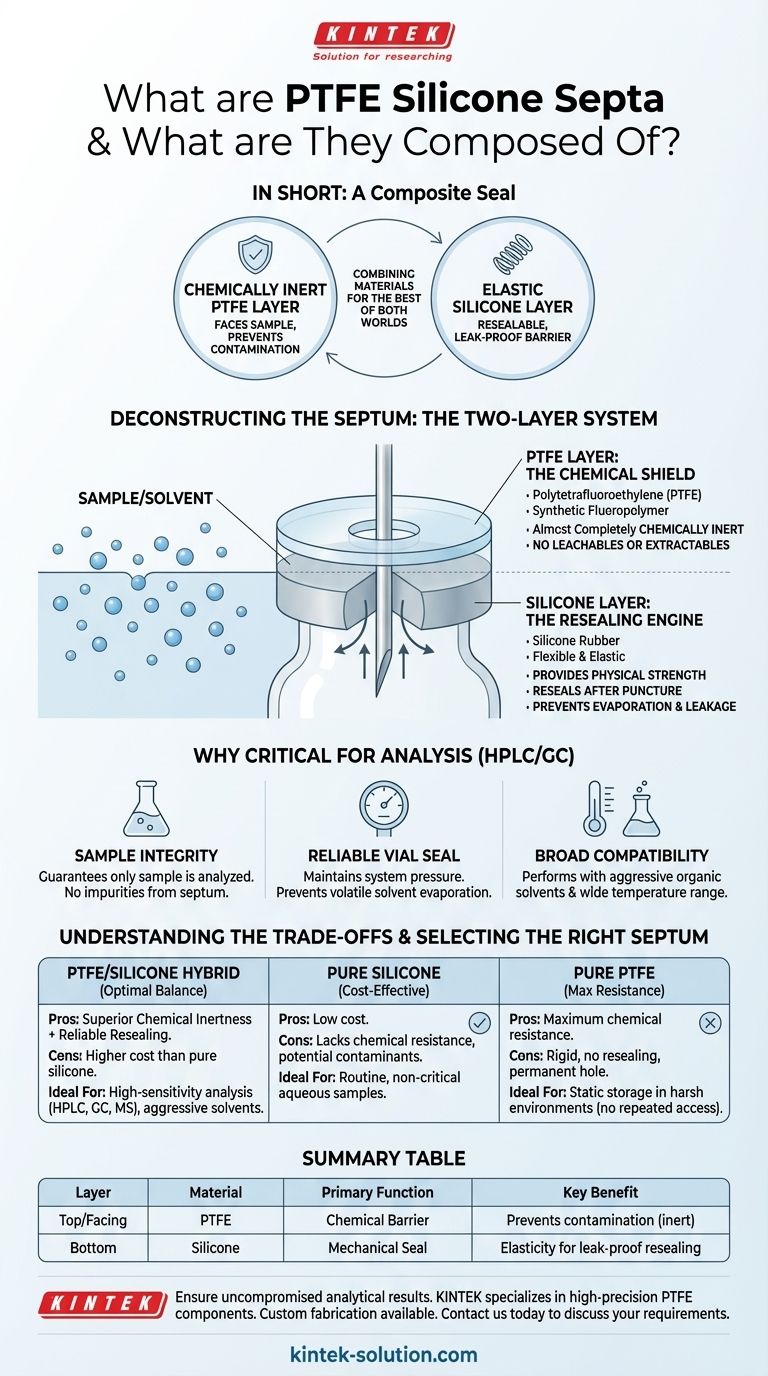
In short, a PTFE/silicone septum is a composite seal used in analytical science, particularly for chromatography vials. It consists of two fused layers: a chemically inert PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) film that faces the sample to prevent contamination, and a thicker, elastic silicone layer that provides a resealable, leak-proof barrier after being punctured by a needle.
The core purpose of combining these materials is to get the best of both worlds. The PTFE layer acts as a perfect chemical shield for the sample, while the silicone layer provides the mechanical elasticity needed for a reliable, repeatable seal.

