In short, PTFE reducing flanges are exceptionally versatile in any application requiring a sterile, chemically resistant connection between two pipes of different sizes. Their primary use cases are in demanding industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food and beverage production, where material integrity is paramount.
The true versatility of a PTFE reducing flange is not just its ability to connect different pipe diameters. It is the ability to do so safely and reliably within highly corrosive or ultra-pure environments where other materials would fail.
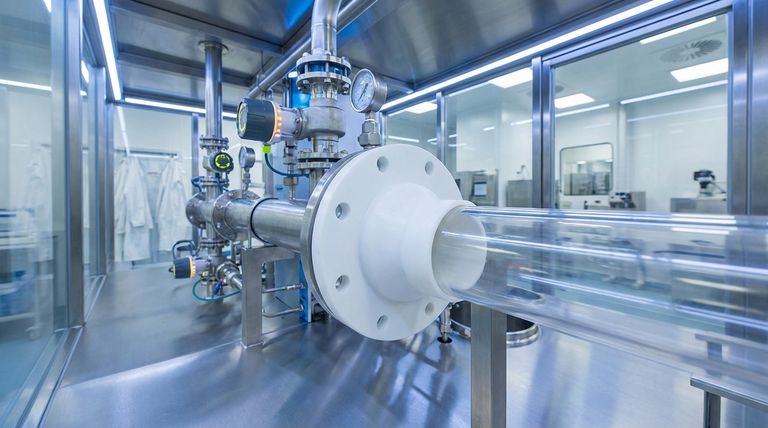

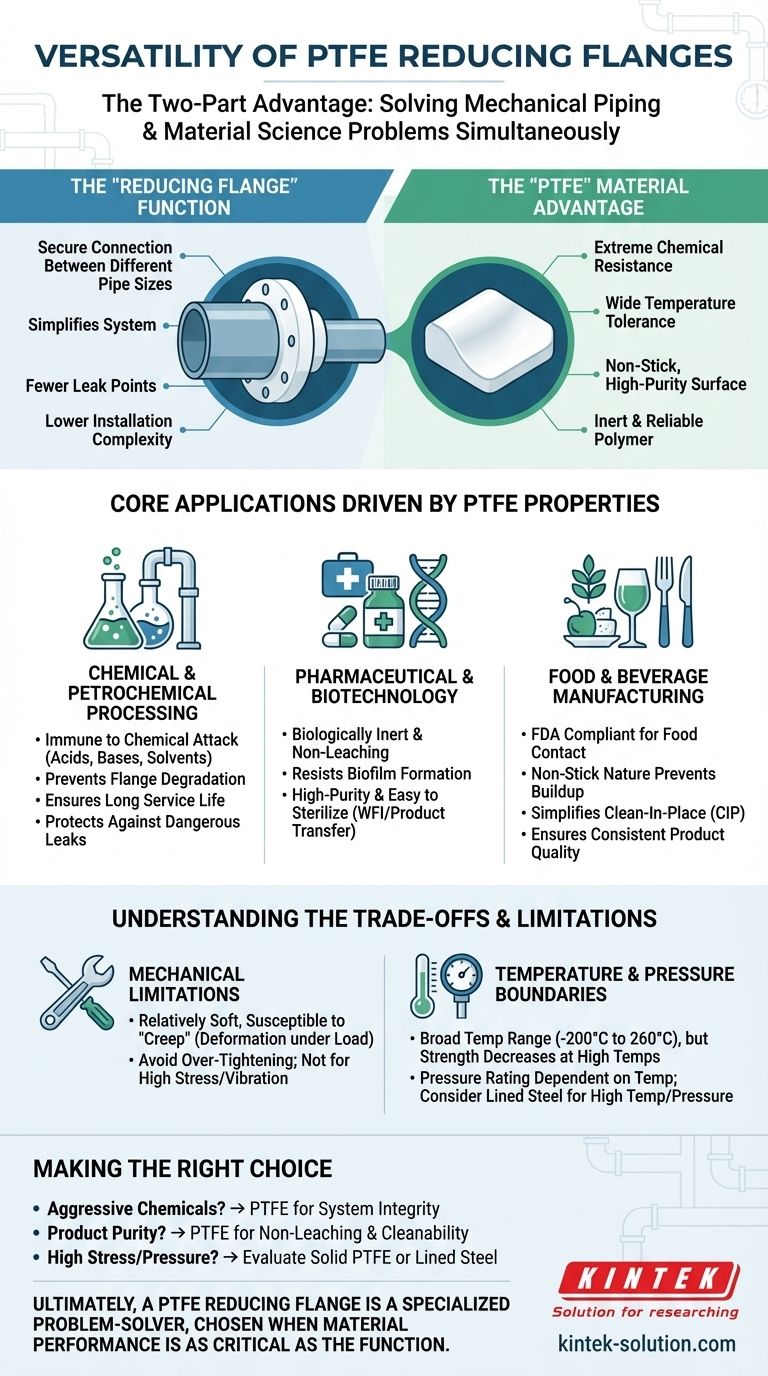
Understanding the Two-Part Advantage
A PTFE reducing flange is not a single-purpose component. Its value comes from solving two distinct problems simultaneously: a mechanical piping problem and a material science problem.
