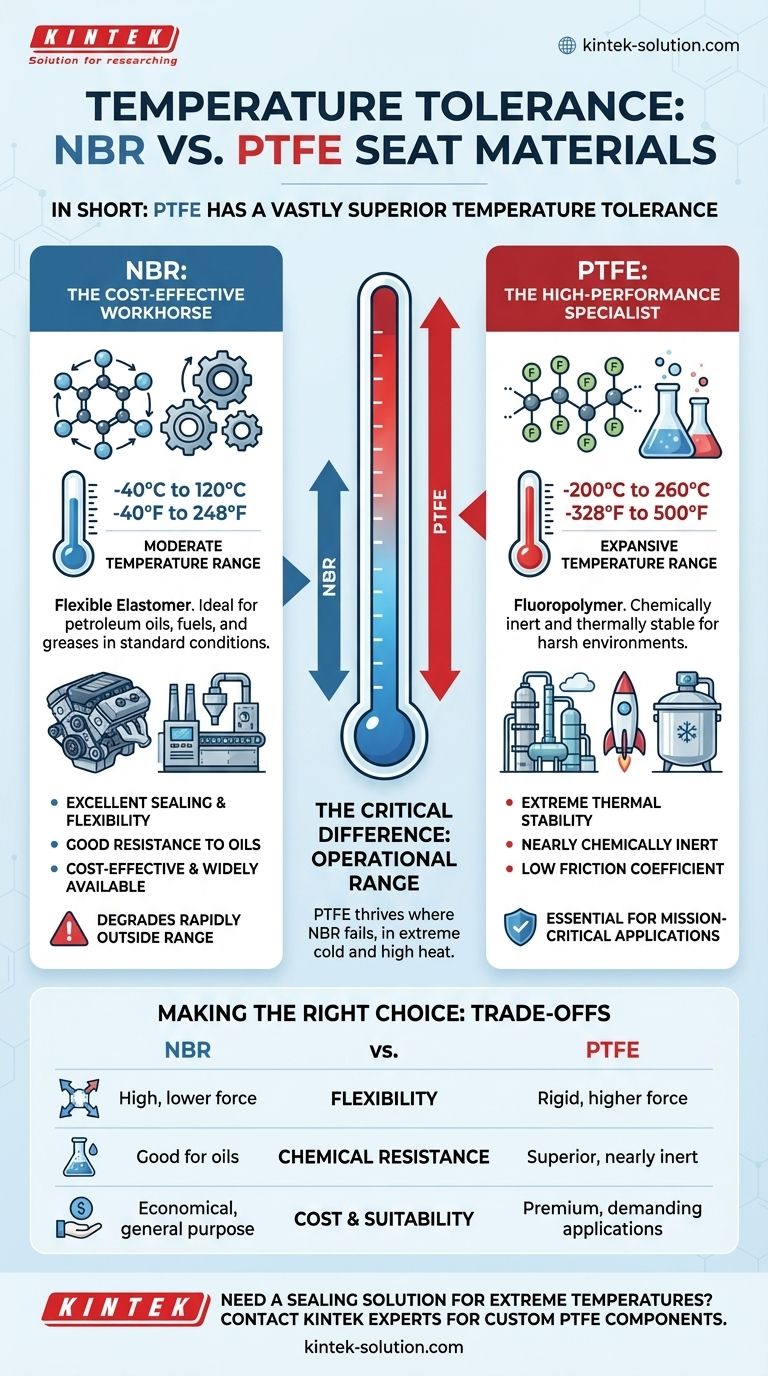
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a vastly superior temperature tolerance compared to Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR). PTFE can operate reliably in extreme cold and high-heat environments where NBR would quickly fail. NBR is a dependable elastomer for moderate temperature ranges, but PTFE is a high-performance fluoropolymer engineered for thermal extremes.
The choice between NBR and PTFE is a classic engineering trade-off. It forces a decision between NBR's cost-effective flexibility for standard conditions and PTFE's exceptional thermal and chemical resilience required for harsh, mission-critical applications.

A Tale of Two Materials: NBR vs. PTFE
To understand the difference in temperature tolerance, we must first understand the fundamental nature of each material. They are designed for entirely different operational challenges.
Understanding NBR (Nitrile Rubber): The Workhorse
NBR is an elastomer, a type of synthetic rubber. Its molecular structure gives it excellent flexibility and sealing capability.
It is highly regarded for its resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and greases, making it a staple in automotive and industrial applications.
However, its properties are best suited for environments without extreme thermal or chemical demands.
Understanding PTFE (Teflon): The Specialist
PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, is a fluoropolymer. Its strong carbon-fluorine bonds make it one of the most chemically inert and thermally stable plastics available.
This unique structure also gives it an extremely low coefficient of friction. PTFE is the go-to material for harsh environments found in chemical processing, oil and gas, and aerospace.
Temperature Tolerance: The Critical Difference
The operational temperature range is the most significant differentiator between these two materials when used for seats, seals, or gaskets.
The Operational Range of NBR
NBR performs reliably within a moderate temperature window, typically from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F).
Outside this range, its performance degrades rapidly. At colder temperatures, it loses flexibility and becomes brittle, compromising its ability to form a proper seal. At higher temperatures, it will soften and degrade.
The Expansive Range of PTFE
PTFE operates across an exceptionally wide temperature spectrum, generally from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
It maintains its properties in cryogenic applications and remains stable at high temperatures that would destroy most elastomers. This makes it essential for processes involving extreme temperature cycling.
Understanding the Trade-offs Beyond Temperature
While temperature is a primary factor, selecting the right material requires considering other critical performance characteristics.
Flexibility and Sealing Ability
As a flexible elastomer, NBR conforms easily to surfaces and requires less compressive force to create a tight seal. This makes it ideal for many standard valve and gasket applications.
PTFE is a more rigid material. While it creates a highly durable seal, it may require higher seating forces and more precise surface finishes to prevent leaks, especially in dynamic applications.
Chemical Resistance
NBR offers good resistance to oils, hydraulic fluids, and alcohols. However, it can be attacked by ketones, halogenated hydrocarbons, and strong acids.
PTFE is nearly chemically inert and is unaffected by almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This superior resistance is often as critical as its temperature tolerance.
Cost and Application Suitability
NBR is a cost-effective and widely available material, making it the default choice for a vast range of general-purpose applications where conditions are not extreme.
PTFE is a premium, higher-cost material. Its use is justified in demanding applications where material failure would lead to safety risks, costly downtime, or product contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your selection should be dictated entirely by the demands of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose sealing with exposure to oils and moderate temperatures: NBR is the most reliable and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is extreme high or low temperatures: PTFE is the only suitable choice to ensure operational integrity and safety.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical processing: PTFE's chemical inertness is non-negotiable to prevent material degradation and system failure.
Ultimately, choosing the right seat material is about matching the polymer's capabilities to the precise demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Temperature Range (°C) | Typical Temperature Range (°F) | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile Rubber) | -40°C to 120°C | -40°F to 248°F | Cost-effective, flexible elastomer for moderate conditions |
| PTFE (Teflon) | -200°C to 260°C | -328°F to 500°F | High-performance fluoropolymer for extreme thermal/chemical environments |
Need a Sealing Solution for Extreme Temperatures?
Choosing the wrong seat material can lead to equipment failure, safety risks, and costly downtime. For mission-critical applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, the superior thermal and chemical resistance of PTFE is essential.
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware. We work with you from prototype to high-volume production to deliver parts that guarantee reliability in your most demanding environments.
Ensure your system's integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