Deconstructing the Septum: The Two-Layer System
A PTFE/silicone septum is not a simple mixture; it's a strategically engineered laminate. Each layer serves a distinct and critical function.
The PTFE Layer: The Chemical Shield
Polytetrafluoroethylene, or PTFE, is a synthetic fluoropolymer composed entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms.
The exceptionally strong carbon-fluorine bonds give PTFE its signature property: it is almost completely chemically inert. This layer faces the sample inside the vial.
Its purpose is to prevent any interaction between the seal and the sample or solvent. This eliminates the risk of leachables or extractables—impurities from the septum material—contaminating the sample and compromising your analytical results.
The Silicone Layer: The Resealing Engine
The bulk of the septum is made from silicone rubber. Unlike the rigid PTFE, silicone is highly flexible and elastic.
This layer provides the physical strength and resealability of the septum. When an autosampler needle pierces the septum, the silicone's elasticity allows it to form a tight seal around the needle and close back up after withdrawal.
This function is crucial for preventing solvent evaporation, sample leakage, and maintaining pressure within the vial, especially when performing multiple injections from the same vial.
Why This Combination is Critical for Analysis
The dual-layer design directly addresses the core requirements of high-precision analytical techniques like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Gas Chromatography (GC).
Ensuring Uncompromised Sample Integrity
For sensitive analyses, even trace contaminants can skew results. The PTFE layer guarantees that the only thing your instrument sees is your sample, not impurities dissolved from the septum itself.
Maintaining a Reliable Vial Seal
Chromatography systems often operate under pressure. The silicone's ability to reliably reseal after puncture is essential for maintaining system pressure and preventing the volatile solvents from evaporating, which would change the sample's concentration.
Offering Broad Application Compatibility
The combination of PTFE's chemical resistance and silicone's thermal stability creates a septum that performs reliably with a wide range of aggressive organic solvents and across a broad spectrum of temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the PTFE/silicone septum is the industry standard for high-performance applications, it's helpful to understand it in contrast to its alternatives.
Pure Silicone Septa
These are a more cost-effective option. However, they lack the chemical resistance of PTFE and can introduce contaminants into certain solvents. They are best reserved for routine procedures where the sample is aqueous or chemical inertness is not a primary concern.
Pure PTFE Septa
While offering maximum chemical resistance, a solid piece of PTFE is rigid and lacks the resealing capabilities of silicone. Puncturing it can create a permanent hole, leading to evaporation or leaks, making it unsuitable for applications requiring multiple injections.
The PTFE/Silicone Hybrid
This septum represents the optimal balance. It offers the superior chemical inertness of PTFE where it matters most—at the point of sample contact—while leveraging silicone's mechanical properties to ensure a reliable seal. This makes it the default choice for most analytical chromatography.
Selecting the Right Septum for Your Application
Choosing the correct septum is a foundational decision for generating reliable data. Your choice should be guided by your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is high-sensitivity analysis (HPLC, GC, MS) or working with aggressive solvents: A PTFE/silicone septum is the required standard to ensure data integrity.
- If your primary focus is cost-savings for routine, non-critical aqueous samples: A pure silicone septum may be a sufficient and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is static storage in a harsh chemical environment without repeated access: A solid PTFE-lined cap without resealing properties could be considered.
Ultimately, selecting the appropriate septum is a critical step in controlling variables and achieving accurate, repeatable analytical results.
Summary Table:
| Layer | Material | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top/Facing Sample | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | Chemical Barrier | Prevents sample contamination (inert) |
| Bottom/Resealing | Silicone Rubber | Mechanical Seal | Provides elasticity for leak-proof resealing |
Ensure your analytical results are never compromised by seal failure or contamination. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including PTFE/silicone septa, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing the chemical inertness and mechanical reliability your sensitive applications demand. Contact us today to discuss your specific sealing requirements and request a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE react to ammonia? Discover Its Superior Chemical Resistance
- What are the chemical resistance properties of PTFE labware? The Ultimate Guide to Inert Labware
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What are the key features of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Chemical Integrity and Purity for Your Samples



















