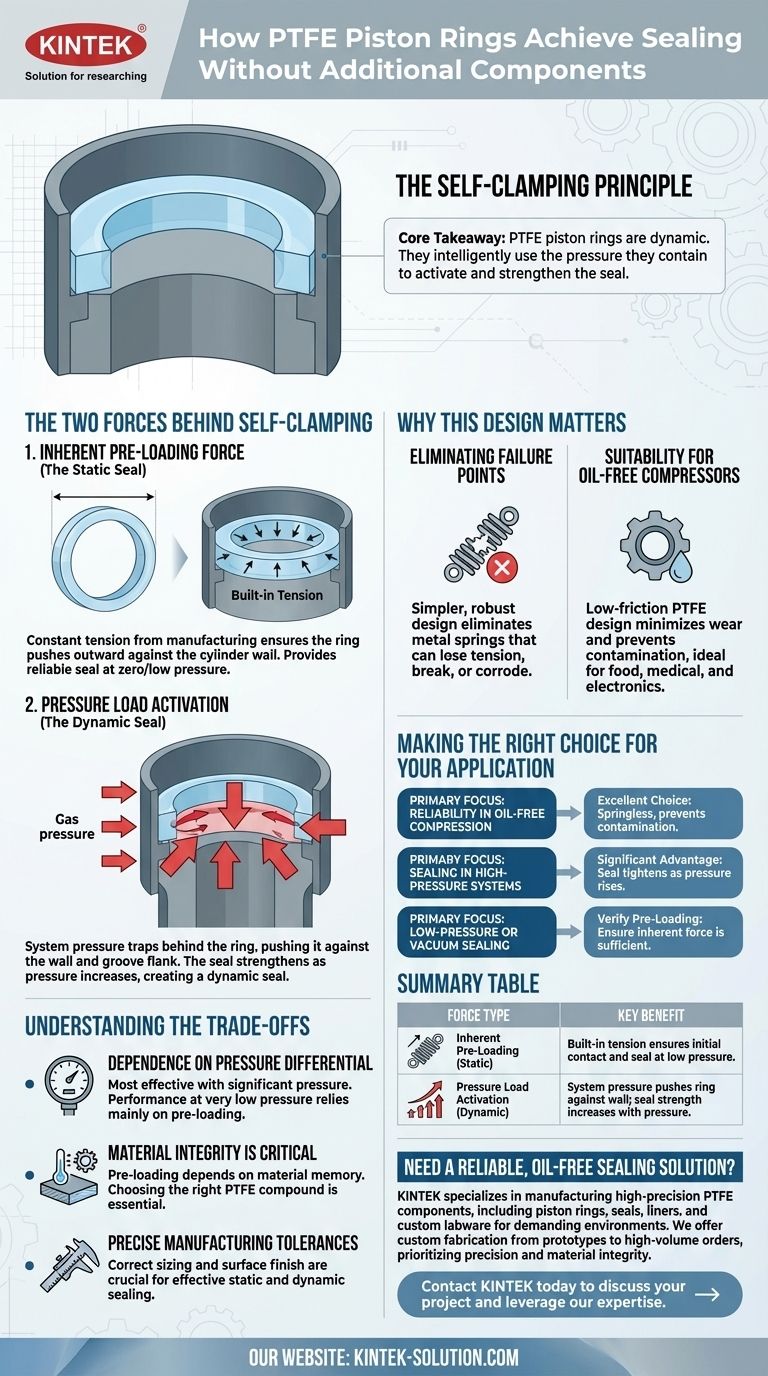
The sealing mechanism of a PTFE piston ring is based on an elegantly simple principle known as self-clamping. Instead of relying on separate components like springs, these rings use a combination of their own inherent tension and the system's operating pressure to press against the cylinder wall and piston groove, creating a highly effective seal.
The core takeaway is that PTFE piston rings are designed to be dynamic. They intelligently use the very pressure they are meant to contain as the primary force to activate and strengthen the seal, making them both simple and highly efficient.

The Two Forces Behind Self-Clamping
The term "self-clamping" refers to two distinct forces working in concert to ensure a reliable seal across different operating conditions. Understanding both is key to appreciating the design's effectiveness.
Inherent Pre-Loading Force (The Static Seal)
PTFE piston rings are manufactured to be slightly larger in diameter than the cylinder bore they will be installed in.
When the ring is compressed to fit inside the cylinder, this size difference creates a constant, built-in tension. This inherent pre-loading force ensures the ring is always pushing outward against the cylinder wall.
