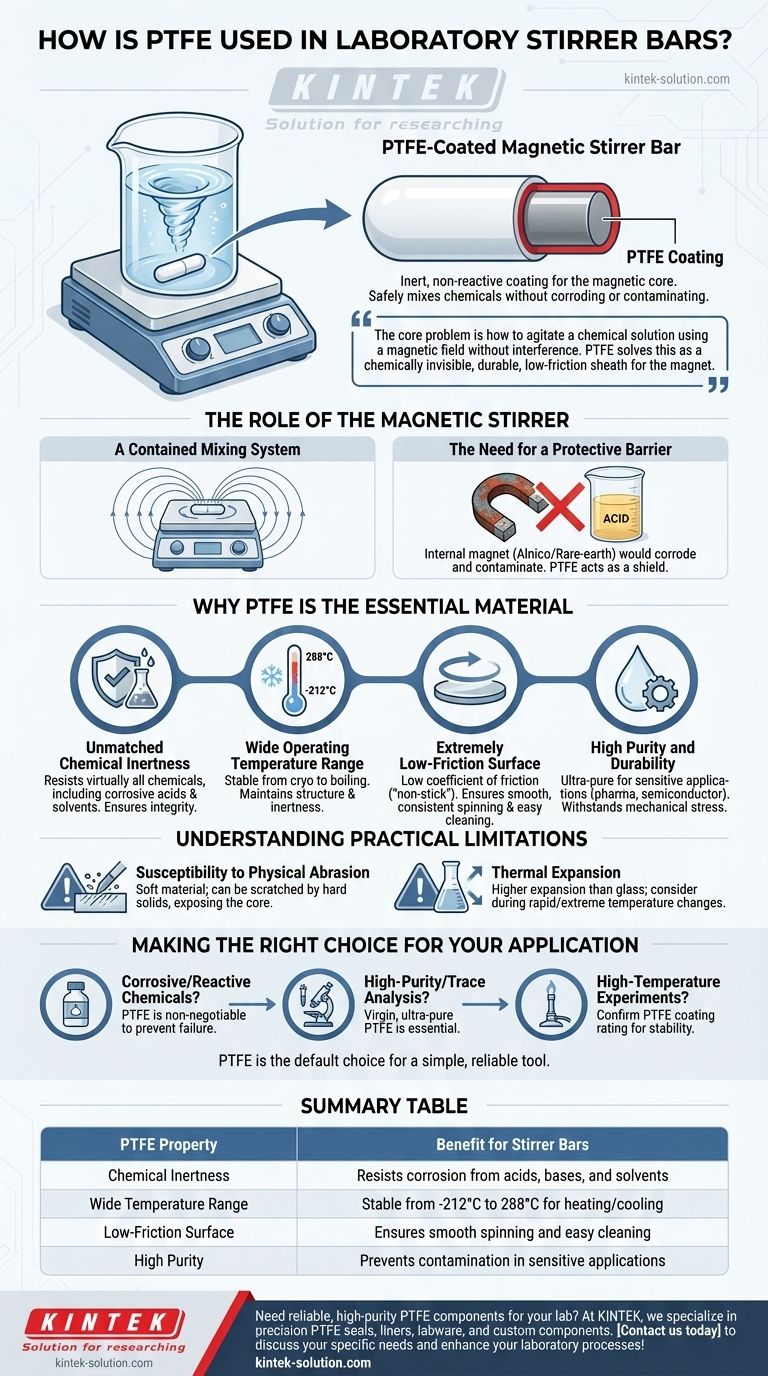
In laboratory settings, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is used as an inert, non-reactive coating for the magnetic core of a stirrer bar. This encapsulation allows the magnet to safely and effectively mix a vast range of chemicals without corroding, reacting with, or contaminating the solution.
The core problem is how to agitate a chemical solution using a magnetic field without the stirring device itself interfering with the experiment. PTFE solves this by acting as a chemically invisible, physically durable, and low-friction sheath for the internal magnet.

The Role of the Magnetic Stirrer
A Contained Mixing System
A magnetic stirrer bar works in tandem with a stir plate. The bar is placed inside a container of liquid, and the stir plate below generates a rotating magnetic field, causing the bar to spin and create a vortex that mixes the solution.
The Need for a Protective Barrier
The internal component of a stir bar is typically a strong magnet, often made from an Alnico alloy or a rare-earth metal. These magnetic materials would corrode or react instantly with many laboratory reagents, such as strong acids or bases, destroying the bar and contaminating the experiment.
Why PTFE is the Essential Material
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. Its primary function on a stir bar is to create a complete barrier that is impervious to virtually all chemicals, including highly corrosive acids, solvents, and reactive agents. This ensures the integrity of both the magnet and the solution.
Wide Operating Temperature Range
Experiments often require heating or cooling. PTFE maintains its structural integrity and chemical inertness across a vast temperature range, from approximately -350°F to 550°F (-212°C to 288°C). This allows a single stir bar to be used for cryogenic applications as well as for boiling liquids.
Extremely Low-Friction Surface
Often known by the brand name Teflon, PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. This "non-stick" quality is critical for a stir bar, as it ensures smooth, consistent spinning with minimal resistance inside the flask and prevents solutes from clinging to its surface, making it easy to clean.
High Purity and Durability
For sensitive applications like pharmaceutical research or semiconductor manufacturing, preventing contamination is paramount. PTFE can be manufactured to ultra-pure standards, ensuring it does not leach impurities into a solution. It is also durable enough to withstand the mechanical stress of constant spinning.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
Susceptibility to Physical Abrasion
While chemically robust, PTFE is a relatively soft material. When mixing solutions containing hard or abrasive solids, the PTFE coating can be scratched or worn away over time. This can eventually expose the magnetic core and compromise the stir bar.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than the glass containers it's used in. During rapid or extreme temperature changes, this difference can be a factor, though it is rarely an issue in standard laboratory protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct equipment is fundamental to reliable and repeatable results. While PTFE is the standard, understanding why it's used helps you evaluate its importance for your specific task.
- If your primary focus is working with corrosive or reactive chemicals: A PTFE-coated stir bar is non-negotiable to prevent equipment failure and sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or trace analysis: Using a stir bar made with virgin, ultra-pure PTFE is essential to avoid introducing contaminants.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature experiments: Confirm your stir bar's PTFE coating is rated for your target temperature to ensure stability and inertness.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of properties makes it the default choice, providing a simple and reliable tool that removes a significant variable from countless chemical processes.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Property | Benefit for Stirrer Bars |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from acids, bases, and solvents |
| Wide Temperature Range | Stable from -212°C to 288°C for heating/cooling |
| Low-Friction Surface | Ensures smooth spinning and easy cleaning |
| High Purity | Prevents contamination in sensitive applications |
Need reliable, high-purity PTFE components for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for semiconductor, medical, and industrial applications. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures your equipment meets the highest standards of chemical resistance and durability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and enhance the integrity of your laboratory processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Magnetic Stirring Bar
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Deep Evaporating Dishes Customizable Laboratory and Industrial Solutions
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















