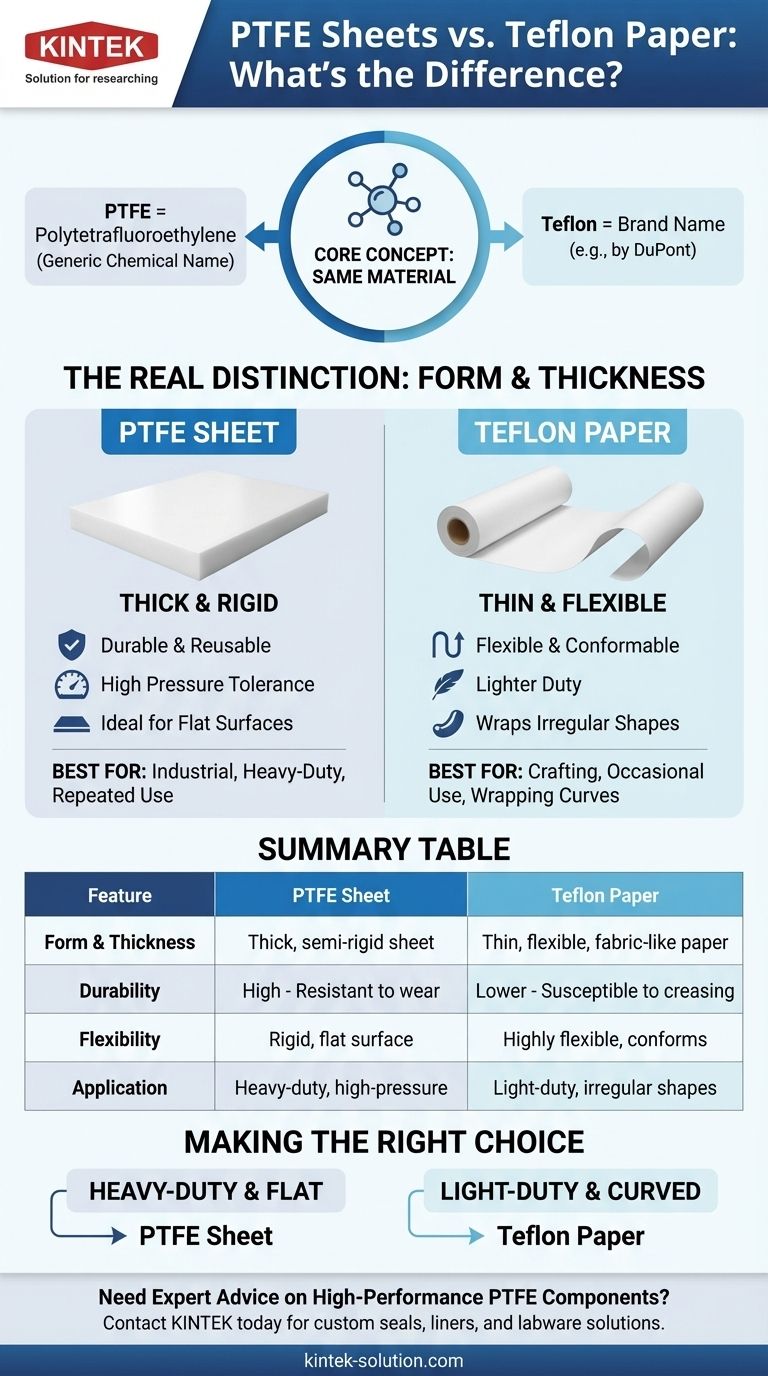
At its core, there is no material difference between PTFE and Teflon. Teflon is simply a well-known brand name for the polymer polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The true distinction you are asking about is between the form of the material: a thick, durable PTFE sheet versus a thin, flexible Teflon paper. Both offer the same fundamental non-stick and heat-resistant properties, but their physical construction dictates their use.
The decision between a "PTFE sheet" and "Teflon paper" is not about the chemical makeup, but about physical form. You are choosing between a durable, rigid sheet for long-term, high-pressure tasks and a thin, flexible paper for lightweight jobs or wrapping irregular surfaces.

Deconstructing the Terminology
To make an informed choice, you must first understand the language used. The confusion between these products stems from the interchangeable use of a technical name and a brand name.
The Material is the Same: Polytetrafluoroethylene
PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene, is the generic chemical name for the synthetic fluoropolymer. Teflon is the trademarked brand name for PTFE, created by the DuPont company.
