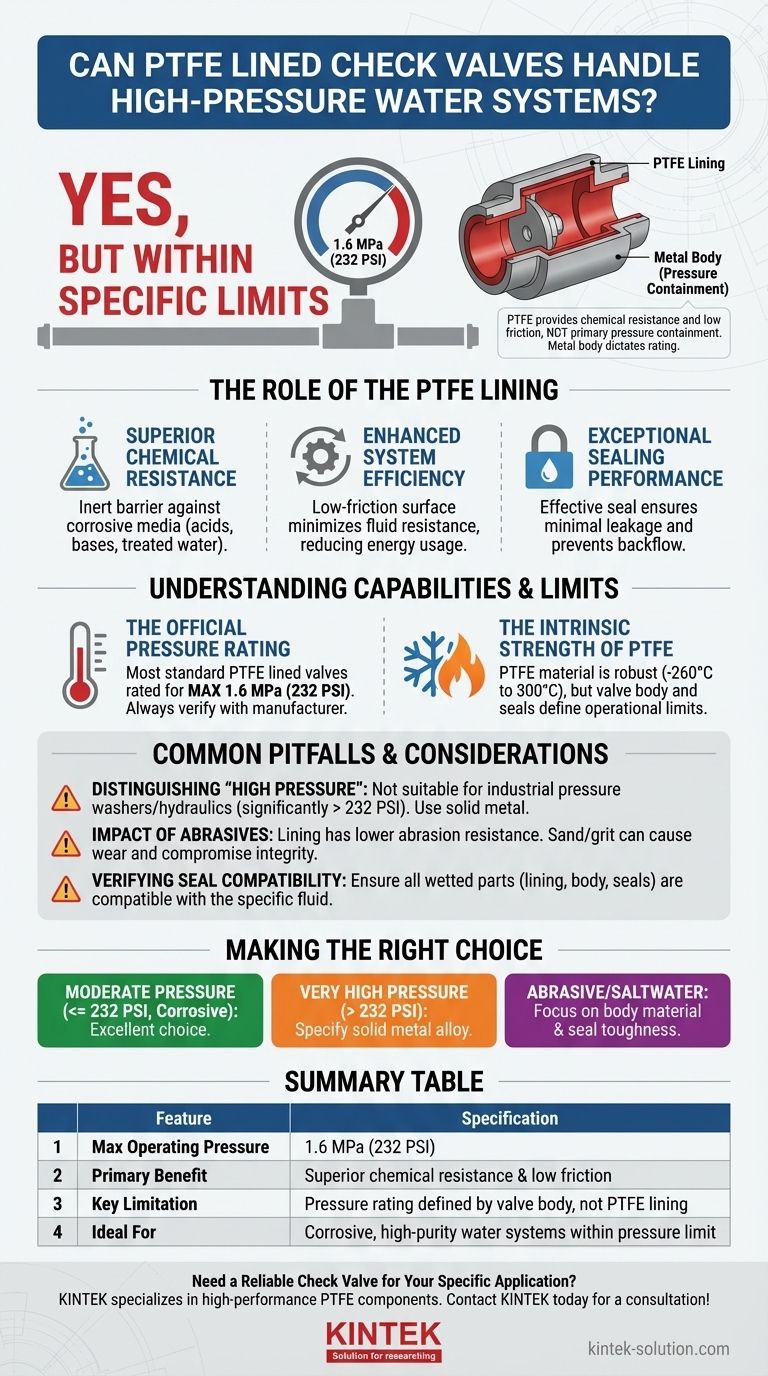
Yes, but within specific limits. A typical PTFE lined check valve is rated to handle pressures up to 1.6 MPa (232 PSI). While the PTFE material itself is exceptionally resilient to high pressure and temperature, the valve's ultimate capability is determined by its overall mechanical design, including the body and seals.
The critical point to understand is that the PTFE lining provides exceptional chemical resistance and a low-friction surface; it does not provide the primary pressure containment. The valve's metal body dictates the absolute pressure rating you must adhere to.
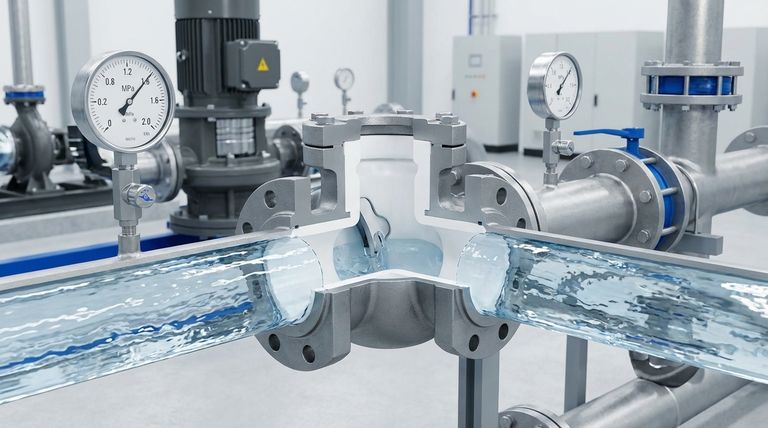

The Role of the PTFE Lining
To properly evaluate these valves, you must first understand what the PTFE lining is designed to accomplish. It's less about raw pressure handling and more about performance and longevity within the specified pressure range.
