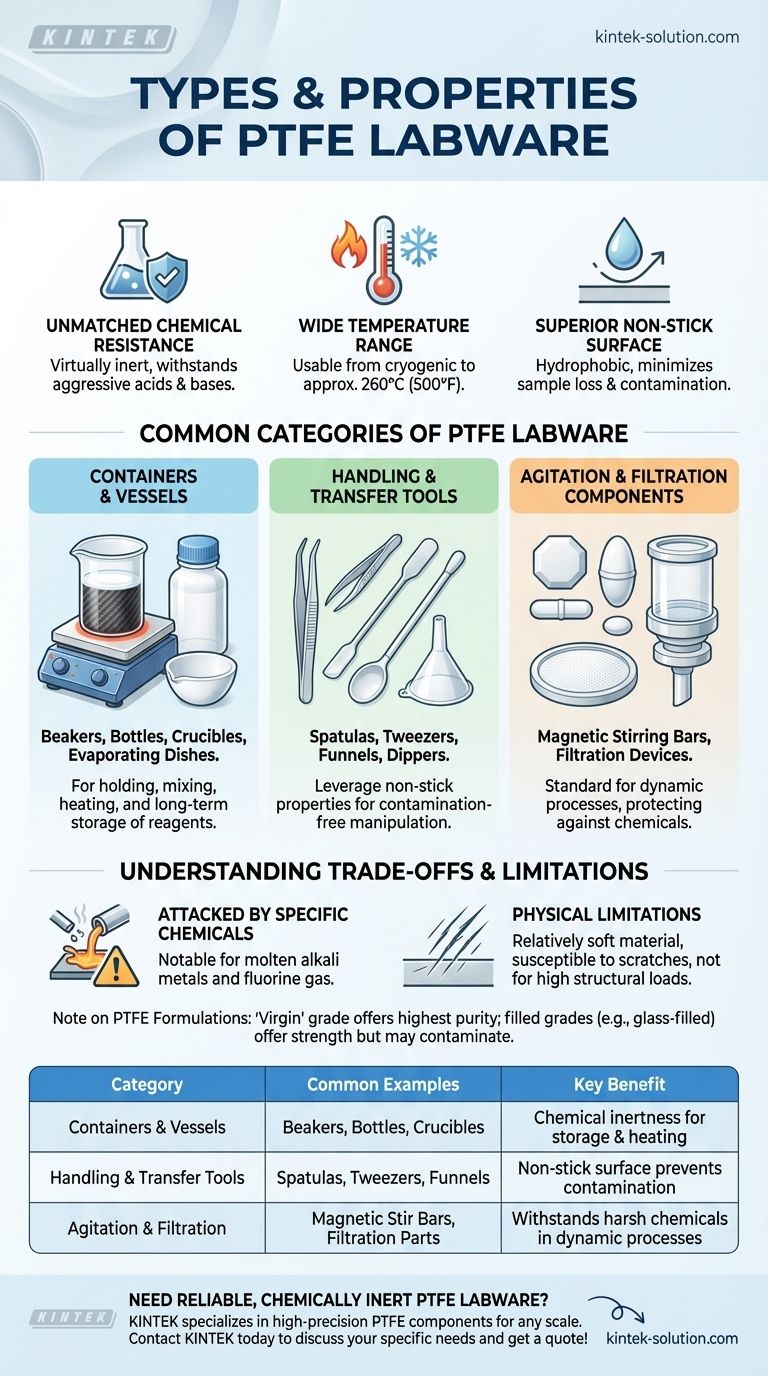
The most common types of PTFE labware include containers like beakers, bottles, and flasks; handling tools such as spatulas and tweezers; and specialized items like magnetic stirring bars, funnels, and evaporating dishes. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is prized in laboratory settings for its extreme chemical resistance, wide temperature tolerance, and non-stick surface, making it suitable for a vast range of applications.
The specific shape of the labware—beaker, flask, or stir bar—is less important than the underlying properties of the PTFE material itself. Understanding these properties is the key to determining where and why you should use it over alternatives like glass or metal.

The Core Properties of PTFE Labware
Before examining the specific types of labware, it's crucial to understand the material's fundamental characteristics. These properties are the reason PTFE is selected for demanding lab environments.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and resistant to attack by almost all chemicals, including highly corrosive acids and bases. This makes it an ideal material for handling and storing aggressive reagents where glass or metal would fail.