Think of it like facial tissues and the brand Kleenex. All Kleenex are facial tissues, but not all facial tissues are Kleenex. Similarly, all Teflon is PTFE, but not all PTFE products are branded as Teflon.
Where the Real Difference Lies: Form and Thickness
The terms "sheet" and "paper" describe the product's physical form factor, which is the most critical difference for your application.
- A PTFE sheet is a thick, semi-rigid, and highly durable product designed for repeated use under pressure and heat.
- A Teflon paper (or PTFE-coated fiberglass fabric) is a much thinner, more flexible material. It feels more like a fabric or heavy paper.
Comparing Key Attributes: Sheet vs. Paper
The physical differences between sheets and paper create distinct advantages depending on the job.
Durability and Reusability
PTFE sheets are engineered for longevity. Their thickness makes them resistant to wear, tearing, and the stress of repeated high-pressure applications, such as in industrial heat presses.
Teflon paper, being thinner, is more susceptible to creases, wrinkles, and eventual tearing. It's better suited for lighter-duty work or tasks where it may be considered a semi-disposable item.
Flexibility and Conformity
This is where Teflon paper has a clear advantage. Its fabric-like flexibility allows it to easily wrap around curved or irregularly shaped objects without cracking or breaking.
PTFE sheets are rigid. They are ideal for providing a perfectly flat, stable surface but are not suitable for wrapping or conforming to complex shapes.
Heat and Pressure Tolerance
Both materials have excellent heat resistance derived from their PTFE coating. However, the thicker PTFE sheet provides better insulation and handles the physical stress of high pressure far more effectively over the long term.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these materials involves balancing performance with cost and recognizing their inherent limitations.
The Cost Factor
Generally, a thick PTFE sheet represents a higher upfront investment due to the greater amount of material and its robust construction.
Teflon paper is typically less expensive, making it a cost-effective choice for occasional use, short-term projects, or when you need to cover a large area on a budget.
Enhanced Formulations
It's important to recognize that not all PTFE products are pure. High-performance PTFE sheets are often reinforced with fillers like glass or aramid fibers to dramatically improve mechanical strength. Others may contain ceramic fillers to modify thermal properties.
Material Vulnerabilities
Despite its strengths, PTFE is not indestructible. It has poor resistance to high-energy radiation and can be attacked by certain highly reactive chemicals like elementary fluorine and specific fluorinating agents, especially at high temperatures and pressures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be driven entirely by the demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty heat pressing or industrial use: A thick, solid PTFE sheet is the correct choice for its superior durability and longevity under pressure.
- If your primary focus is occasional crafting or home use: The more affordable and flexible Teflon paper will serve your needs perfectly.
- If your primary focus is protecting a curved or irregularly shaped item: The flexibility of Teflon paper makes it the only practical option.
By understanding the distinction between the base material (PTFE) and its physical form (sheet vs. paper), you can confidently select the precise tool for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Sheet | Teflon Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
| Form & Thickness | Thick, semi-rigid, durable sheet | Thin, flexible, fabric-like paper |
| Best For | Heavy-duty, high-pressure, repeated use | Light-duty, wrapping irregular shapes, occasional use |
| Durability | High - Resistant to wear and tear | Lower - Susceptible to creasing and tearing |
| Flexibility | Rigid, provides a flat surface | Highly flexible, conforms to curves |
Still Unsure Which PTFE Product is Right for Your Project?
At KINTEK, we are experts in high-performance PTFE components. Whether you need a custom-fabricated, heavy-duty PTFE sheet for industrial machinery or a flexible Teflon paper for specialized applications, our team can help you select the perfect material.
We specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver solutions that meet your exact specifications for durability, heat resistance, and performance.
Let's discuss your requirements and find the optimal PTFE solution for you. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE seals and rings? Unlock Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What is a PTFE rotary seal and how is it designed? A Guide to High-Performance Sealing
- How is PTFE used in football protective gear? Enhancing Performance and Safety
- What factors should be considered when choosing the thickness of a PTFE gasket? Optimize Your Seal for Flange Condition & Pressure
- What makes PTFE an excellent material for insulation in wires and cables? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Conditions
- Why are Metal-Polymer Bronze Backed PTFE Plain Bearings considered versatile? Unlock Maintenance-Free, High-Performance Solutions
- What are the overall benefits of spring-energized PTFE seals? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What are the main benefits of using PTFE envelope gaskets? Achieve Superior Sealing in Harsh Environments



