### Superior Chemical Resistance
The primary function of a PTFE lining is to create an inert barrier between the process fluid and the valve's metal body.
This makes it ideal for handling corrosive media, including acids, bases, and various treated water types that could otherwise damage the valve's core components.
### Enhanced System Efficiency
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction. This "slick" surface minimizes fluid resistance as water passes through the valve.
This reduction in drag decreases the energy required by pumps to move the fluid, contributing to overall system efficiency.
### Exceptional Sealing Performance
The properties of PTFE allow for a very effective seal, which is critical in a check valve.
This ensures minimal leakage when the valve is closed, preserving system pressure and preventing backflow that could damage pumps or other equipment.
Understanding the Pressure and Temperature Capabilities
The final pressure rating of a valve is a result of its entire construction, not just one material.
### The Official Pressure Rating
Most standard PTFE lined check valves are specified for a maximum operating pressure of 1.6 MPa or 232 PSI.
You must always verify this rating in the manufacturer's technical data sheet for the specific model you are considering.
### The Intrinsic Strength of PTFE
The PTFE material itself is remarkably robust. As a sealing material, it can function in extreme temperatures, from cryogenic lows of -260°C up to 300°C.
This wide operating window means the lining is rarely the point of failure in a properly specified water system. The valve's metallic body and other components will define the operational limits.
### Why Valve Body Construction is Key
The valve body (often stainless steel or another alloy) is the component that contains the system pressure.
For corrosive fluids like seawater or chemically treated water, a stainless steel body is recommended to work in concert with the PTFE lining, ensuring the entire assembly resists degradation.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While effective, a PTFE lined valve is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to preventing system failure.
### Distinguishing "High Pressure"
The term "high pressure" is relative. For chemical dosing or municipal water lines, 232 PSI is a significant rating.
However, for applications like industrial pressure washers or hydraulic systems, where pressures can be many times higher, a PTFE lined valve is not suitable. In those cases, a solid, high-strength metal alloy valve is required.
### The Impact of Abrasives
The PTFE lining provides excellent chemical resistance but has lower resistance to physical abrasion.
If your water system contains significant abrasive particles like sand or grit, the lining can wear prematurely, compromising the valve's integrity.
### Verifying Seal Compatibility
While the body is lined with PTFE, the valve's internal seals may be made of different alloys or elastomers.
For aggressive water chemistries, you must ensure all wetted parts—the lining, body, and seals—are compatible with your specific fluid.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Base your decision on the specific operational demands of your water system.
- If your primary focus is moderate-pressure systems (up to 232 PSI) with corrosive or high-purity water: A PTFE lined check valve is an excellent choice that offers robust chemical protection and reliable flow control.
- If your primary focus is very high-pressure systems (significantly above 232 PSI): You must specify a solid metal alloy check valve without a liner that is explicitly engineered and certified for those higher pressures.
- If your primary focus is reliability in saltwater or abrasive environments: Pay equal attention to the valve's body material (e.g., stainless steel) and the toughness of its seals, as the lining alone cannot guarantee system longevity.
Ultimately, selecting the correct valve requires matching the component's certified system rating to the precise demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Max Operating Pressure | 1.6 MPa (232 PSI) |
| Primary Benefit | Superior chemical resistance & low friction |
| Key Limitation | Pressure rating defined by valve body, not PTFE lining |
| Ideal For | Corrosive, high-purity water systems within pressure limit |
Need a Reliable Check Valve for Your Specific Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and custom labware. We understand that selecting the right valve is critical for the efficiency and safety of your systems in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring the component perfectly matches your operational demands, pressure rating, and fluid compatibility.
Let our expertise guide you to the optimal solution. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What makes Teflon bushings suitable for harsh environments? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What role do PTFE coatings play in automotive engineering? Boost Engine Efficiency & Durability
- What alternatives to PTFE are available for sealing applications? Find the Right Material for Your Sealing Needs
- How does gland packing function in sealing systems? Achieve Reliable, Controlled Sealing
- What are the advantages of PTFE balls over metals or alloys? Superior Chemical & Friction Resistance
- What are the thermal properties of PTFE balls? Unlock Extreme Temperature Performance
- How can AI and machine learning improve CNC machining processes for PTFE parts? Boost Precision & Reduce Waste
- What are the properties of Teflon PFA encapsulated o-rings? Achieve Superior Sealing in Extreme Environments



















