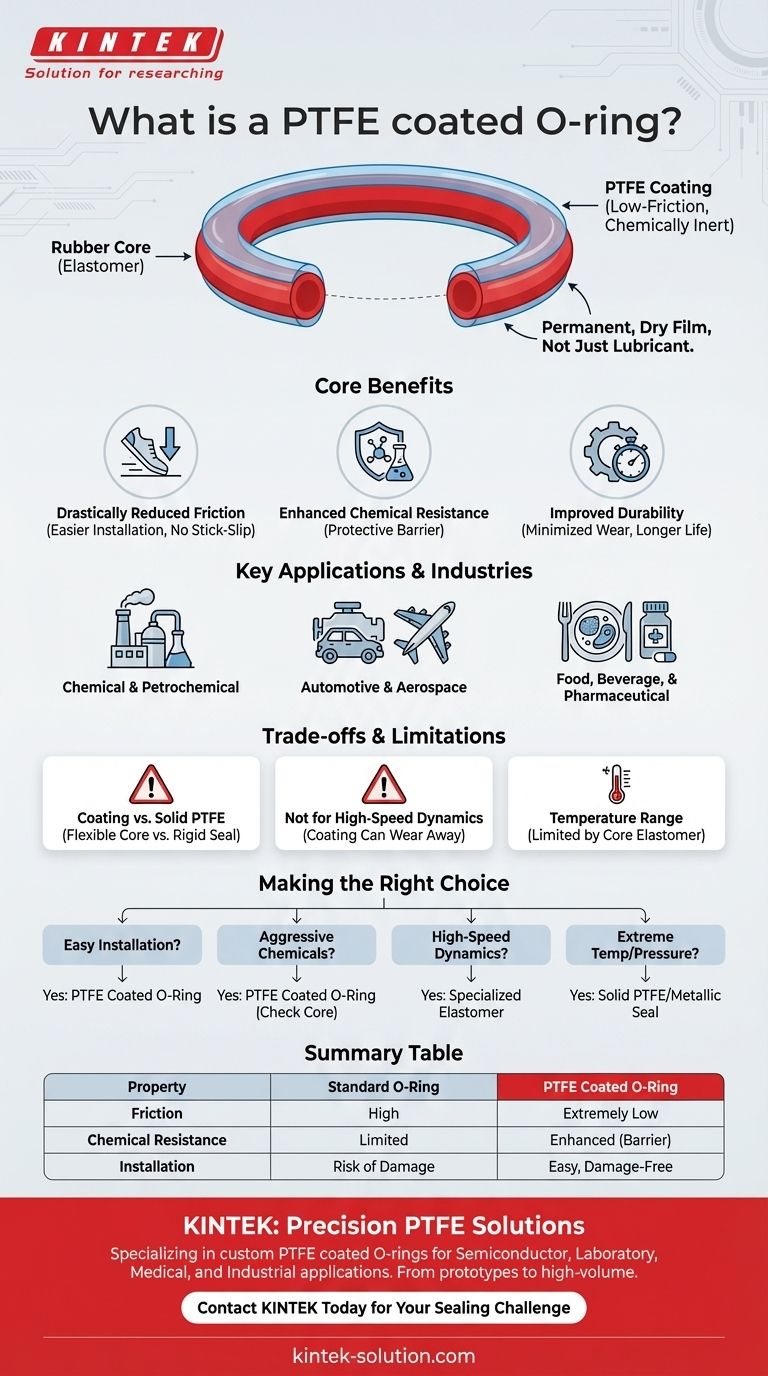
At its core, a PTFE coated O-ring is a standard elastomeric (rubber) O-ring that has a thin layer of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) bonded to its surface. This coating is not merely a lubricant but a permanent, dry film that fundamentally enhances the O-ring's properties, primarily by creating an incredibly low-friction surface.
The central concept is simple yet powerful: combine the flexibility and reliable sealing pressure of a rubber O-ring with the exceptional low-friction and chemical inertness of a PTFE surface. This creates a hybrid seal that solves problems where standard O-rings might fail.
Why Coat an O-Ring? The Core Benefits
The decision to use a PTFE coated O-ring stems from the need to overcome the inherent limitations of standard elastomers, particularly their high coefficient of friction.