This initial force provides a reliable seal even at zero or very low system pressures, preventing leakage before the primary sealing mechanism takes over.
Pressure Load Activation (The Dynamic Seal)
The true ingenuity of the design becomes apparent once the system is pressurized.
As gas pressure builds on one side of the piston, that pressure finds its way behind the ring, into the groove. This trapped pressure then acts on the back surface of the ring.
This pressure load pushes the ring radially outward with immense force, pressing it firmly against the cylinder wall. Simultaneously, it pushes the ring axially against the flank of the piston groove, sealing that potential leak path as well.
This means the seal becomes stronger as the system pressure increases, creating a responsive, dynamic seal that adapts to operating conditions.
Why This Design Matters
Eliminating external components like springs is not just about cost-saving; it fundamentally improves the reliability and suitability of the seal for specific, demanding applications.
Eliminating Failure Points
In a traditional design, a metal spring is a potential point of failure. It can lose tension over time due to heat or fatigue, break, or corrode.
By removing the need for a separate spring, the self-clamping PTFE ring presents a simpler, more robust design with fewer components that can fail.
Suitability for Oil-Free Compressors
This design is particularly critical for oil-free or non-lubricated compressors. The low-friction properties of PTFE combined with a springless design minimize wear and prevent contamination.
The seal functions perfectly without the lubrication that a metallic spring might require, making it ideal for applications in food, medical, and electronics manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the performance of a self-clamping PTFE ring is dependent on specific conditions and proper design.
Dependence on Pressure Differential
The dynamic, pressure-activated component of the seal is its greatest strength. However, this means it is most effective when there is a significant pressure differential to energize the ring.
In very low-pressure or vacuum applications, the sealing performance relies almost entirely on the ring's inherent pre-loading force.
Material Integrity is Critical
The "pre-loading" force depends entirely on the elasticity and material memory of the specific PTFE compound used.
Factors like temperature, chemical exposure, and time can affect the material's properties. Choosing the right grade of filled or unfilled PTFE is essential for the longevity of the seal.
Precise Manufacturing Tolerances
The effectiveness of both the static and dynamic seal hinges on precise manufacturing of the ring, piston, and cylinder. Incorrect sizing or a poor surface finish on the cylinder wall can compromise the seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use a self-clamping PTFE ring depends on your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is reliability in oil-free compression: The springless, self-clamping design is an excellent choice, as it eliminates a common point of failure and prevents product contamination.
- If your primary focus is sealing in high-pressure systems: The pressure-activated nature of these rings is a significant advantage, as the seal becomes tighter and more effective as system pressure rises.
- If your primary focus is low-pressure or vacuum sealing: You must verify that the ring's inherent pre-loading force alone is sufficient to meet the application's leakage requirements.
By understanding this self-activating principle, you can confidently leverage a simpler and more reliable sealing solution in the right applications.
Summary Table:
| Force Type | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Inherent Pre-Loading (Static) | Built-in tension from manufacturing ensures initial contact. | Provides a reliable seal at zero/low pressure. |
| Pressure Load Activation (Dynamic) | System pressure pushes the ring against the cylinder wall. | Seal strength increases with system pressure. |
Need a reliable, oil-free sealing solution for your application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including piston rings, seals, liners, and custom labware. Our expertise ensures your seals perform reliably in the most demanding environments, from semiconductor and medical equipment to industrial compressors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision and material integrity for your specific operational needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and leverage our expertise for a superior sealing solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary materials used for oil seals? NBR vs. PTFE for Your Application
- What are the components of an assembly PTFE sliding bearing pad? A Guide to the Engineered System
- What temperature range can custom Teflon rotary shaft seals withstand? Master Extreme Heat & Cryogenic Cold
- What role does low friction play in Medical Grade PTFE Liners? Unlocking Superior Clinical Performance
- How do PTFE O-rings compare to Teflon O-rings? The Real Difference Between Solid and Encapsulated Designs
- What makes PTFE an excellent electrical insulator? Superior Performance for High-Frequency & High-Voltage Applications
- How does the built-in spring help PTFE shaft seals adapt to varying conditions? Ensure a Reliable, Long-Lasting Seal
- What are the primary applications of extra-thick PTFE washers (5mm – 6mm)? Critical for High-Pressure Sealing & Load-Bearing



















