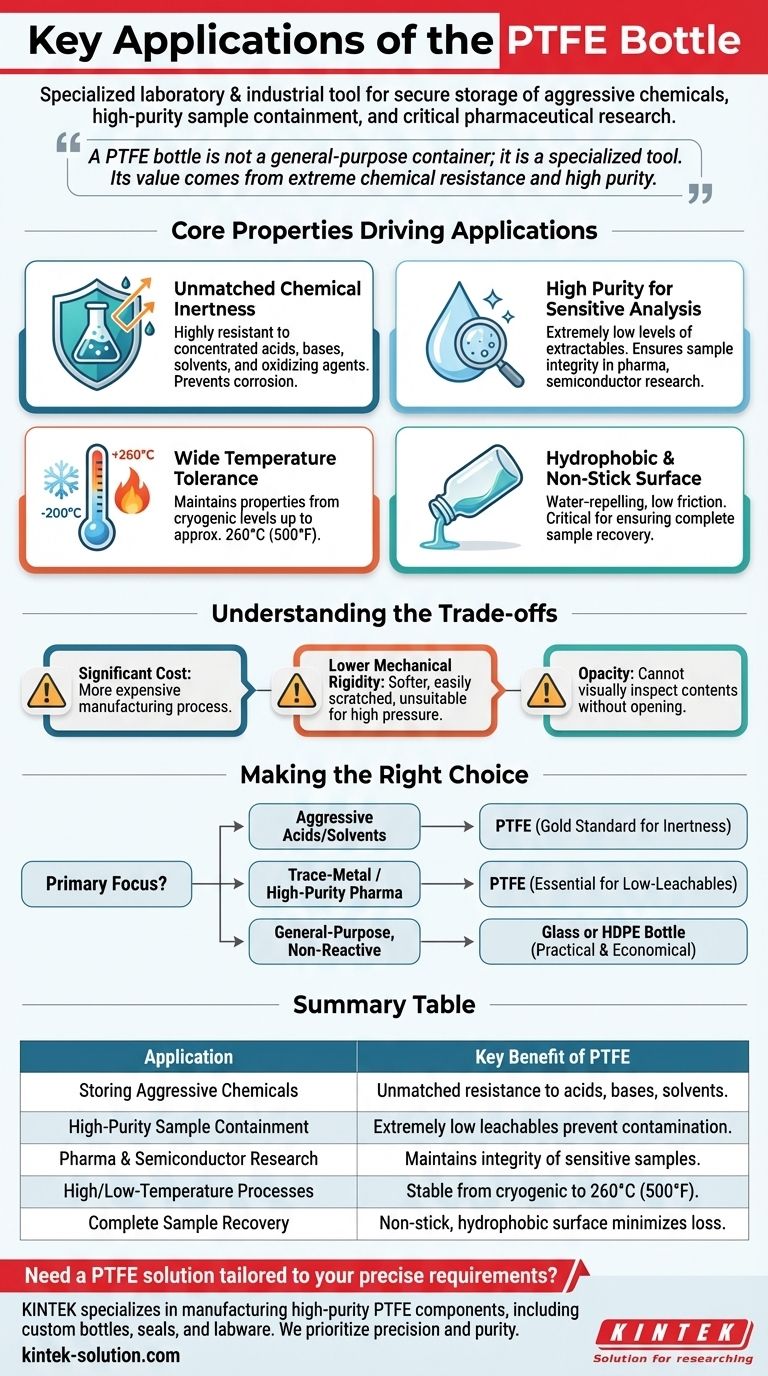
In specialized laboratory and industrial settings, PTFE bottles are used for the secure storage of aggressive chemicals, high-purity sample containment, and critical pharmaceutical research. They are specifically chosen when the contents are either too corrosive for standard glass and plastic or when even trace contamination from the container itself must be avoided.
A PTFE bottle is not a general-purpose container; it is a specialized tool. Its value comes from PTFE's extreme chemical resistance and high purity, making it essential for handling substances that would degrade or be contaminated by standard glass or plastic.
