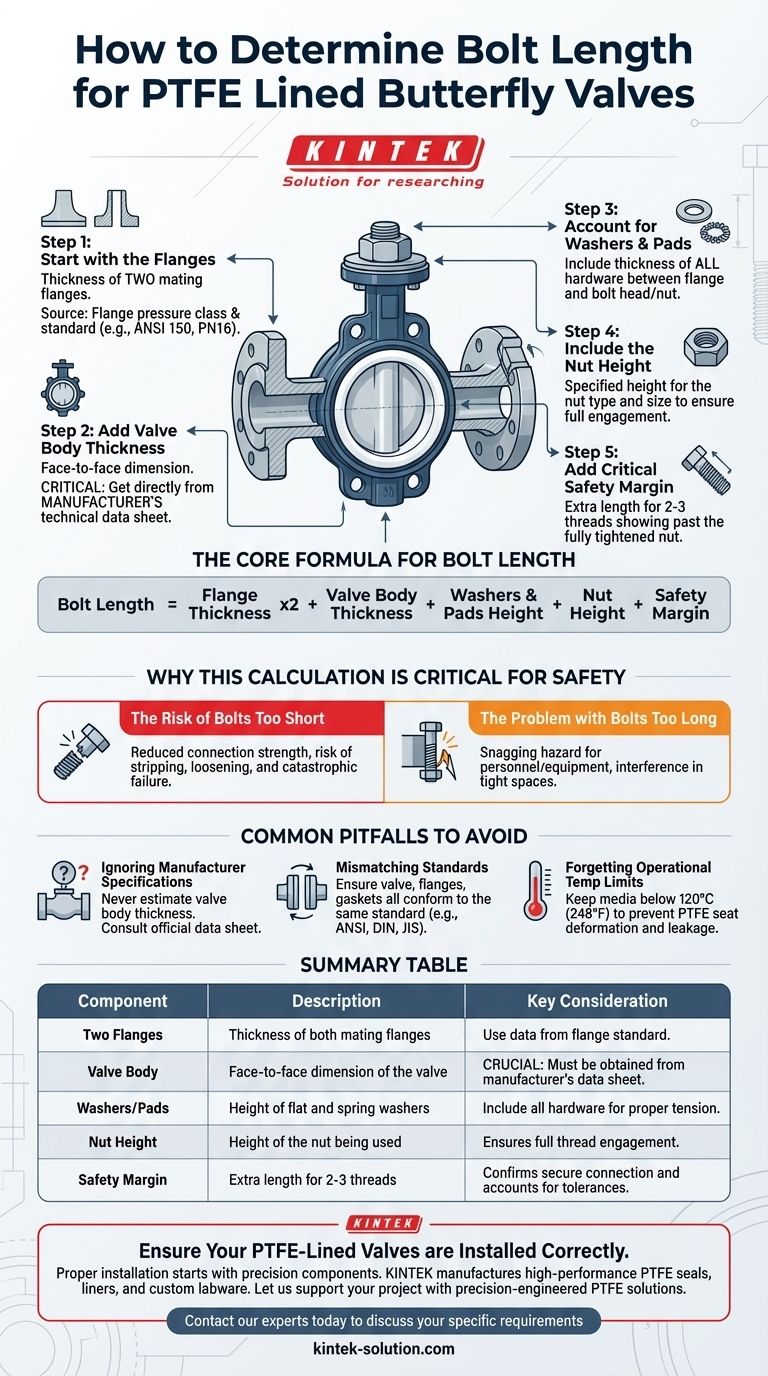
To determine the correct bolt length for a PTFE lined butterfly valve, you must calculate the total thickness of all components the bolt will pass through. The final length is the sum of the valve body thickness, the thickness of two mating flanges, the height of any washers or pads, the height of the nut, and a small safety margin for proper thread engagement.
The correct bolt length is not a single standard value but a calculated sum. It must account for the thickness of the two flanges, the valve body, all washers and nuts, and a necessary safety margin to ensure a secure, leak-proof connection.

The Core Formula for Bolt Length
Calculating the bolt length is a straightforward process of addition. The goal is to ensure the bolt is long enough to fully engage the nut with a few threads to spare, but not so long that it creates a hazard or interferes with other components.
Step 1: Start with the Flanges
The foundation of your calculation is the set of flanges the valve will be sandwiched between. You need the thickness of two flanges, as the bolt must pass through both. This data is determined by the flange pressure class and standard (e.g., ANSI 150, PN16).
Step 2: Add the Valve Body Thickness
This is the "face-to-face" dimension of the butterfly valve. This critical measurement must be taken directly from the valve manufacturer's technical data sheet, as it can vary between brands.