Wide Temperature Range
Standard PTFE labware can typically be used in a wide temperature range, often from cryogenic temperatures up to approximately 260°C (500°F). This allows for its use in both extreme cold and high-heat applications without degrading.
Superior Non-Stick Surface
The surface of PTFE is extremely hydrophobic and non-stick (low coefficient of friction). This property is invaluable for minimizing sample loss and preventing cross-contamination between experiments, as materials do not easily adhere to it.
Common Categories of PTFE Labware
While the list of specific items is long, most PTFE labware falls into a few functional categories.
Containers and Vessels
This is the most common category, designed for holding, mixing, and heating substances.
- Beakers: Often used for general mixing and gentle heating. Some are designed specifically with a carbon-fiber-filled base for more efficient heating on a hot plate.
- Bottles: Ideal for the long-term storage of highly reactive or pure chemicals that might leach ions from glass containers.
- Crucibles & Evaporating Dishes: Used for high-temperature work where chemical inertness is paramount.
Handling and Transfer Tools
These tools leverage PTFE's non-stick and non-reactive properties to manipulate materials without contamination.
- Spatulas & Tweezers: Perfect for handling sensitive or corrosive powders and solids.
- Funnels: Ensure a clean, complete transfer of liquids or fine powders without material clinging to the surface.
- Dippers: Used for safely sampling corrosive liquids from larger containers.
Agitation and Filtration Components
PTFE is a standard material for components used in dynamic laboratory processes.
- Magnetic Stirring Bars: The universal standard for stir bars is a magnet encapsulated in PTFE. This protects the magnet from the chemicals being stirred and prevents contamination of the solution. They come in many shapes, including octagonal, egg-shaped, and micro sizes.
- Filtration Devices: Components within vacuum pumps and filtration systems are often made of PTFE to withstand harsh chemical exposure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While extremely versatile, PTFE is not an infallible material. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Attacked by Specific Chemicals
Despite its exceptional resistance, PTFE can be attacked by a few substances. The most notable are molten alkali metals (like sodium) and certain halogenated compounds, particularly fluorine gas at high temperatures and pressures.
Physical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material compared to glass or stainless steel. It can be scratched or damaged by abrasive materials, and it is not suitable for applications requiring high structural rigidity or load-bearing strength unless it is reinforced.
Understanding PTFE Formulations
Not all PTFE is the same. The "virgin" or unfilled grade offers the highest chemical purity. However, you may encounter labware made from filled grades, such as glass-filled PTFE, which offers enhanced strength and stiffness but may not be suitable for applications sensitive to glass contaminants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct labware depends entirely on the demands of your specific procedure.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical purity and inertness: Choose labware made from 100% virgin PTFE for storing ultra-pure reagents or handling highly corrosive acids.
- If your primary focus is thermal applications: Select heatable PTFE beakers or crucibles, but always operate within the manufacturer's specified temperature limits (typically around 260°C).
- If your primary focus is preventing sample loss or contamination: The non-stick surface of any PTFE tool, from a simple spatula to a complex flask, is your greatest asset.
By understanding the core properties and limitations of the material, you can confidently select the right PTFE labware to ensure the integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Category | Common Examples | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Containers & Vessels | Beakers, Bottles, Crucibles | Chemical inertness for storage & heating |
| Handling & Transfer Tools | Spatulas, Tweezers, Funnels | Non-stick surface prevents contamination |
| Agitation & Filtration | Magnetic Stir Bars, Filtration Parts | Withstands harsh chemicals in dynamic processes |
Need reliable, chemically inert PTFE labware?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—from standard labware like beakers and stir bars to custom fabrications for unique applications. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise ensures you get components that guarantee purity, durability, and performance.
We support projects of any scale, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What role does precision play in the use of PTFE silicone septa for pharmaceutical analysis? Ensure Reliable, Compliant Data
- What is the primary function of PTFE/silicone septa in HPLC autosampler vials? Ensure Sample Integrity and Accuracy
- What types of solvents and reagents are PTFE vials compatible with? Ensure Purity in Your HPLC/GC Analysis
- What are the key applications of the PTFE bottle? Ensure Chemical Safety and Sample Purity
- Why are PTFE/silicone septums considered essential in chromatographic analysis? Ensure Data Integrity and Purity
- What are PTFE silicone septa and what are they composed of? The Key to Reliable Chromatography Seals
- What are the main materials used for septa in laboratory settings? PTFE vs. Silicone Explained
- What makes Teflon membranes versatile for use in various laboratory environments? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability



