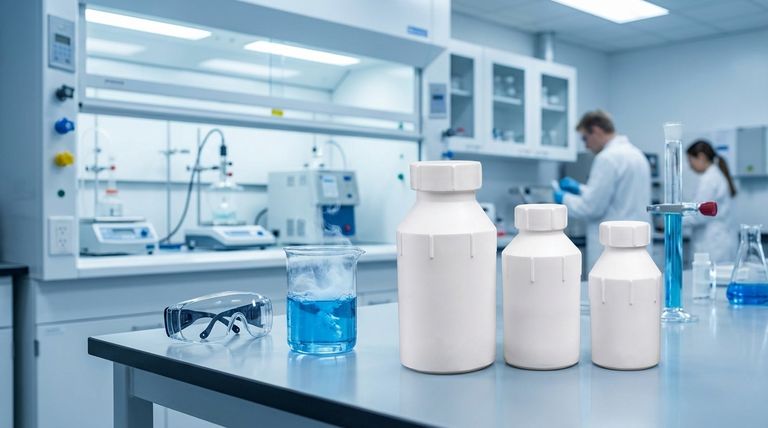

The Core Properties Driving PTFE Bottle Applications
The decision to use a PTFE bottle is driven by the unique material properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the same material known commercially as Teflon™. These properties solve problems that common container materials like glass or polyethylene cannot.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert and does not react with the vast majority of chemicals. It is highly resistant to concentrated acids, bases, solvents, and oxidizing agents.
This makes PTFE bottles the default choice for safely storing and transporting aggressive substances that would corrode glass or dissolve other plastics.
High Purity for Sensitive Analysis
In fields like pharmaceutical research, environmental testing, and semiconductor manufacturing, sample purity is paramount.
PTFE has extremely low levels of extractables, meaning the container will not leach ions or other impurities into the sample it holds. This ensures the integrity of analytical results.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
PTFE maintains its properties across a very broad temperature range, from cryogenic levels up to approximately 260°C (500°F).
This allows PTFE bottles to be used for applications that involve freezing, heating, or autoclaving samples without the container becoming brittle or melting.
A Hydrophobic and Non-Stick Surface
The surface of PTFE is hydrophobic (water-repelling) and has an extremely low coefficient of friction, making it "non-stick."
This property is critical for ensuring complete sample recovery. When a valuable or low-volume sample is poured out, virtually none of it remains clinging to the container walls, which is a common issue with other materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PTFE is not the solution for every situation. Its specialized nature comes with practical and economic trade-offs that must be considered.
Significant Cost
PTFE is a specialty polymer, and manufacturing it into a bottle is a more complex process than molding common plastics or glass. As a result, PTFE bottles are significantly more expensive than their glass, HDPE, or polypropylene counterparts.
Lower Mechanical Rigidity
Compared to glass, PTFE is a much softer material. It can be easily scratched or punctured, and it is not suitable for high-pressure or vacuum applications without specialized design.
Opacity
Most PTFE bottles are opaque white. This means you cannot visually inspect the contents to check for volume, color change, or phase separation without opening the container, a clear disadvantage compared to transparent glass or plastic.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right container requires balancing chemical compatibility, purity requirements, and budget.
- If your primary focus is storing aggressive acids or harsh solvents: PTFE is the gold standard due to its unmatched chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is trace-metal analysis or high-purity pharmaceutical work: PTFE's low-leachable properties are essential to prevent sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, non-reactive sample storage: A standard glass or HDPE bottle is a far more practical and economical choice.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE bottle is a decision to prioritize sample integrity and safety above all other factors.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit of PTFE |
|---|---|
| Storing Aggressive Chemicals | Unmatched resistance to acids, bases, and solvents. |
| High-Purity Sample Containment | Extremely low leachables prevent contamination. |
| Pharmaceutical & Semiconductor Research | Maintains integrity of sensitive samples. |
| High/Low-Temperature Processes | Stable from cryogenic to 260°C (500°F). |
| Complete Sample Recovery | Non-stick, hydrophobic surface minimizes loss. |
Need a PTFE solution tailored to your precise requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-purity PTFE components, including custom bottles, seals, liners, and labware. Whether you are in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we prioritize precision and purity to protect your critical processes and samples.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications. Let's discuss how our PTFE expertise can solve your containment challenges – contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE-layered septa used in high-performance applications? Ensure Sample Integrity & Accuracy
- How does chemical compatibility of PTFE silicone septas benefit pharmaceutical research? Ensure Sample Integrity
- How should PTFE plugs be handled with corrosive liquids? Prevent Costly Glassware Damage
- What are the advantages of using PTFE stirrers and shafts in corrosive applications? Ensure Purity and Reliability
- What types of samples are compatible with PTFE lined vials? Ensure Sample Integrity for Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE used in laboratory stirrer bars? Ensuring Chemical Inertness and Purity in Mixing
- What are the main materials used for septa in laboratory settings? PTFE vs. Silicone Explained
- What are the chemical compatibility properties of PTFE-lined bottle caps? Ensure Maximum Safety and Purity



