The "Reducing Flange" Function
A reducing flange is a fundamental plumbing and piping component. Its sole purpose is to create a secure connection between a larger pipe and a smaller pipe.
This avoids the need for multiple fittings (like a standard flange plus a separate reducer), simplifying the system, reducing potential leak points, and lowering installation complexity.
The "PTFE" Material Advantage
The choice of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as the material is what unlocks its use in specialized industries. PTFE provides a unique combination of properties that make it invaluable.
Its key features include extreme chemical resistance, a wide temperature tolerance, and a non-stick, high-purity surface. This makes it one of the most inert and reliable polymers for industrial use.
Core Applications Driven by PTFE Properties
The versatility of PTFE reducing flanges is a direct result of the material's characteristics. Different industries leverage different properties to solve their unique challenges.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
In these environments, the primary concern is corrosion from aggressive media like acids, bases, and solvents.
A PTFE reducing flange is effectively immune to chemical attack. This prevents flange degradation, ensures a long service life, and protects against dangerous leaks that could occur if a less resistant material were used.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology
Purity is the non-negotiable requirement in this sector. Any material that leaches, corrodes, or reacts with the product can lead to contamination and batch failure.
PTFE is biologically inert and non-leaching. Its smooth, non-stick surface also resists biofilm formation and is exceptionally easy to clean and sterilize, making it ideal for high-purity water systems (WFI) and product transfer lines.
Food and Beverage Manufacturing
Similar to pharmaceuticals, this industry requires materials that are food-safe and do not impart any taste or odor to the product.
PTFE reducing flanges meet FDA requirements for food contact. Their non-stick nature prevents product buildup, which simplifies Clean-In-Place (CIP) cycles, improves efficiency, and ensures consistent product quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly capable, PTFE is not an infallible solution. Acknowledging its limitations is critical for proper application and system safety.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material compared to metal. It is susceptible to "creep," which is the tendency to deform slowly over time under a constant load (e.g., from bolt torque).
Over-tightening a PTFE flange can cause it to deform, leading to a failed seal. It is not suitable for systems with very high mechanical stress or significant vibration.
Temperature and Pressure Boundaries
While PTFE has a broad operating temperature range (typically -200°C to 260°C), its mechanical strength decreases at higher temperatures.
The pressure rating of a PTFE flange is highly dependent on temperature. For applications involving high pressure at elevated temperatures, a PTFE-lined steel flange is often a more robust and safer alternative.
Cost Justification
PTFE reducing flanges are a premium component and are more expensive than standard flanges made from PVC, carbon steel, or stainless steel.
Their cost is only justified when the application demands extreme chemical resistance or purity. Using them in a simple water line where a less expensive material would suffice is not cost-effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct component requires you to match the material's strengths to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE's complete inertness makes it the superior choice for ensuring system integrity and preventing corrosion.
- If your primary focus is maintaining product purity: The non-leaching and non-stick properties of PTFE are essential for any pharmaceutical, biotech, or food-grade process.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical stress or pressure: You must carefully evaluate if a solid PTFE flange meets your system's pressure/temperature ratings, or if a PTFE-lined metallic flange is the more appropriate choice.
Ultimately, a PTFE reducing flange is a specialized problem-solver, chosen when the performance of the material is just as critical as the function of the fitting.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Benefit of PTFE Reducing Flange |
|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Extreme chemical resistance to acids, bases, and solvents. |
| Pharmaceutical/Biotech | High-purity, non-leaching, and easy-to-sterilize surfaces. |
| Food & Beverage | FDA-compliant, non-stick, and easy-to-clean for product integrity. |
Need a reliable, high-purity connection for your specialized system?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom reducing flanges, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components meet the exact demands of your application, from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution that guarantees performance and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What pressure ranges are common in oil and gas applications, and how do PTFE seals perform? Reliable Sealing from 1,500 to 25,000 PSI
- How does temperature tolerance differ between NBR and PTFE seat materials? A Guide to Extreme Conditions
- How do PTFE piston rings achieve sealing without additional components? Discover the Self-Clamping Principle
- What type of glass is used in glass-filled PTFE? The Definitive Answer for Superior Performance
- How do PTFE components compare to metal components? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What installation methods are available for PTFE slide bearings? Choose the Right Method for Your Structure
- Why are PTFE Bellows suitable for electroplating processes? Master Harsh Chemical & Thermal Environments
- Why are PTFE Teflon washers used in aerospace applications? Solving Critical Engineering Challenges



