Step 3: Account for Washers and Pads
The calculation must include the thickness of any hardware between the flange and the bolt head or nut. This often includes a flat washer and sometimes a spring washer (or "spring pad") to maintain tension. Add the thickness of each washer used.
Step 4: Include the Nut Height
The bolt must pass completely through the nut to achieve proper thread engagement and clamping force. Use the specified height for the type and size of nut you are using.
Step 5: Add the Critical Safety Margin
Finally, add a small amount of extra length, often referred to as a "margin." A best practice is to have 2-3 threads showing past the fully tightened nut. This margin confirms full engagement and accounts for minor tolerance stacking in the components.
Why This Calculation is Critical for Safety
A seemingly simple bolt length calculation has direct consequences for the safety and performance of the entire piping system. Getting it wrong introduces significant risk.
The Risk of Bolts That Are Too Short
If a bolt is too short, it cannot achieve full thread engagement with the nut. This dramatically reduces the connection's strength, making it susceptible to stripping, loosening from vibration, and catastrophic failure under pressure.
The Problem with Bolts That Are Too Long
Excessively long bolts can protrude far past the nut, creating a snagging hazard for personnel and equipment. In tight spaces, the excess length might also interfere with adjacent piping, supports, or machinery.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Beyond the simple math, several common errors can compromise the integrity of the valve installation. Awareness of these issues is key to a successful outcome.
Ignoring Manufacturer Specifications
Never estimate or assume the valve body's thickness. Always consult the official technical data sheet from the manufacturer. Different designs can have surprisingly different face-to-face dimensions.
Mismatching Flange and Valve Standards
Ensure the valve, flanges, and gaskets all conform to the same standard (e.g., ANSI, DIN, JIS). A mismatch can lead to improper alignment and an inability to create a reliable seal, regardless of bolt torque.
Forgetting Operational Temperature Limits
While not a bolt length issue, ignoring the valve's material limits is a critical pitfall. The PTFE lining in these valves is excellent for corrosion resistance but has strict temperature limits.
For long-term use, the media temperature should be kept below 120°C (248°F). Exceeding this can cause the PTFE seat to soften and deform, destroying the valve's ability to seal properly and leading to leaks.
Applying This to Your Project
Use the following guidelines to ensure you select the correct hardware for your specific installation goals.
- If your primary focus is accurate specification: Always start with the manufacturer's data sheets for both the valve and the matching flanges to get precise thickness dimensions.
- If your primary focus is on-site installation: Lay out all components—the valve, gaskets, and flanges—and measure the total stack-up before calculating the final bolt length with the required safety margin.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Verify that your system's operating temperature will remain well within the PTFE lining's specified limits to prevent seat failure and ensure a lasting seal.
A methodical approach to bolt calculation is the foundation for a safe and reliable piping system.
Summary Table:
| Component | Description | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Two Flanges | Thickness of both mating flanges. | Use data from the flange standard (e.g., ANSI 150). |
| Valve Body | Face-to-face dimension of the valve. | Crucial: Must be obtained from the manufacturer's data sheet. |
| Washers/Pads | Height of flat washers and spring washers. | Include all hardware for proper tension. |
| Nut Height | Height of the nut being used. | Ensures full thread engagement. |
| Safety Margin | Extra length for 2-3 threads past the nut. | Confirms a secure connection and accounts for tolerances. |
Ensure Your PTFE-Lined Valves are Installed Correctly
Proper installation starts with precision components. At KINTEK, we manufacture high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and custom labware for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get the exact parts you need for reliable, leak-proof systems.
Let us support your project with precision-engineered PTFE solutions. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of multi-axis CNC machines for PTFE machining? Achieve Superior Precision for Complex Parts
- Why is Teflon suitable for bridge bearing pads? Unlock Smooth, Durable Movement for Your Structure
- What types of environments are PTFE rotary shaft seals suitable for? Engineered for Extreme Chemical, Temperature, and Speed
- What are some common applications of PTFE washers? Ideal for Sealing, Insulation, and Low-Friction Needs
- What is the difference between PTFE sheets and Teflon paper? A Guide to Choosing the Right Form
- What are the key advantages of PTFE bushings for high-speed and high-temperature applications? Unlock Maintenance-Free Performance
- Is a Teflon sheet necessary for all heat press applications? Essential Protection for Consistent Results
- What temperature limitations should be considered when using PTFE lined butterfly valves? Ensure Safe & Reliable Operation



