Drastically Reduced Friction
The primary advantage is the reduction in friction. PTFE is one of the most slippery materials known, which makes installation significantly easier and smoother.
This low-friction surface prevents the O-ring from sticking, pinching, or tearing during assembly, especially in tight-tolerance grooves. It also eliminates the "stick-slip" phenomenon in slow-moving dynamic applications.
Enhanced Chemical Resistance
The PTFE coating acts as a protective barrier, encapsulating the more vulnerable rubber core.
This makes the O-ring suitable for use in aggressive chemical environments where the base elastomer might otherwise degrade. It offers an extra layer of protection against corrosive fluids, solvents, and oxidizing media.
Improved Durability
By reducing friction during both installation and operation, the PTFE coating minimizes abrasive wear on the O-ring's surface. This directly contributes to a longer service life and more reliable sealing performance over time.
Key Applications and Industries
The unique combination of properties makes PTFE coated O-rings valuable across a wide range of demanding sectors.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
These seals are critical in equipment like pumps, valves, and pipeline connections. Their ability to withstand corrosive chemicals and prevent leaks ensures both safety and operational efficiency in handling aggressive media.
Automotive and Aerospace
In these industries, O-rings are often used in fuel systems, hydraulic controls, and various engine components. The low friction is essential for smooth actuation, while chemical resistance protects against degradation from oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids.
Food, Beverage, and Pharmaceutical
PTFE's non-corrosive and inert nature makes it ideal for sanitary applications. The coating ensures that the seal does not contaminate the product, a critical requirement in food production equipment and pharmaceutical processing lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, a PTFE coated O-ring is a specialized component, not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Coating vs. Solid PTFE
It is crucial to distinguish a PTFE coated O-ring from a solid PTFE O-ring. A coated O-ring has a flexible rubber core, providing the elasticity needed for effective sealing. A solid PTFE O-ring is rigid and non-compressible, serving very different, high-stress static sealing applications.
Not Ideal for High-Speed Dynamics
The PTFE coating is a very thin layer. In high-speed or highly abrasive dynamic applications, this coating can eventually wear away, exposing the underlying elastomer and negating the benefits. For this reason, they are often preferred for static seals or slow, intermittent motion.
Temperature Range is Dictated by the Core
While PTFE itself has a very wide temperature range (from -73°C to 204°C), the performance of the coated O-ring is ultimately limited by the temperature rating of the underlying rubber core (e.g., NBR, FKM, EPDM). The elastomer provides the sealing force, and if it fails, the seal fails.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right seal depends entirely on the operational demands and primary goal of your design.
- If your primary focus is easy, damage-free installation: A PTFE coated O-ring is an excellent choice to prevent tearing and pinching during assembly.
- If your primary focus is sealing in a chemically aggressive environment: The coating provides a robust protective barrier, but ensure the core elastomer is also a suitable secondary choice.
- If your primary focus is a high-speed, continuously moving dynamic seal: Consider a specialized low-friction elastomer or a different seal design, as the PTFE coating may wear prematurely.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature and pressure in a static seal: A solid PTFE O-ring or a metallic seal might be a more appropriate, though less flexible, solution.
Ultimately, a PTFE coated O-ring offers a sophisticated, hybrid solution that solves specific engineering challenges where friction and chemical exposure are the primary concerns.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard O-Ring | PTFE Coated O-Ring |
|---|---|---|
| Friction | High | Extremely Low |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited (depends on elastomer) | Enhanced (PTFE barrier) |
| Installation | Can stick, pinch, or tear | Easy, damage-free |
| Ideal Use | General-purpose static seals | Demanding static/slow dynamic seals in harsh environments |
Need a high-performance seal for a demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom PTFE coated O-rings. Our seals are designed for industries where reliability is critical, such as:
- Semiconductor and Laboratory equipment requiring contamination-free, chemical-resistant seals.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical applications demanding sanitary, inert components.
- Industrial and Chemical Processing systems that need durable seals for aggressive media.
We combine precision production with custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to deliver a seal that perfectly matches your requirements for friction, chemical resistance, and durability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific sealing challenge and get a solution engineered for performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















